This is an automatically translated article.
Because of their lipid-rich cell wall structure, Mycobacteria cannot be detected by conventional gram staining. Diagnosis of a Mycobacterial infection can be made through an "acid-fast bacillus" (AFB) sputum staining technique for bacteria.
1. Characteristics of Mycobacteria
Mycobacteria are a group of cell walls rich in lipids and fatty acids. Among them, mycolic acid fatty acid makes up about 60% of the cell membrane weight of bacteria. Although Mycobacteria have the cell membrane structure of Gram-positive bacteria, the high lipid content of the cell membrane prevents the penetration of Gram dye, so conventional Gram staining techniques do not allow observation. Morphology of Mycobacteria under the microscope. Diagnosis is usually made via “acid-fast bacillus” (AFB) staining for mycobacteria.
The most common strain in this group is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis bacteria, also known as tubercle bacilli, are about 0.4 x 3-5mm in size. They do not have hairs, shells and spores. This is an aerobic bacteria that cannot be grown in normal environments, but needs to be cultured in a nutrient-rich environment, growing slowly with a division time of about 18 hours/dividing time. Tuberculosis mainly affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body such as lungs, bones, lymph nodes, peritoneum, etc. Thanks to its high resistance to physical and chemical factors, chemicals Used to kill TB bacteria, it needs to have a high concentration and a long enough contact time to be effective.
2. When is sputum staining for Mycobacteria indicated?
Sputum staining is a test performed on sputum samples to detect pathogenic bacteria belonging to the group of Mycobacteria. Doctors usually order this test to determine if a person has tuberculosis or another Mycobacterial infection. The doctor may order the test to evaluate the effectiveness in patients who are taking medicine for tuberculosis or another Mycobacterial infection.
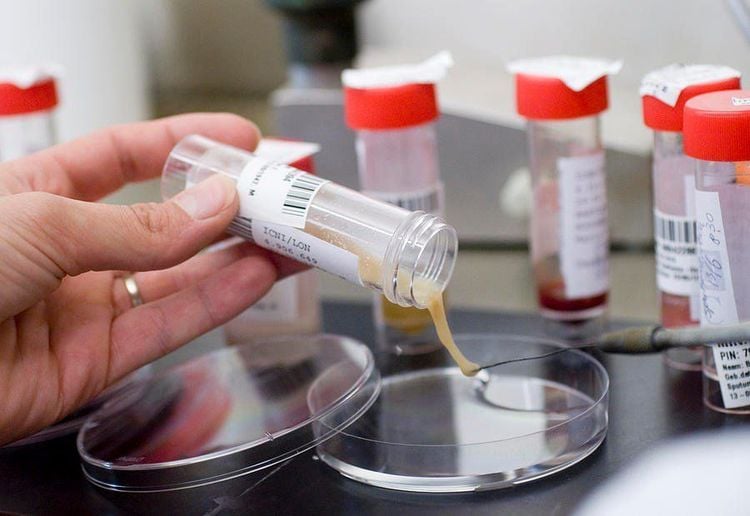
Nhuộm đờm là một xét nghiệm được thực hiện trên mẫu đờm nhằm phát hiện vi khuẩn gây bệnh
3. How is sputum sampling for Mycobacteria conducted?
To prepare for a sputum sample the next day, the night before the test, drink plenty of fluids, such as water or tea, to help your body produce more phlegm. Taking a morning sputum sample will make the test more accurate because more bacteria appear at this time.
Regarding sputum samples, according to the provisions of the National TB Program, it is necessary to take 2 samples on the spot: Sample 1 is taken immediately after medical examination, sample 2 is taken about 2 hours after sample 1. If conditions allow, it is best to take sputum samples in the morning for testing. It is best to take 2 samples in the early morning after waking up. It is necessary to collect about 2-3 ml of sputum in unusual places such as mucus, blood, and food.
For convenient sputum sampling and accurate results, you should do the following:
Brush your teeth and rinse your mouth without using antiseptic water. Take a few deep, long breaths. Take a deep breath again and cough vigorously until there is phlegm. Sputum into the sample cup. Continue coughing up phlegm until the cup is full, about 1 teaspoon. Unscrew the lid of the cup, wash and dry the outside of the cup. If you are unable to cough up sputum, your doctor will use a bronchoscope to draw sputum directly from your lungs. Bronchoscopy is a simple procedure that takes about 30 to 60 minutes. It is usually done in a clinic and does not require anesthesia. There are some risks during bronchoscopy such as bleeding, reaction to anesthetic or sedative drugs, infection, bronchospasm,...
4. Advantages and disadvantages of sputum staining technique for Mycobacteria
4.1. Ziehl-Neelsen direct staining AFB Advantages:
This diagnostic technique is relatively simple and can be performed in microbiological laboratories. The cost is quite low, so this method can be applied to the screening diagnosis of Mycobacteria, especially tuberculosis in the community. Disadvantages:
Can only assess whether the bacteria in the specimen is an acid-resistant alcohol-resistant bacillus; It is not clear whether it is tuberculosis or other specific Mycobacteria. The sensitivity of this technique is quite low, detecting bacteria only if the concentration of bacteria is > 10^5 bacteria/mL of sputum when scanning at least 10 microspheres.
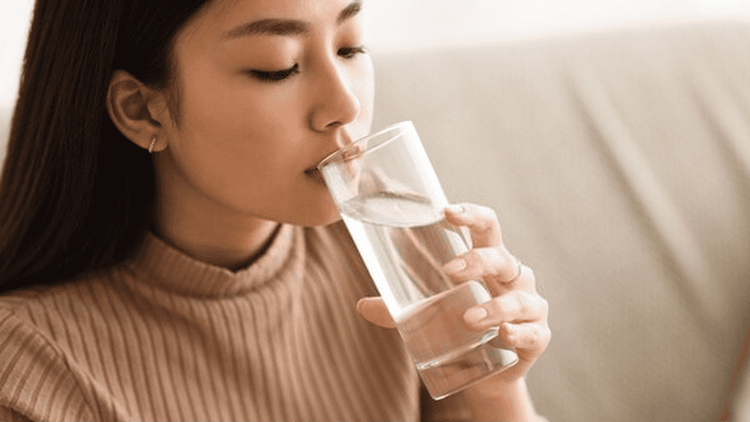

Để chuẩn bị lấy mẫu đờm trong ngày hôm sau, vào đêm trước khi xét nghiệm, bạn hãy uống nhiều chất lỏng
4.2. AFB direct fluorescence staining Advantages:
Fluorescence microscopy is capable of scanning faster than optical microscopes. There is a higher sensitivity, especially in patient samples with less bacteria due to the larger field of view. Cons:
This technique is relatively expensive. False positives are likely to occur if other luminescent substances are confused with bacteria. Mycobacteria are common pathogens. The technique of staining sputum to find Mycobacteria will help doctors quickly detect the disease to give appropriate treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the medical facilities that ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology, and outstanding examination and consulting services. Comprehensive, professional medical treatment. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of the results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com