This is an automatically translated article.
Anomalies in the lungs - air - bronchi are divided according to the development pattern of birth defects. Respiratory malformations include: lung malformations, tracheobronchial malformations, malformations of the vascular and lymphatic systems of the lungs, benign tumors of the lungs, bronchi.1. Birth defects of lungs, trachea, bronchi
The respiratory system includes: nose, nasal airway, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.Congenital malformations of the lung-tracheobronchial-bronchi include:
Lung malformations: congenital lung deficiency, pulmonary hypoplasia, pulmonary emphysema,... Air-bronchial malformations: pneumothorax - bronchi, tracheal and bronchial diverticulum, tracheobronchial - esophageal fistula. Anomalies of the vascular and lymphatic systems of the lungs: malformations of arteries, veins, lymphatics, arteriovenous aneurysms - pulmonary veins. Benign tumors of the lung and bronchi: adenomas (adenomas), dysplastic tumors (hamarotoma), hemangiomas (hemangima).
2. Birth defects of the mate
2.1. Defect of missing a lung
This malformation is often associated with various congenital malformations such as: diaphragmatic hernia, esophageal stricture, congenital heart defects, and Botanian ductus (ductus botalli)... combined with other malformations often die very early. About 50% of children with a single lung defect do not live beyond 5 years due to an infection in the lung.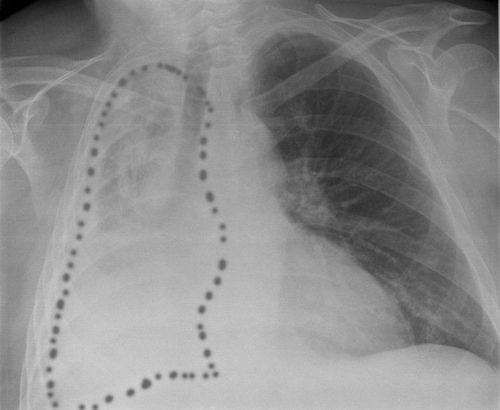
Dị tật thiếu 1 bên phổi
2.2. Deformity missing both lungs
The patient was born with only one stump of the trachea, while the bronchi and lungs were completely absent. Deficiency of both lungs is not clinically significant, because the child is already born without the ability to live.2.3. Lung hypoplasia
Lung parenchymal deficiency is caused by a disorder in the early stages of the fetus. It is worth noting that pulmonary hypoplasia is often associated with congenital heart diseases such as atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, and foramen ovale. The disease is also often accompanied by gastrointestinal abnormalities such as: no anus, tracheoesophageal fistula, Meckel's diverticulum.2.4.Congenital emphysema
This malformation is common in the left upper lobe of the lung, and rarely in the entire lung. Due to the increased volume of the lobe of the lung with emphysema, it has put pressure on the remaining lung parts, making the healthy lung parts unable to participate in respiration, the organs of the mediastinum are pushed to the opposite side. In some cases, the lobe of the lung that is enlarged with emphysema presses on the opposite side of the chest, compressing the lung on that side.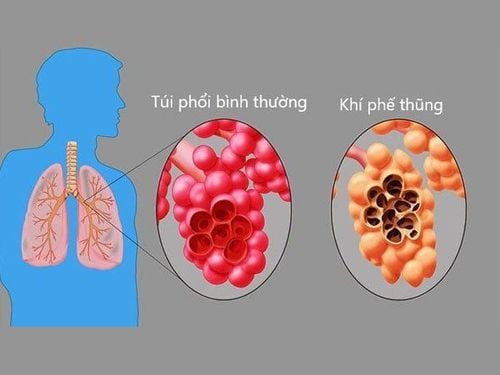
Khí thũng phổi bẩm sinh
3. Developmental malformations of tracheobronchial
Simple tracheobronchitis: Simple tracheobronchial dilatation is a rare disease. Aneurysms limited to the wall of the trachea: Common malformations of the cervical trachea. Patients often cough accompanied by sputum, coughing up blood. There are some cases without clinical symptoms. Bronchial diverticulum: Bronchial diverticulum is usually located in the medial bronchial wall and has many different forms Tracheoesophageal fistula: When there is a tracheoesophageal fistula, the lungs will aspirate food or reflux from the stomach into the lungs, leading to pneumonia and atelectasis. If not diagnosed and treated early, the baby will die within the first day after birth.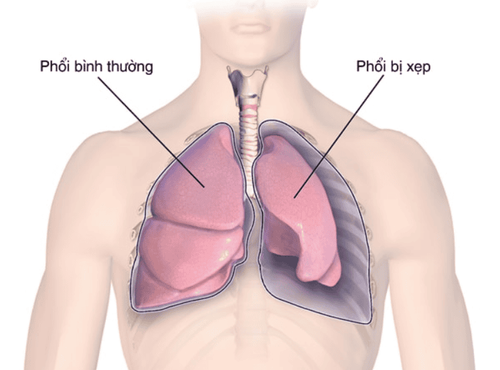
Xẹp phổi
For detailed advice on birth defects, please come directly to Vinmec medical system or book online HERE.