This article is prepared in consultation with doctors from the Department of Emergency Medicine at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Sinusitis, particularly ethmoid sinusitis, is a common respiratory condition. This article aims to provide you with essential information about ethmoid sinusitis.
1. What is Ethmoid Sinusitis?
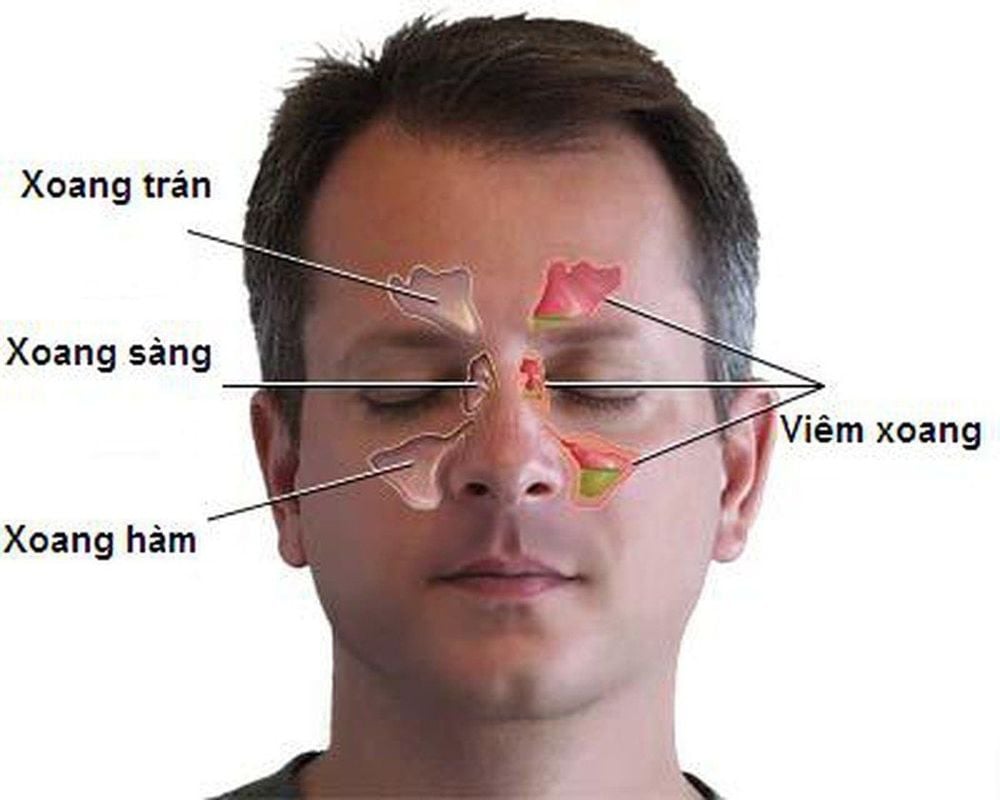
Ethmoid sinusitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the mucosal lining in the ethmoid sinuses, which leads to stagnant pus and blockage in this area. The ethmoid sinuses consist of four interconnected cavities located between the eyes.
There are two types of ethmoid sinusitis: Anterior Ethmoid Sinusitis (the sinus adjacents to the frontal and maxillary sinuses, as well as the nasal cavity and eye socket.) and Posterior Ethmoid Sinusitis (the sinus located behind the anterior ethmoid sinus, towards the neck.)
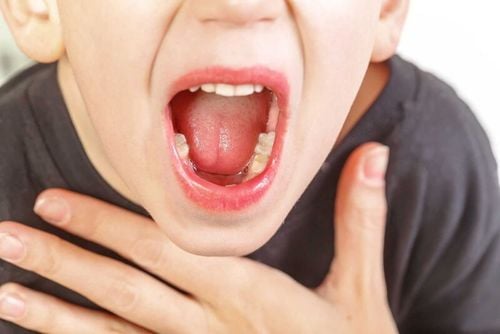
2. Symptoms of Ethmoid Sinusitis
Ethmoid sinusitis can lead to the following symptoms:
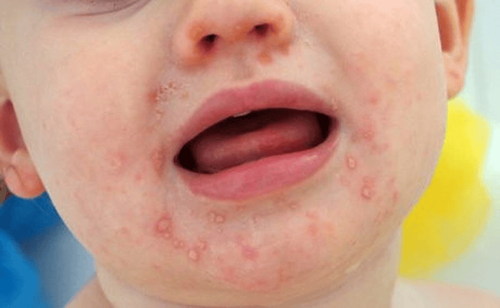
- Headache: Patients may experience dull pain in various areas including the temples, between the corners of the eyes, the top of the head, the forehead, the bridge of the nose, and the back of the neck.
- Reduced or blurred vision: Some patients may suddenly experience severe blurred vision, which could potentially lead to loss of vision.
- Tinnitus and dizziness: Patients may feel a heaviness in the ears, accompanied by dizziness.
- Phlegm in the throat: This can cause throat irritation, leading to coughing, and in severe cases, may result in difficulty breathing or wheezing during sleep.
- Bad breath: The drainage of sinus fluid down the throat can lead to persistent bad breath, which may impact self-confidence and cause stress, affecting daily activities and communication. This condition often worsens with dehydration or poor oral hygiene.
3. Treatment of Ethmoid Sinusitis
3.1 Medical Treatment
Mild cases of ethmoid sinusitis can often be managed with medical treatments.
Medications for Ethmoid Sinusitis:
Medications need to be effectively delivered to the sinuses to eliminate fungi and bacteria, reduce pus buildup that causes congestion, and enhance the body's immune system to prevent future occurrences.While some medications provide immediate relief from congestion, prolonged and high-dose use can lead to dependency. Additionally, certain treatments for sinusitis may have side effects and can negatively impact the liver and kidneys if misused. Therefore, patients need to use medications only as prescribed by a healthcare professional and to avoid unsupervised use.
- Supportive measures for Sinusitis relief:
- Drink plenty of fluids and use steam with essential oils to help clear the nasal passages. Essential oils can also alleviate pain and provide relaxation.
- Rinse the nasal cavity with saline solution 1-2 times a day to combat bacteria and prevent viral infections.
- Incorporate foods like garlic into your diet to help reduce symptoms associated with respiratory issues, such as sinusitis and the flu.
3.2 Surgical Treatment
If a patient does not show signs of improvement after undergoing medical treatment, it may indicate that the disease has progressed significantly, potentially leading to dangerous and even life-threatening complications. In such cases, the treating physician will assess the situation and may recommend surgery.
The current surgical approach for treating ethmoid sinusitis is Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS). This method aims to restore normal circulation and drainage functionality in the nose and sinuses. It is important to note that patients with allergies or compromised immune systems have a higher risk of disease recurrence.
4. Complications of Ethmoid Sinusitis
If left untreated, sinusitis, including ethmoid sinusitis, can lead to serious complications due to the sinus's proximity to the eyes and skull. Some of these dangerous complications include:
- Eye pain: Acute ethmoid sinusitis can result in symptoms such as red eyes, eyelid inflammation, swelling, possible pus accumulation, eyeball abscesses, optic neuritis, decreased vision, and in severe cases, progressive vision loss.
- Lower respiratory tract complications: It may lead to tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or even pharyngeal abscesses.
- Ear infections: Sinusitis can spread to the ears, resulting in otitis media and pus build-up in the ear. If untreated for an extended period, this pus can create pressure on the eardrum, leading to a rupture and potential deafness. In severe cases, serious ear infections can develop into purulent meningitis, which poses life-threatening risks.
5. How to prevent Ethmoid Sinusitis?
- Limit and avoid exposure to allergens, including dust, polluted environments, chemicals, pollen, and places with high pathogen levels.
- Maintain good personal hygiene and ensure that your living environment is clean.
- Keep your body warm, particularly in the sinus area, during weather changes, especially when it turns cold or when humidity levels fluctuate.
The ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) Department at Vinmec International General Hospital specializes in diagnosing and treating common conditions such as rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, sore throat, tinnitus, non-allergic rhinitis, throat cancer, tumors in the head, face, and neck, as well as congenital defects in the ear, nose, and throat using standard surgical methods.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.