This is an automatically translated article.
Vitamin C plays an important role in the body. It is necessary to maintain the health of skin, cartilage, teeth, bones and blood vessels. It is also used to protect your body's cells from aging. The use of vitamin C in different doses will give different good or bad effects.
1. Side effects of vitamin C
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Vitamin C is safe for pregnant or nursing women when taken by mouth in amounts no more than 2000mg per day for women over 19 years old and 1800mg per day for women 14-18 years old. age or when administered intravenously (by IV) or intramuscularly. Taking too much vitamin C during pregnancy can cause problems for the unborn baby. Vitamin C may not be safe when taken by mouth in excessive amounts.
Infants and young children : Vitamin C is safe when taken by mouth in appropriate doses. Vitamin C is possibly unsafe when taken by mouth in amounts higher than 400 mg per day for children 1 - 3 years old, 650mg daily for children 4 - 8 years old, 1200mg daily for children 9 - 13 years and 1800 mg daily for adolescents 14 - 18 years.
Alcoholism: Drinking alcohol can cause the body to excrete vitamin C in the urine. People who regularly use alcohol, especially those with other medical conditions, are often deficient in vitamin C. These people may need treatment for a longer time than usual to restore vitamin C to its normal state. normal level.
Alzheimer's disease: Taking vitamin C along with vitamin E and alpha-lipoic acid might decrease mental well-being in people with Alzheimer's disease.
Angioplasty, cardiac procedures: Avoid taking supplements containing vitamin C or other antioxidant vitamins (beta-carotene, vitamin E) immediately before and after angioplasty without supervision. doctor's supervision. These vitamins seem to interfere with the healing process.
Weight loss surgery: Weight loss surgery can cause the body to absorb more oxalates from foods. This can increase the amount of oxalate in the urine. Too much oxalate in the urine can cause problems like kidney stones. Vitamin C can also increase the amount of oxalate in the urine. Taking large amounts of vitamin C after weight loss surgery may increase your risk of having too much oxalate in your urine.
Cancer: Cancer cells also need to use high concentrations of vitamin C in growing cancer cells. Therefore, only use high doses of vitamin C under the direction of a doctor treating cancer.
Kidney disease: Vitamin C can increase the amount of oxalate in the urine. Too much oxalate in the urine can increase the risk of kidney failure in people with kidney disease.
Diabetes: Vitamin C can increase blood sugar. In older women with diabetes, vitamin C in amounts greater than 300 mg per day increases the risk of death from cardiovascular diseases. Do not take vitamin C in larger doses than a basic multivitamin.
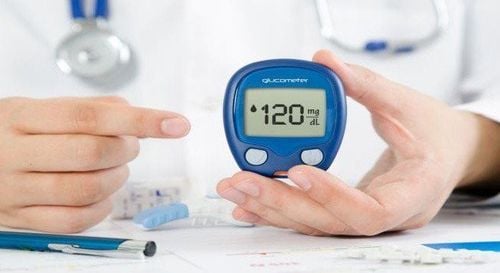
Vitamin C có thể làm tăng đường huyết
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency: Large amounts of vitamin C can cause red blood cells to break down in people with this condition. Avoid taking too much vitamin C with G6PD deficiency.
Iron disorders, including thalassemia and hemochromatosis: Vitamin C can increase iron absorption, which can make these conditions worse. Avoid taking large amounts of vitamin C when suffering from these conditions.
Kidney stones, or a history of kidney stones: Large amounts of vitamin C can increase your chances of getting kidney stones. Do not take vitamin C in larger amounts than a basic multivitamin.
Heart attack: Vitamin C levels are reduced during a heart attack. However, low vitamin C is not associated with an increased risk of heart attack.
Kidney transplantation: Long-term use of high doses of vitamin C before a kidney transplant may increase the risk of rejection or delay the time until the transplanted kidney is functional.
Schizophrenia: Taking vitamin C along with vitamin E might worsen psychosis in some people with schizophrenia while taking antipsychotics.
Smoking and chewing tobacco: Smoking and chewing tobacco lowers vitamin C levels. Dietary vitamin C intake should be increased in people who smoke or chew tobacco.

Lượng vitamin C trong chế độ ăn nên được tăng lên ở những người hút thuốc lá
2. Instructions for safe use of vitamin C
Oral: Take vitamin C by mouth, with or without food, usually 1-2 times/day. Follow all directions on the product package, or as directed by your doctor.
Release capsules: If you are taking extended release capsules, swallow them whole. Do not crush or chew extended-release capsules or tablets. Doing so can release all of the drug at once, increasing the risk of side effects. Also, do not split extended-release tablets unless they are marked and your doctor or pharmacist tells you to. Swallow the tablet whole or split it without crushing or chewing. Take this product with a full glass of water (8 ounces / 240 ml) unless your doctor directs you otherwise.
Wafers or chewable tablets: If you are taking a wafer or chewable tablet, chew thoroughly, then swallow. If you are taking a lozenge, place the lozenge in your mouth and let it dissolve.
Powder form: If you are using powder, mix thoroughly in the appropriate amount of liquid or soft food and stir well. Drink / eat immediately, do not deduct for the next time. If you are using the liquid form of this vitamin, carefully measure the dose using a special measuring instrument/spoon. Do not use household spoon as you may not get the correct dose.
Dosage is based on medical condition and response to treatment. Use this vitamin regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, use it at a time each day. If you experience serious health problems while taking vitamin C, see your doctor immediately.
3. Preventive measures

Trước khi dùng vitamin C, hãy nói kỹ với bác sĩ về tình trạng của mình, đặc biệt nếu bạn có dị ứng
Before taking vitamin C, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients (such as peanuts/soybeans), which may cause allergic reactions or other problems.
Before using this vitamin, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: kidney disease (such as kidney stones), certain enzyme deficiencies (G6PD deficiency).
During pregnancy, vitamin C is safe when used in recommended doses. Higher doses should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
Vitamin C passes into breast milk and is considered safe during breastfeeding when used in recommended doses. Consult your doctor for more information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com












