This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Nguyen Cong Nghia - Head of Obstetrics Department - Obstetrics Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Sexually transmitted infections or sexually transmitted diseases are infections that are spread through sexual contact. STIs can have serious long-term health consequences: infertility, ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, even death, and problems with pregnancy.
Having a sexually transmitted infection also increases your risk of getting HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) if you are exposed to it.
1. How are sexually transmitted infections spread?
Sexually transmitted infections caused by bacteria or viruses. Infections caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics. Infections caused by viruses cannot be treated, only symptoms can be reduced.
A person with an STI can be passed on to others through skin contact, genitals, mouth, rectum, and bodily secretions. Any individual who has vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person is at risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection. Sexually transmitted infections can cause no symptoms, and even when there are no symptoms, health status can still be affected.
2. What are the most common sexually transmitted infections?

Viêm gan B có thể lây qua đường tình dục
Sexually transmitted infections include:
Chlamydia (also known as chlamydia trachomatis) Gonorrhea Syphilis HSV (Genital Herpes) HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) HPV (human papillomavirus) ) Trichomonas (also known as Trichomonas vaginalis) Hepatitis B. Bacterial vaginosis or candida albicans vaginitis are common infections that are not sexually transmitted. This infection is caused by an imbalance of bacteria and fungi that normally develop in the vaginal environment, due to antibiotic use, hormonal changes, vaginal douching or a weakened immune system.
3. What factors increase the risk of STIs?
Factors that increase the likelihood or risk of STIs include:
Having more than one sexual partner Having a new sex partner Having a partner with more than one other sexual partner History of having an STI sex Sexual contact with an infected person Do not use condoms regularly when having sex with more than one partner.
4. Who is recommended for STI screening?
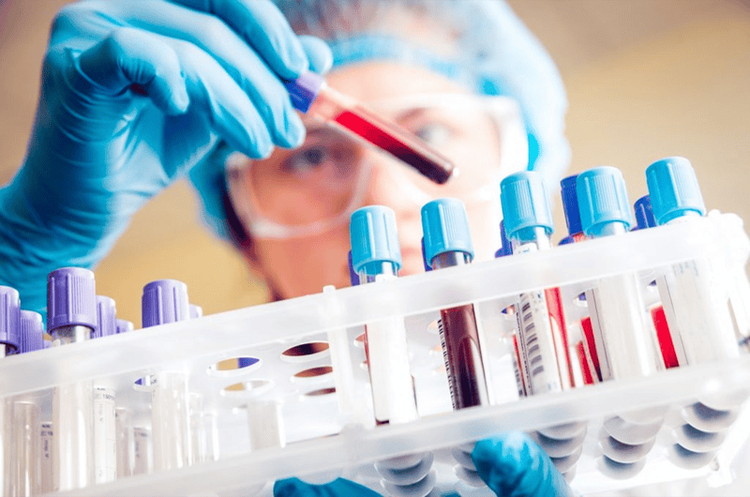
Phụ nữ có sinh hoạt tình dục đều đặn nên thường xuyên xét nghiệm HIV, chlamydia và lậu dù chưa có dấu hiệu
Before performing screening on a patient, the physician will perform a simple risk assessment questionnaire needed to screen for STIs. However, even if there are no symptoms, sexually active women are advised to regularly get tested for HIV, chlamydia and gonorrhea. Chlamydia is so common in young people that sexually active women under 25 years of age are usually recommended for screening.
5. Steps to screen for sexually transmitted diseases
After completing the questionnaire and ordering a screening test, the doctor will conduct a more detailed history, symptoms and conduct a physical examination. The doctor will examine the genitals, rectum, urethra and surrounding tissues for abnormalities. Your doctor will collect vaginal fluid, urine, and blood for the necessary tests, including smears, staining, cultures, and PCR tests.
6. How to prevent the risk of sexually transmitted infections?
Know your sexual partners well and limit the number, their sexual history is just as important as yours. The more sexual partners you or your partner have, the higher your risk of getting a sexually transmitted infection. Use a condom every time you have sex, whether vaginal, anal, or oral. Avoid sex that causes tearing of the skin is high risk, even if there is no bleeding, pathogens can still be exchanged. Anal intercourse is high risk because the rectum is very easy to tear. Body secretions also carry pathogens. Vaccination: Vaccines against hepatitis B and some common strains of HPV are currently available.
7. How do sexually transmitted infections affect the fetus?

Bệnh nhiễm khuẩn lây qua đường tình dục có nguy cơ ảnh hưởng xấu đến thai nhi
Having a sexually transmitted infection has many risks for the unborn baby. Gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause neonatal eye infections or pneumonia. Syphilis can cause miscarriage or stillbirth. HIV can be passed from mother to child if there is no preventive treatment.
Tests for STIs are recommended for pregnant mothers because early treatment can reduce the risk of fetal infection. Often both you and your partner need treatment at the same time.
Package of Social Diseases Examination and Screening of Vinmec International General Hospital helps customers to screen for social diseases in order to detect diseases early for effective treatment and avoid complications.
Package of screening for social diseases for all ages, for both men and women. For consultation and to book an appointment, you can contact HERE.