This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Atrioventricular block is a condition in which the transmission of electrical impulses in the heart from the atria to the ventricles is partially or completely interrupted. Atrioventricular block is classified into 3 different grades, of which second-degree AV block is moderate but can still cause many dangerous complications.
1. Normal electrophysiology of the heart and electrocardiogram
The heart is considered one of the most important organs in the body. The heart acts as a pump, both sucking oxygen-poor blood to exchange with oxygen in the lungs, and pumping oxygen-rich blood to supply oxygen for the activities of other organs in the body.
To work effectively, the heart needs to work according to the rhythmic electrical conduction mechanism, from the sinus node, atrium to the ventricle, through the pacemaker nodes and the electrical impulse conduction system of the heart muscle fibers. .
In the normal person, the sinus node is the site of the first electrical impulse and conducts it through the atria. At that time, the image shown on the electrocardiogram is the image of the P wave. Then, the electrical impulse from the atria travels down to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node. Next, the electrical impulse is conducted through the entire ventricle through the His system and Purkinje fibers, represented on the electrocardiogram by the QRS complex. Finally, the myocardium will repolarize to start a new cycle and the electrocardiogram will record a T wave.
See also: Diagnosis and treatment of atrioventricular block
2. What is 2nd degree AV block?
Atrioventricular block is a partial or complete obstruction of the conduction of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles. Atrioventricular block is divided into:
First degree atrioventricular block: electrical impulses are successfully conducted from the atria to the ventricles, but the duration is slightly slower than normal.
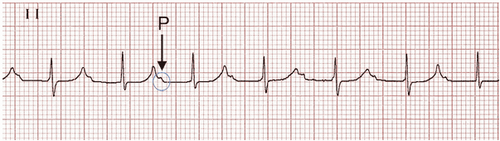
Second degree atrioventricular block: electrical impulses travel from the atria to the ventricles from time to time, so the heart rhythm is sometimes irregular or may lose rhythm. Third degree atrioventricular block: electrical impulses are not conducted at all from the atria to the ventricles, causing the atria and ventricles to contract but not contact each other (called atrioventricular dissociation). In which, 2nd degree atrioventricular block is divided into 2 different types, including:
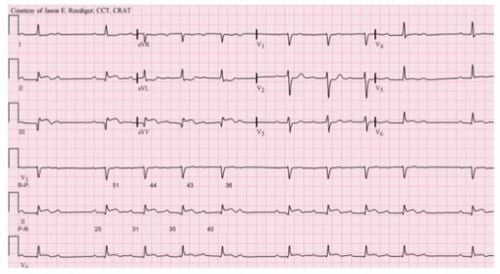
2nd degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz I (Wenckebach cycle): ECG 2nd degree atrioventricular block Mobitz I is characterized by PR interval becomes progressively longer until there is a complete block cycle (with P waves but no QRS complexes following). Second-degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz I is usually a relatively benign disorder with little hemodynamic impact and the possibility of progression to third-degree AV block is not high. 2nd degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz II: Electrocardiogram of second-degree atrioventricular block Mobitz II is characterized by PP intervals that remain the same but suddenly have a complete block cycle, with P waves but no QRS complexes. Second-degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz II can cause more hemodynamic instability in patients than Mobitz I, which can cause severe bradycardia and progression to third-degree AV block.
3. Causes of 2nd degree atrioventricular block
In most cases of second-degree atrioventricular block, the exact cause of the disease cannot be found. Some common causes of second-degree AV block include:
Vagal hyperfunction (eg, athletes...) After cardiac surgery, especially proximal surgery septums such as mitral valve repair. After myocardial infarction, myocardial damage... Myocarditis. Low heart. Excessive effects of some antiarrhythmic drugs such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers or digoxin... Autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus. Electrolyte disturbances, especially severe and persistent hypokalemia.
4. Symptoms of 2 degree atrioventricular block
Similar to first-degree, second-degree atrioventricular block may still not cause any symptoms or clinical signs. However, some patients develop relatively dangerous symptoms if the arrhythmia causes the heart to not pump enough blood, including:
Chest pain, chest tightness due to lack of blood supply to the heart. Tired, short of breath. Dizziness, dizziness, lightheadedness. Fainting or threatened to faint. Some can cause transient ischemic attack or stroke, cerebrovascular accident due to lack of blood supply to the brain.
5. How to treat 2nd degree atrioventricular block?
5.1. 2nd degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz I Most patients are diagnosed with 2nd degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz I if there are no symptoms, no treatment is needed, just periodic monitoring to detect any associated abnormalities early. .
When patients have symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, electrocardiogram 2nd degree atrioventricular block, most often respond to treatment of increased heart rate with Atropine. Permanent mechanical pacing is rarely indicated.
5.2. Atrioventricular block 2 - Mobitz II Patients who are diagnosed with 2nd degree atrioventricular block - Mobitz II need immediate hospitalization for cardiac function monitoring, temporary pacemaker placement and mandatory permanent pacemaker implantation. in the heart chambers.
A pacemaker (temporary or permanent) is a small electrical device that is connected to the heart muscle and controls the action of the ventricles, helping the ventricles contract and create a fixed rhythm or help the heart beat faster in response to with strenuous activity as needed.
6. Lifestyle of patients with 2 degree atrioventricular block
Follow your doctor's treatment and instructions. Monitor your health regularly, follow up with your doctor's appointment to detect possible abnormalities. If the patient is put on a pacemaker, it is necessary to stay away from electronic devices, transmitters and strictly follow the treatment and instructions of the doctor. A heart-healthy diet, low in fat and protein, with lots of green vegetables and fruits. Maintain weight, avoid overweight and obesity. Do not smoke and drink alcohol. Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases, including Cardiology. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used modern facilities and machinery along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of doctors. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.