This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International Hospital
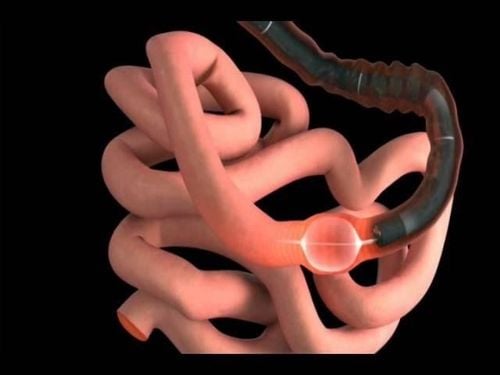
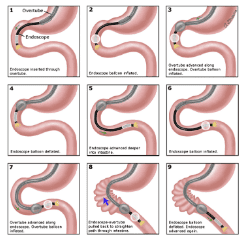
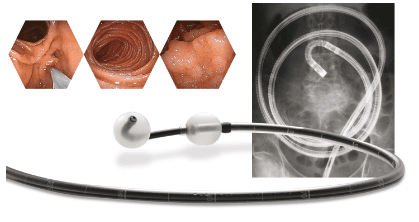
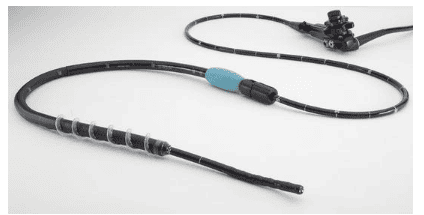
Single-balloon colooscopy is usually done by two endoscopists, but it may be easier with a dual-balloon colooscopy done with a single colonoscope. Enteroscope and overube are advanced techniques similar to the insertion technique of double-balloon colostrum.
1. Small bowel endoscopic techniques
Single-balloon colooscopy is usually done by two endoscopists, but it may be easier with a dual-balloon colooscopy done with a single colonoscope. Enteroscope and overube are advanced techniques similar to the insertion technique of double-balloon colostrum.
Balloon-guided small bowel endoscopy (BGE) is performed using a balloon-tipped bronchoscope (TTS) that is inserted into the working channel of any endoscope. The balloon is then inflated, allowing fixation of the tube in the small intestine, and tube entry is achieved with repeated push-and-pull movements by sliding the endoscope through the catheter. Balloon catheters can be removed for therapeutic interventions. The main limitation of this technique is the low stability of the endoscope during treatment due to the lack of an anchor ball. To overcome this shortcoming, recently developed a colposcope with integrated latex-free balloon in the flexure. These colonoscopes, combined with a disposable support balloon applied through the device channel, provide the assembly for performing deep double-balloon enteroscopy. The balloon endoscopes as well as the balloon assist devices are controlled simultaneously by the air pump system. The feasibility and safety of BGE using the NaviAid AB device was recently evaluated in children with IBD.
2. Results of small bowel endoscopy in adult patients with suspected inflammatory bowel disease IBD
Five studies evaluating the impact of assistive small bowel endoscopy on adults with suspected IBD.
In a German retrospective study, 16 adult patients with clinically suspected small bowel Crohn's disease underwent assistive small bowel endoscopy after gastroscopy and colonoscopy. normal colon. Abnormal small bowel findings were detected in 7 patients (44%) but histological findings of Crohn's disease were found in only one case (6%). However, the diagnosis of Crohn's disease was confirmed in 11 of 16 (69%) patients taking into account clinical, endoscopic, and radiological features.
3.The role of small bowel endoscopy in small intestine biopsy samples
Tun et al retrospectively evaluated the impact of dual-balloon endoscopy and histology on the diagnosis and management of 100 adult patients with suspected small bowel Crohn's disease, based on clinical and laboratory data. and after colonoscopy and radiographic studies or capsule endoscopy, a diagnosis of Crohn's disease is not reached.
Abnormal double-balloon endoscopic findings were detected in 60 patients (ulcer, n = 47; stenosis, n = 11; mucosal abnormality, n = 2), and biopsies were collected Okay. There were 23 patients who showed no histological abnormalities despite the macroscopic appearance of Crohn's disease on dual-balloon endoscopy, while in the remaining 37 patients, the diagnosis of Crohn's disease was confirmed by histological examination. confirmed in 8 patients (22%), and 15 (41%) with histology suggestive of Crohn's disease.
However, combining clinical, biochemical, endoscopic, and histological findings, 45% of all patients were treated for Crohn's disease. After a median follow-up of 27 months, the diagnosis of Crohn's disease was confirmed in 38% of patients with imaging suggestive of Crohn's disease with dual-balloon endoscopy.
The diagnostic efficacy and impact on clinical outcomes of the use of single-balloon endoscopy for suspected small bowel Crohn's disease was evaluated in an Italian retrospective study, including 13 adult patients. The diagnostic efficiency was 39%, detecting four patients with active ileitis and one patient with ileal stricture. For the remaining eight patients, a new diagnosis of Crohn's disease was achieved in 4 patients (8%) and excluded in the remaining 4 patients (8%).
4.Endoscopy of small intestine in children with suspected inflammatory bowel disease
Five studies, two on single-balloon endoscopy, two on dual-balloon endoscopy, and one on small-bowel enteroscopy (BGE), evaluating the impact of dual-balloon endoscopy on children with suspected inflammatory bowel disease IBD.
In a previously published study by several authors, 16 pediatric patients with suspected Crohn's disease and nonspecific findings after comprehensive evaluation by upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy, abdominal MRI, and colonoscopy Cysts were evaluated by small-bowel endoscopic examination. Single-balloon enteroscopy made the histological diagnosis of Crohn's disease in 12 patients and eosinophilic enteropathy in 2, with no lesions found in the remaining 2 patients. Furthermore, single-balloon enteroscopy allowed dilation of small bowel strictures identified on MRI in 2 patients with suspected Crohn's disease.
De Ridder et al evaluated the diagnostic results of single-balloon small bowel endoscopy for pediatric Crohn's disease. In this study, the patients were directly evaluated by bidirectional single-balloon enteroscopy (oral and anal), and in 8 of 14 patients with suspected Crohn's disease, the diagnosis was confirmed after small bowel endoscopy with a single bulb.
Urs et al performed double-balloon enteroscopy in 3 patients with suspected Crohn's disease after capsule endoscopic examination revealed mucosal abnormalities. Dual-balloon enteroscopy resulted in a diagnosis of Crohn's disease in 2 out of 3 patients, and Crohn's disease was excluded in the remaining child because of the absence of mucosal lesions and normal histology.
Study from Uchida et al., evaluating the efficacy and safety of dual-balloon small bowel endoscopy in 8 children with suspected Crohn's disease after gastroscopy, colonoscopy, and a contrast study. small intestine is inconclusive. Dual-balloon enteroscopy confirmed the diagnosis of Crohn's disease in 2 of 8 patients, resulted in an alternative diagnosis in 4, and found no mucosal lesions or histological abnormalities in the remaining 2 patients. .
5.The role of the NaviAid AB . small bowel endoscope
Recently, Broide et al evaluated the feasibility and safety of a NaviAid AB balloon-assisted colonoscopy system in children with suspected IBD. Technical success was achieved at 95.23% and 85.7% of the upstream and downstream approaches, respectively. Furthermore, the total procedure time is significantly shorter and the learning curve faster than the ball-assisted endoscopic system, because of its intuitive and simple operation. Unfortunately, the diagnostic outcome of this technique has not been evaluated. Of the 15 patients with suspected IBD, 3 were diagnosed with UC and 3 with Crohn's disease; The remaining 9 patients did not have intestinal abnormalities.
According to the authors, in children with suspected IBD, the following approach would be suggested: Device-assisted small bowel endoscopy is recommended during routine endoscopy, imaging of the small intestine by CT Scan or MRI and capsule endoscopy are inconclusive and tissue sampling and/or therapeutic procedures will change the management of the disease. Device-assisted small bowel endoscopy should be the preferred primary endoscopic procedure only when a narrowing or easily accessible lesion (ie, small bowel wall thickness) is suspected on imaging. This is justified due to the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of assistive small bowel endoscopy and the high risk of capsule retention.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.