This is an automatically translated article.
Gallbladder cancer is a relatively rare but dangerous disease, because the cancer grows quickly and easily metastasizes to other organs. Therefore, people at high risk of gallbladder cancer, such as people with gallstones or cholecystitis, should have good control of the disease and have regular check-ups for cancer screening.
1. What is gallbladder cancer?
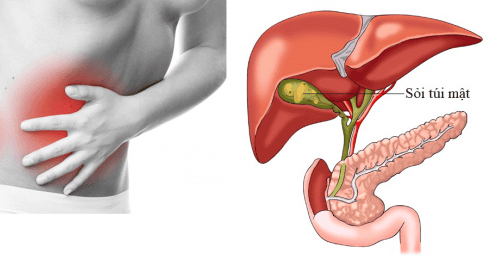
Gallbladder cancer is cancer that begins in the gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just below your liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by your liver. Gallbladder cancer is uncommon.
When gallbladder cancer is detected at its earliest stage, the chances of a cure are very good. But most gallbladder cancers are detected at a late stage, when the prognosis is often poor.
Gallbladder cancer is difficult to diagnose because it often causes no specific signs or symptoms. In addition, the relatively hidden nature of the gallbladder makes it easier for gallbladder cancer to grow undetected.
2. Causes of gallbladder cancer
The cause of gallbladder cancer is unknown.
Doctors know that gallbladder cancer forms when healthy gallbladder cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. These mutations cause cells to grow out of control and continue to live when other cells normally die. The cells that accumulate form a tumor that can grow beyond the gallbladder and spread to other areas of the body.
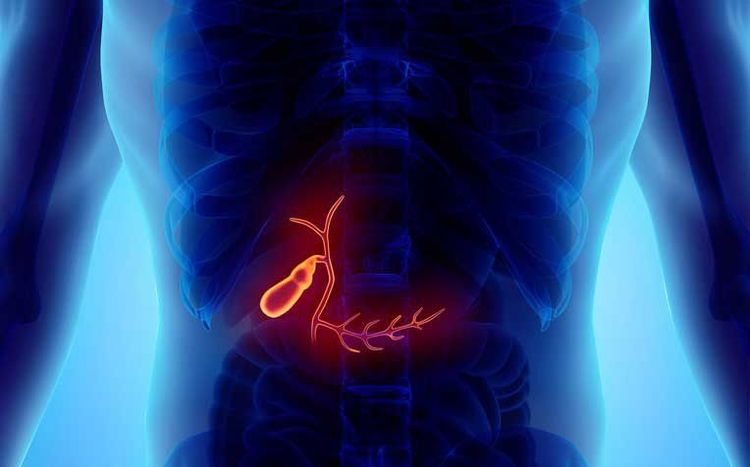
Hiện nay chưa rõ nguyên nhân chính thức gây ung thư túi mật
Most gallbladder cancer begins in the glandular cells located on the inner surface of the gallbladder. Gallbladder cancer that begins in this type of cell is called adenocarcinoma. This term refers to how cancer cells appear when examined under a microscope.
3. Gallbladder Cancer Risk Factors
3.1 Gallstones Gallstones are the most common gallbladder cancer risk factor. These are stone-like components of cholesterol and bile salts that can occur in the gallbladder or bile ducts. However, less than 1% of people with gallstones develop gallbladder cancer. It is not clear why some people develop cancer while most do not.
Up to 4 out of 5 people with gallbladder cancer have gallstones when diagnosed. But gallstones are very common, and gallbladder cancer is quite rare. And most people with gallstones never develop gallbladder cancer.
3.2 Gallbladder Polyps This type of polyp is a growth that sometimes forms when small gallstones are embedded in the wall of the gallbladder. Gallbladder polyps bulge from the inside of the gallbladder wall. Some polyps can also be caused by inflammation. Doctors often recommend cholecystectomy for people with polyps larger than 1cm because these people are more likely to develop cancer.
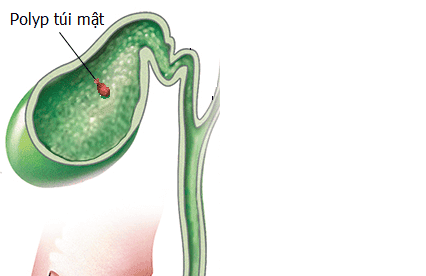
Polyp túi mật là yếu tố nguy cơ gây tình trạng ung thư túi mật
3.3 Gallstones Gallstones Gallstones are a condition in which the wall of the gallbladder becomes covered with calcium deposits. It sometimes occurs after long-term inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), which can be caused by gallstones. People with this condition have a higher risk of gallbladder cancer, possibly because both of these conditions can be associated with inflammation.
3.4 Age, sex Gallbladder cancer is seen mainly in the elderly, but younger people can also develop it. The average age of people when they are diagnosed is 72. Most people with gallbladder cancer are 65 or older.
Gender. Women are twice as likely to develop gallbladder cancer than men. Gallbladder cancer occurs three to four times more often in women than in men.
3.5 Carcinogens Toxic substances are normally filtered by the liver and excreted into the bile. Bile flows through the gallbladder. This exposes the gallbladder to these substances. Workers in rubber factories and textile factories have higher rates of gallbladder cancer. But because gallbladder cancer is relatively rare, it's hard to know if exposure to substances actually causes gallbladder cancer.
Khi vô tình sử dụng chất động hại, gan và mật là các cơ quan tiếp nhận và xử trí chúng
3.6 Bile duct abnormalities Bile ducts are the tubes that carry bile from the liver and gallbladder through the pancreas to the small intestine. Bile is a liquid used by the body to break down fats in the foods you eat. Abnormal bile ducts can slow the flow of bile from the gallbladder or they can let pancreatic juice into the gallbladder. This seems to increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Cysts along the bile duct may also increase the risk.
3.7 Primary cholangitis This disease causes inflammation and scarring in the bile ducts and increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
3.8 Smoking Tobacco use can increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
3.9 Obesity Gallbladder cancer patients are more often overweight or obese than those without the disease. Obesity is also a risk factor for gallstones, which may help explain this link.
3.10 Family history A family history of gallbladder cancer slightly increases a person's risk of gallbladder cancer.
Periodic health check-ups help detect diseases early, thereby planning treatment for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy.
The results of the patient's examination will be returned to the home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties right at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.