This is an automatically translated article.
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are both terms for the destruction of joints in the body, causing swelling, pain and stiffness. Both diseases are classified as autoimmune diseases, where the immune system attacks the body's normal components. However, there are differences between rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
1. Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis
Arthritis is a general term for pain and destruction of joints. Arthritis is divided into several different types, including rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
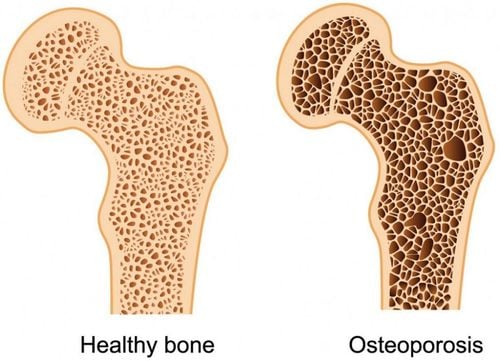
Psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune disease affecting up to 30% of all patients with psoriasis and about 1% of the general population. Of the most diagnosed cases of psoriatic arthritis, the patient has a history of psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis occurs in men and women, the average age of onset is between 40 and 50 years old. Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic disease, and currently there is no complete cure. Arthritis is not the only sign of the disease. Psoriatic arthritis can damage many other organs in the body, such as the heart, lungs, and eyes. Osteoporosis and tendinitis are also possible complications.
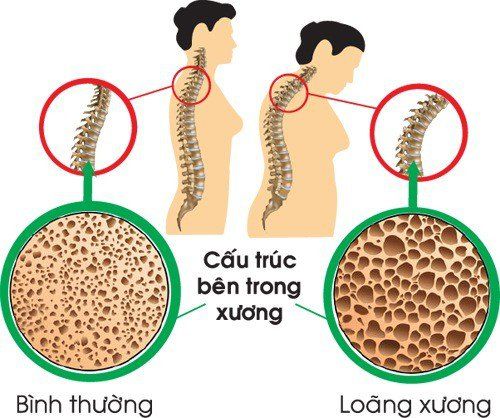
Viêm khớp vảy nến có thể gặp biến chứng loãng xương
Rheumatoid arthritis is also an autoimmune disease caused by the immune system attacking the joints. This leads to an inflammatory response that thickens the tissue lining the inside of the joint, reducing the secretion of joint fluid that causes stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is considered a systemic disease that affects the entire body. Initially, the disease affects only the joints, later on, other complications can appear in many organs. Women are 3 times more likely to get the disease than men. The average time of disease onset is about 30 to 60 years old, in which the onset of the disease is later in men. It is estimated that about 1.5 million Americans have rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Causes of disease
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes swelling and pain in the joints, especially in places like the hands, feet, wrists, elbows, knees, ankles and cervical vertebrae. The cause of the disease is thought to be a malfunction in the immune system, which attacks the synovial lining of the joints, but the exact mechanism is not fully understood. Rheumatoid arthritis is a familial disease. The chance of getting the disease is higher when there are family members with rheumatoid arthritis. Psoriatic arthritis is also a familial disease. Several specific genes are involved in disease onset. Researchers still don't know the exact trigger that triggers the disease in these two types of arthritis. However, the accepted hypothesis is a combination of genes and other factors, including hormones, viruses, bacteria.
3. Clinical symptoms
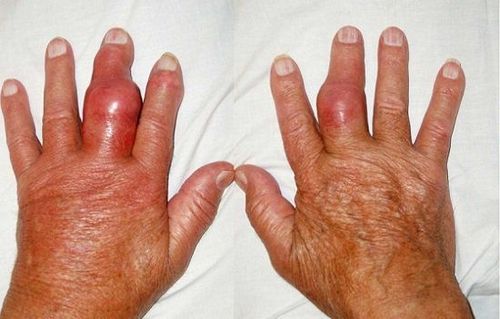
Các ngón tay sưng nề nhiều là dấu hiệu viêm khớp vảy nến trên lâm sàng
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis both cause swelling, pain, and stiffness in the joints. Both of these conditions mainly affect the joints in the hands and feet.
Clinical signs of rheumatoid arthritis include:
Onset in small joints such as fingers and toes. Over time, the disease affects other joints such as the wrists, knees, pelvis, and ankles. Symptoms appear symmetrically on both sides of the body Often stiffness appears in the morning Patients may feel tired, low-grade fever and weight loss Clinical manifestations of psoriatic arthritis include:
Affects joints in back and pelvis area concurrently with finger and toe joints Present in joints asymmetrical, usually only on one side Occasional leg pain, especially in soles and heels Severe swelling of the fingers , there is a fistula near the nails Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis appear strongly in the acute stages of the disease. Between exacerbations, symptoms improve or disappear.
4. Diagnosis of disease
Because both diseases have similar clinical symptoms, the differential diagnosis should be based on laboratory tests. Determination of low factor in the blood helps in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Patients with psoriatic arthritis alone do not have low levels of factor in the blood. Quantitative testing of certain other antibodies, such as anti-CCP, also helps differentiate rheumatoid arthritis from psoriatic arthritis.
Doctors can distinguish these two diseases based on the appearance of the skin and nails. If there are red, scaly patches of skin, nails with many needle holes, the patient is likely to have psoriatic arthritis.
X-ray film is indicated to distinguish when the disease has progressed for a while based on the lesions in the joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis can co-occur but is rare. At this point, the diagnosis and treatment are sometimes more complicated.
5. Treatments

Thuốc kháng viêm không steroid
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are both chronic diseases, there is no cure to completely cure the disease. Treatment focuses only on easing symptoms and improving quality of life.
5.1. Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis can affect people in many ways. If the pain is only mild, the patient is prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). When symptoms are more severe, doctors will prescribe anti-rheumatic drugs instead of NSAIDs. When exacerbations occur, parenteral steroids are chosen for pain relief or surgical repair of the joints.
5.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
There are many rheumatoid arthritis treatments that help control the course of the disease and relieve symptoms. Many drugs that have been studied for a long time have shown good therapeutic effects such as anti-rheumatic drugs to slow the progression of the disease. Physical therapy and surgery are also applied.
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are both autoimmune diseases and currently there is no cure. Therefore, in order to minimize the complications caused by the disease, the patient should go to reputable medical facilities for timely examination and treatment to limit the progression of the disease as well as limit the complications affecting the patient. to health.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a modern medical facility with the function of examining and treating musculoskeletal, immunological - allergic diseases. At Vinmec, there are all necessary medical equipment to perform simple to complex treatment methods such as medical treatment, medical intervention. Accordingly, the entire examination and treatment process at Vinmec is carried out by a team of highly qualified medical professionals who have undergone training and are granted technical certificates, able to handle quickly and effectively. , especially in cases of urgent need. Therefore, patients with musculoskeletal diseases or many other diseases can rest assured with a strict, methodical and effective treatment process at Vinmec.
For detailed advice on treatment methods at Vinmec, please go directly to Vinmec medical system nationwide or register online HERE.