This is an automatically translated article.
Intussusception is a common condition in children, which can cause necrosis if not detected and treated early. Laparoscopic intussusception surgery is an effective treatment, minimizing the risk of recurrence of this pathology.
1. What is intussusception?
Intussusception is a condition in which a segment of intestine turns upside down, entering the lumen of the adjacent intestine. Intussusception can occur at any age but is more common in children under 2 years of age (accounting for up to 80% of intussusception cases). The disease is common in boys, especially in chubby babies.
Children with intussusception often have symptoms such as:
Abdominal pain intermittently: Children cry intermittently, sudden, severe abdominal pain, children hunched over, twisted, stopped playing, stopped feeding. The pain lasts 5-15 minutes, comes and goes suddenly. After that, the child becomes weak and tired, the interval between pain is shorter and shorter; Vomiting: Occurs with the first episode of abdominal pain, at first the child vomits food, then vomits green or yellow fluid; Bloody stools: Symptoms appear from the first pain or appear late after 24 hours. Children have bloody stools with mucus, red or brown, sometimes with a few drops of fresh blood coming out of the anus; Constipation - defecation: Occurs if the intussusception causes complete intestinal obstruction. In case the intussusception is not completely blocked, the child can still defecate. In terms of treatment, the common intussusception treatment options are air intubation, water intubation, and surgery. In which, the rate of recurrence of intussusception after nonsurgical intussusception is 8 - 12%. Meanwhile, if surgery, the recurrence rate is only 0 - 3%.

Lồng ruột khiến trẻ đau bụng đột ngột từng cơn
2. The method of removing the intussusception by laparoscopic surgery
Intussusception can occur in the small intestine - small intestine, small intestine - colon or ileocecal intussusception. Recently, laparoscopic surgery method is being widely applied in the treatment of intussusception, especially for the ileocecal region.
2.1 Indications/Contraindications Indications
Indications for intussusception for small bowel intussusception or ileocecal intussusception have the following characteristics:
There are contraindications to perform enema; Failure to remove cage with steam or water; Time to diagnose intussusception after 24 hours; There is no primary lesion such as tumor, diverticulum, Henoch-Schonlein purpura,...; Repeated intussusception (> 2 times) with unknown cause Indications for ileocecal fixation:
Intussusception in the ileocecal region recurs more than 2 times; There are no primary causes of intussusception; The cage can be completely removed with steam, water or through laparoscopic surgery. Contraindications
Coagulation disorders, hemodynamic disorders, severe heart or lung disease; Peritonitis ; Complete intestinal obstruction or large bowel distention.
Không tiến hành tháo lồng ruột đối với bệnh nhân bị rối loạn đông máu
2.2 Preparation for surgery Personnel: Gastrointestinal surgeon, anesthesiologist, anesthesiologist; Technical facilities: Standard laparoscopic surgery tools and equipment; Patient: The surgery is explained; perform preoperative tests; perform imaging tests such as ultrasound, computed tomography X-ray to rule out bowel obstruction, secondary intussusception, peritonitis, motile caecum syndrome; replenish water, electrolytes; prophylactic antibiotic use; nasogastric tube placement; Medical records: Complete the documents in accordance with regulations. 2.3 Performing surgery Check the patient's profile and patient, make sure the right person, the right disease; Anesthesia: Perform endotracheal anesthesia; Patient position: Lying supine, legs apart; The surgical team stands in a convenient position for manipulation; Place the 10mm trocar at the umbilicus, inject CO2; Observe the entire abdomen, evaluate for intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, combined lesions (tumor, appendicitis, diverticulitis), place 2 5mm manipulator trocars depending on the location of the intussusception; Use 2 soft clamps to work on the cage block, pull the cage neck out of the cage head with one hand. Pay attention to moderate traction to avoid injuring the intestinal wall; When successfully intubated, the intussusception should be re-examined for ischemic or necrotic lesions, and at the same time, the gastrointestinal circulation of the entire intestine should be assessed; Consider switching to open surgery if: Laparoscopy has other associated lesions (inflammation, tumor), peritonitis, large bowel distension that cannot be manipulated, intestinal wall damage, intussusception is too tight to be removed by surgery. endoscope,...; Stitch the caecum if indicated: Let the patient lie down with the head low, on the left side, identify the cecum, appendix, and terminal ileum, check to make sure there is no primary injury, then perform a bowel resection. excess. Next, stitch 3 - 5 stitches, respectively, to fix the positions of the cecum, the base of the appendix and the end of the ileum to the lateral abdominal wall with undissolved sutures; Close the trocar holes, ending the surgery.
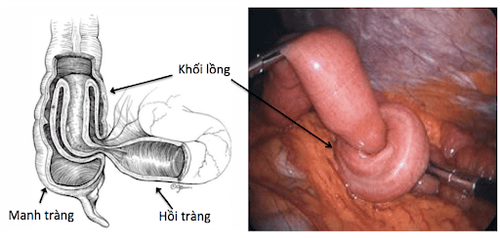
Phẫu thuật nội soi tháo lồng ruột
2.4 Post-operative monitoring Monitor the patient's vital indicators including blood pressure, pulse, temperature, respiration,...; Monitor bleeding and inflammation; The gastric tube can be removed, early feeding on the first day after surgery, combined with early mobilization of the patient; Monitor complications of paralytic ileus and bowel obstruction early after surgery; Patients can be discharged after 3-5 days depending on their health situation; Remote monitoring because conditions such as adhesions or recurrent intussusception can still occur. 2.5 Complications and management 2.5.1 Intraoperative complications Bleeding, intestinal perforation or mesenteric tear,... due to trocar manipulation: Treatment according to standard protocol; Intestinal perforation due to intestinal traction: Perform open surgery to suture the perforation and wash the abdomen; 2.5.2 Complications after surgery Surgical site infection: Need to take care of incision hygiene, use antibiotics; Dissection of the appendix root after appendectomy: Depending on the situation, there will be an appropriate treatment. Specifically, if postoperative peritonitis is indicated, re-surgery is indicated for treatment. If the abscess persists, then perform antibiotic treatment and may re-operate depending on the doctor's assessment; Postoperative peritonitis due to missed lesions on the intestinal wall: Re-operation is required for management; Intestinal paralysis and early intestinal obstruction after surgery: This is a rare complication, usually managed conservatively. Intussusception is a disease that can cause many dangerous complications. Therefore, when there are warning signs of intussusception, family members should take the patient to the doctor soon for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment with methods of intubation by steam, water or laparoscopic surgery.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the nationwide health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.