This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Thanh Binh - Rehabilitation Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital. The doctor has 30 years of experience in the specialty of Rehabilitation, especially experienced in Rehabilitation of musculoskeletal diseases.For cases of trauma that can no longer be preserved or have diseases such as tumors, tuberculosis, embolism, ... the patient will be assigned to amputate the limb, forming a stump. Rehabilitation of the stump is very necessary to ensure the aesthetics and quality of life of the patient later.
1. An overview of the stump
Amputation is done in some cases of pathology or accident, severe trauma. The principle when performing amputation is to ensure the length of the stump with the ratio of skin, muscle, bone, ... and handle nerve blood vessels to facilitate the fitting of prostheses later.1.1 What is a stump? An amputation is the remains of a limb after an amputation. The stump levels in the legs are toes, feet, legs, knees, thighs, and hips. The hand amputation levels are hand, wrist, finger, forearm, elbow, arm, shoulder joint.
Some causes leading to stump surgery include:
Trauma: Work accident, traffic accident, fire injury; Due to pathology: Tuberculosis, bone cancer, arteritis,...; Due to congenital malformations of the limb: Underdevelopment, missing a limb,... 1.2 What are the consequences of the stump? Patients with stumps face many difficulties in living and working, such as:
Pain: Due to the formation of nerve tumors, surgical scars against nerves or phantom limb pain (the patient feels pain in the extremities). has been omitted); Bleeding: Due to impact of the coccyx or thread drop, bleeding from the tip of the bone or due to poor hemostasis. This case needs to be done by compression, cold compress or surgery to stop the bleeding; Osteomyelitis, muscle abscess: It is necessary to treat by using antibiotics, extracting pus drainage, taking care of the wound site; Missing thread: Causing wound ulceration, which should be handled by taking the missed thread; Dermatitis around the stump: Due to allergies to topical drugs, poor hygiene of the stump, high temperature causes blisters, boils deep in soft tissues,... In this case, it is necessary to treat with antibiotics or perform a curettage. inflammation; Loss of sensation: Because the organization in the stump area is crushed and the doctor will treat it by re-cutting the stump; Other problems: Limiting daily living functions, joint deformity, coccyx muscle contractures, psychological effects, limiting activities in the family and community, affecting study and work .
2. Instructions for taking care of the stump
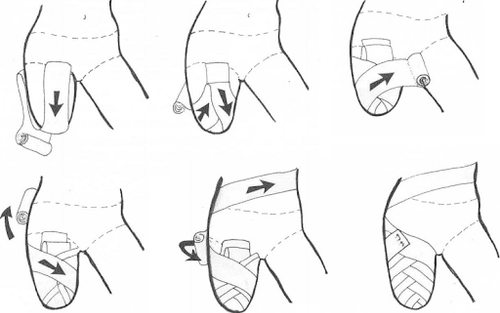
Proper care helps to quickly heal the incision, tighten it, and maintain the strength of the stump. To prevent complications while waiting for the stump to heal completely to install a prosthetic, it is necessary to perform the following care methods:Bandage the stump with elastic to prevent the stump from sagging. When dressing the stump, pay attention: Should be worn obliquely or diagonally, the pressure is gradually reduced from the tip of the limb to the base of the limb, the bandage does not limit the movement of the joint and does not restrict circulation, does not cause pain for the patient. personnel, do not let the bandage slip during activities and do not use a type of bandage that loses its elasticity; Gently massage to help blood circulation, break the adhesion of the skin to the underlying organization, loosen the scar tissue under the skin, reduce numbness and pain in the stump; Exercise joint movement according to the range of motion of the joint to avoid the risk of contracture, joint deformity near the stump later. It is necessary to strengthen the muscles of the stump to enable the muscles to carry the prosthetic limb after insertion. At the same time, medical staff should instruct the patient to wash the stump daily with warm water and soap, dry it, and then apply vaseline to soften the skin. Besides, combined with monitoring abnormal changes on the surface of the stump such as sores, ulcers, redness, itching, ... to promptly intervene.
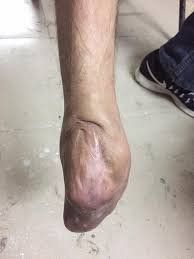
3. Rehabilitation measures of the stump
3.1 Correct Posture This method is aimed at combating the deformed posture of the stump caused by imbalance between the muscle groups on the stump. Specifically:With the stump of the leg: The stump often has a tendency to bend the knee into the thigh, so it is necessary to correct the posture for the stump to stretch. To do so, the patient should be placed on the stomach so that the weight of the remaining limb will stretch the stump, and at the same time encourage the patient to sit up early, stretch the amputated leg on the bed to stretch the stump; With the stump above the knee: The coccyx tends to have a flexion-pattern deformity in the hip joint. Therefore, it is necessary to correct the position so that the stump is stretched - pulled and rotated internally. How to correct the posture as follows: With the patient lying on the stomach, avoiding flexion of the stump, insert a sandbag outside the stump to prevent the stump from coming out. In the case of the patient lying on his back, press the sandbag on the thigh, insert the sandbag outside; With deformed stump: The kneecap is often deformed in hip flexion, flexion, and rotation. The subknee coccyx is more likely to have knee flexion deformity and may have hip flexor contracture. To treat muscle spasms, the patient needs to stretch the contractile muscles, and at the same time strengthen the opposing muscles. Using weights to stretch will have a better effect than stretching by hand. In the process of correcting posture for patients with stump, it is necessary to pay attention to the following movements:
Do not form stump; Do not lie down with knees bent; Do not stand with the stump resting on crutches; Do not lie on your back; Do not insert pillows under hips and knees; Do not sit in a wheelchair with the stump flexed; Do not place the stump next to the edge of the bed or to the wheelchair. 3.2 Strength training for the stump After surgery for about 10 days or until suture removal, the patient should pay attention to minimize all activities of the stump on the knee. This is to help the wound heal faster. The patient can swing the stump slightly. When the wound has healed, the patient can increase the intensity of the exercise, specifically:
Initiating exercise for the stump below the knee: The patient lies on his back, flexes the quadriceps or lies on his back with a knee brace to support the thigh and then flexes. , slightly stretch the knee joint; Strength training, gradually increasing the amplitude of the stump below the knee when combined with resistances such as weights and pulleys or with assistance; Tie a sandbag to the tip of the stump , try to keep the stump in an extended - supine position - 90° hip flexion; Exercise vigorously, gradually increasing the range of the stump on the knee with resistance in many positions such as lying on the back, lying on the stomach, lying on the side, standing, kneeling,...; Exercise with assistive devices and other rehabilitation equipment.
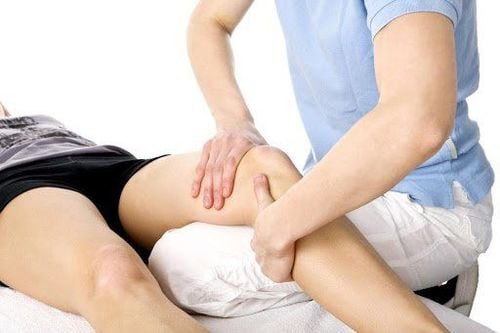
The coccyx muscle is strengthened, especially the extensor, abductor and internal rotator muscles; The stump gets used to being under pressure to prepare for the use of prostheses; Increased muscle tone; Maintain flexibility of joints; Increased circulation; The patient learns the necessary muscle coordination of the stump to prepare for the use of the prosthesis. 3.3 Exercise full-body functional activity After the prosthesis is fitted, the patient needs to learn to walk with the prosthesis or with the hands to improve the grip function of the prosthetic hand. For patients in need of mobility rehabilitation, the following exercises are available:
Practice standing in parallel bars: feet 20cm apart, alternately placing weight on both healthy and prosthetic legs. In addition, it is possible to change the position of 1 front leg - 1 back leg, alternately putting weight on 2 legs; Practice walking in parallel bars: Walk slowly, bringing prosthetic leg forward; Practice walking sideways along a bar, but: Step one leg to the side and then bring the prosthetic leg to follow; Practice getting up from a high chair: Lean forward and then stand up; Practice sitting down - standing up from the floor; Practice standing up from a kneeling position; Fall practice: Put a cushion on the floor so that when the patient falls, he does not hit his whole body on the floor. Patients can practice falling forward - backward or to the side. After having a prosthetic leg or arm, the patient needs to practice daily activities such as eating, personal hygiene, housework, etc. In addition, they can also be guided to perform some exercises. Separate exercises to improve the mobility of hands, fingers, arms, ... or walking, locomotion,...
When following the exercises for rehabilitation of the stump, patients need to follow Follow all instructions of medical staff to ensure an early recovery, so that you can soon return to a normal pace of life, study and work.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination, treatment and rehabilitation at the hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
How to limit phantom limb pain - phantom pain? Why does the incision heal, the patient still has pain? What is the solution for persistent pain after surgery?