This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Pharmacist, Ph.S. Pham Thi Kim Dung, Faculty of Pharmacy - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalDesign of the drug form is an important step in determining the quality of the drug form. When designing a drug form, the relationship between the components in the drug form must be considered under the direct influence of the preparation technique in order to find the optimal solution for each product.
1. What is the dosage form?
The concept of dosage form is defined as follows:Dosage form is the final product of the preparation process, in which the drug substance is prepared and presented in an appropriate form to ensure safe, effective, convenient for users, easy to store and reasonably priced.
Example: Chloramphenicol is a bitter drug that is difficult to drink. It is prepared in the form of tablets, hard capsules or suspension to limit the bitter taste, make it easier for patients to accept the drug, and improve the therapeutic effect of the drug.
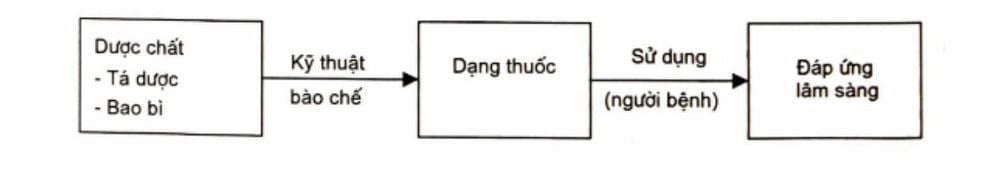
Dosage form includes: Pharmaceutical substances and Excipients + Packaging
2. Why does a drug have many different dosage forms?
In order to maximize the therapeutic effect of the drug when used, the drug form is designed to include the above 3 ingredients, and in addition, based on the study of influencing factors, the manufacturer decides the form of the drug. drug. Factors include:Factors affecting the release and absorption of pharmaceutical substances in the patient's body such as: route of administration, age, disease status,... eg: Painkillers, antipyretics Fever containing paracetamol has different dosage forms to suit a wide range of patients: syrup form, effervescent powder mixed with solution, anorectal tablet form for pediatric patients, babies or people who have difficulty swallowing pills. The form of injection and infusion is for patients who need to reduce fever and relieve pain quickly and in severe disease, unable to drink. The effervescent tablet form dissolves quickly into a solution for faster absorption and faster action than the conventional tablet form.
Physical and chemical properties of the drug substance need to choose appropriate excipients, preparation techniques and packaging to meet the requirements of the drug form to the maximum.

Alkaline glass container can precipitate the alkaloid salt in the injection drug. Some impurities in the plastic bottle containing the eye drop solution can accelerate the decomposition of the drug in the solution.
From the point of view of modern apothecary, the design of the drug form is an important step in determining the quality of the drug form. When designing a drug form, the relationship between the components in the drug form must be considered under the direct influence of the preparation technique in order to find the optimal solution for each product. Preparation techniques are always innovated and perfected in order to maximize the effects of pharmaceutical substances in the body and create new forms of drugs with high therapeutic efficiency.
3. What are the dosage forms of the drug?
Dosage forms of drugs can be classified in several ways:
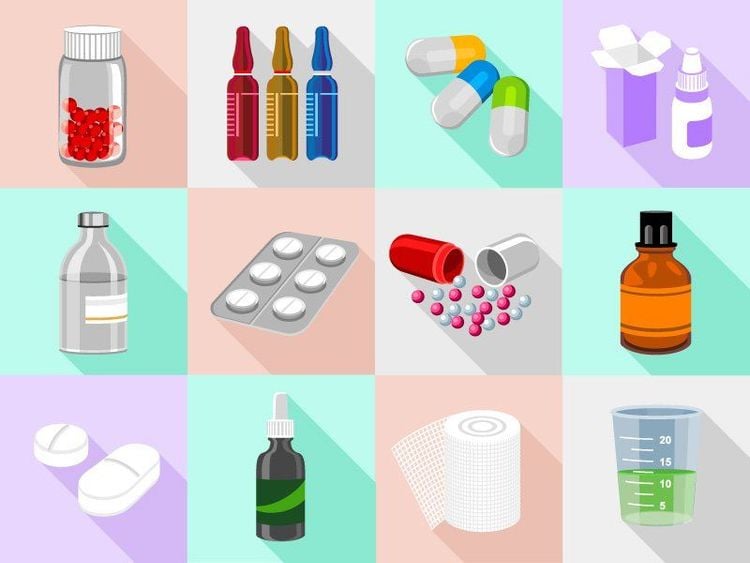

Drug solution: homogeneous drug substance, non-drug drug class segregated. The drug form is usually absorbed more quickly than the solid form, and is less irritating to the gastrointestinal mucosa. The disadvantage is that this form of drug is more susceptible to infection and is not suitable for drugs that are prone to hydrolysis. Drug suspension: is a form of drug that disperses a solid drug in a drug solvent, with the size of the drug substance usually larger than 1 micrometer. Drugs often have to add excipients as surfactants and suspension excipients to evenly disperse the drug in the drug solvent. The drug should be shaken before administration to accurately divide the dose. Drug emulsion: is a form of drug that disperses a liquid drug in a drug solvent, the size of the drug substance is from 0.1 to 100 micrometers in diameter. The drug often has an emulsifying excipient to evenly disperse the two drug phases into each other. In addition, there are other excipients such as buffer systems, antioxidants, preservatives. Syrup is a drug that is dispersed in a sugar solution or as a sweetener instead of sugar. Usually medicine syrup has a sugar content of 60-80% of the drug solution. Soft medicine: Ointment, soft paste, ... used to apply on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes of the body.
Solid drugs: Tablets, hard/soft capsules, powders, nuggets, etc. Some common forms are:
Tablets: may contain 1 or more active ingredients along with excipients. There are chewable tablets, non-chewable tablets, that break down like tablets specially formulated for prolonged or programmed drug release. Tablets with pharmaceutical ingredients are usually more stable when in liquid form, however, there may be disadvantages of difficulty swallowing in some subjects such as young children, the elderly...
Capsules: are drugs with active ingredients and excipients. Medicines are packaged in capsules (usually with gelatin). Capsules are suitable for pharmaceutical substances that need to be masked with unpleasant odors and tastes or for drugs that need to be protected from light...
Drug powder: is a solid mixture of powdered active ingredients and powdered excipients. This form of drug is more stable to the drug than the liquid form and dissolves the drug better than the pill, but it is more difficult to hide the unpleasant taste of the drug than the pill.
Extended-release, or scheduled, form of drug: is a form of medicine specially formulated so that the drug is released stably into the bloodstream at a certain concentration, with the aim of reducing the patient's frequency of taking the drug. These drugs are often abbreviated SR (sustained release), SA (sustained action), ER, XR, XL (extended release), TR (timed release), CR (controlled release), MR (modified release)...
3.2 By route of administration (common classification) The route of administration greatly affects the effect of the drug. A drug that is introduced into the body by different routes can cause different pharmacological effects. eg: magnesium sulphate, if taken orally, has a biliary effect; laxative; and if injected, it has anti-edema effect.
Drugs administered through the gastrointestinal tract often have problems with absorption due to the influence of many factors such as digestive fluid pH, enzymes, food, first-pass metabolism, transit time of the drug...
Injections: There are different types of injections: intramuscular, intravenous or intravenous drip, subcutaneous administration Drugs for oral administration: Drugs to be taken orally, sucked in, or chewed (drugs that are absorbed or have an effect) mainly in the small intestine), suppositories and enemas (locally acting or absorbed through the rectal capillary system).
Drugs used by inhalation: Types of drugs for inhalation, inhalation, fogging, nasal drops...
These forms of drugs can cause local effects on the respiratory mucosa or systemic effects.
Drugs used by the skin: Ointments, lotions, patches, powders, nebulizers, transdermal systems,...
Most of the drugs have local effects (treating rashes, skin protection, ...), but there are also cases where the drug is absorbed through the skin to cause systemic effects (anti-angina, anti-motion sickness...)
In addition, according to the origin of the product Drug formulations, the dosage forms of drugs can be classified into two categories as follows:
Drugs prepared according to pharmaceutical formulations specified in official documents such as the Pharmacopoeia, Pharmacopoeia, National Formulation, etc. ... Pharmaceutical companies must strictly comply with the formulation and quality standards of drugs when producing these preparations. Prescription drugs: to improve the effectiveness of treatment, doctors prescribe specific concoctions in terms of content, concentration, method of preparation, and response to the changing physiological and pathological conditions of the patient. Before mixing drugs, pharmacists must check prescriptions, review dosages, drug combinations in them (pay attention to incompatibilities), dosage forms,... Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the the hospital not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, a system of modern equipment and technology, but also stands out with comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source:Preparation and Biopharmaceutical Techniques of Drugs – Volume 1; Department of Pharmacology, Hanoi University of Pharmacy 2006 Tulane University School of Medicine, Medical Pharmacology, TMedWeb