This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Nguyen Van Duong - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Before antibiotics were widely used, pericarditis was a common complication of pneumococcal pneumonia. Currently, most cases of purulent pericarditis are caused by a medical care-related blood infection such as during dialysis, thoracic surgery, or an immunosuppressive condition such as HIV infection, chemotherapy. Regardless of the cause, early antibiotic treatment with percutaneous empyema or pericardectomy is necessary to rapidly control the foci of infection.
1. What is purulent pericarditis?
Pericarditis is defined as a localized infection of the pericardial cavity characterized by the presence of pus. Evidence of this inflammation is the examination of specimens collected in the pericardium with more than 20 leukocytes in each oil-immersed field.This definition is important because the presence of pus in the pericardial cavity does not equate to infectious pericarditis and not all infections of these organs produce purulent fluid. Therefore, once the diagnosis is confirmed as empyema, this is a serious disease with poor prognosis and the strategy needs to be aggressive from the beginning.
According to epidemiological studies, purulent pericarditis occurs most often in children and middle-aged adults, however, the disease can still occur in other age groups and gender ratios. count is similar.
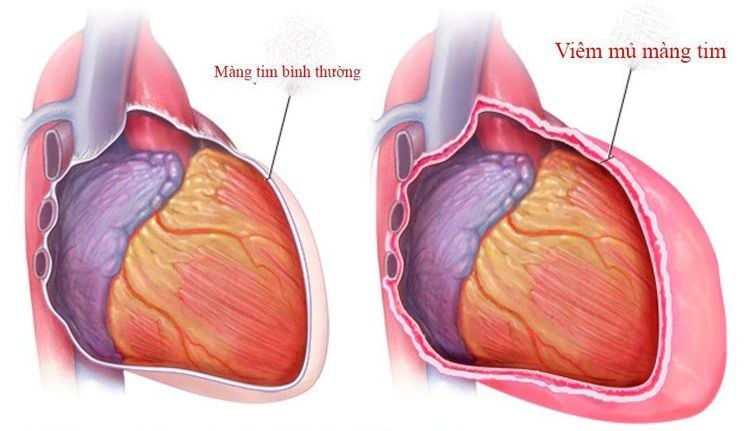
2. What are the symptoms of pericarditis?
Purulent pericarditis is initially characterized by an acute fever like other infectious diseases. However, this diagnosis is often less likely to be first thought as focal signs of infection in adjacent organs tend to be more prominent. Accordingly, the most common infection in cases of purulent pericarditis is pneumonia, especially pneumococcal, otitis media, meningitis, skin infection, staphylococcal myelitis, and staphylococcal meningitis. subdural vehicle.However, with careful history and clinical examination, in addition to signs of fever and infection in other organs, the patient also has the following inexplicable cardiovascular symptoms:
Shortness of breath Chest pain Paradoxical pulse Hepatomegaly, Distended neck veins Pericardial chest pain Ascites Leg edema Thus, while the patient was admitted to the hospital in the setting of lobar pneumonia but had symptoms of pericardial effusion syndrome or cardiac tamponade, Diagnosis of empyema is difficult to exclude. At this point, pathological confirmation can be done quickly and very easily by means of echocardiography.

3. How to diagnose empyema?
The role of echocardiography has been of great help in determining the presence of fluid in the pericardial cavity. However, it does provide useful information on fluid volume, fluid characteristics, and its effect on cardiac contractility without indicating whether the fluid is purulent in nature.Accordingly, the diagnosis can only be confirmed by collecting and testing specimens obtained through pericardial drainage. The purulent fluid will be examined for cellular and biochemical characteristics that correspond to the characteristics of an exudate and also be examined directly under the microscope as well as cultured and screened for pathogens that are bacteria, tuberculosis or other pathogens. fungal or sometimes a malignancy is found. Moreover, this procedure is not only useful for taking samples for analysis, but also for decompressing the pericardial cavity when the volume of pus is too much, there is a risk of acute cardiac tamponade.
In addition, other laboratory markers that help guide the diagnosis of pericarditis are as follows:
Leukocytosis in a complete blood count Biomarker for inflammatory response by reactive protein C Hypertensive response (CRP) in blood Tachycardia, pericarditis-like ST changes but no electrocardiogram kinetics Enlarged heart on chest X-ray
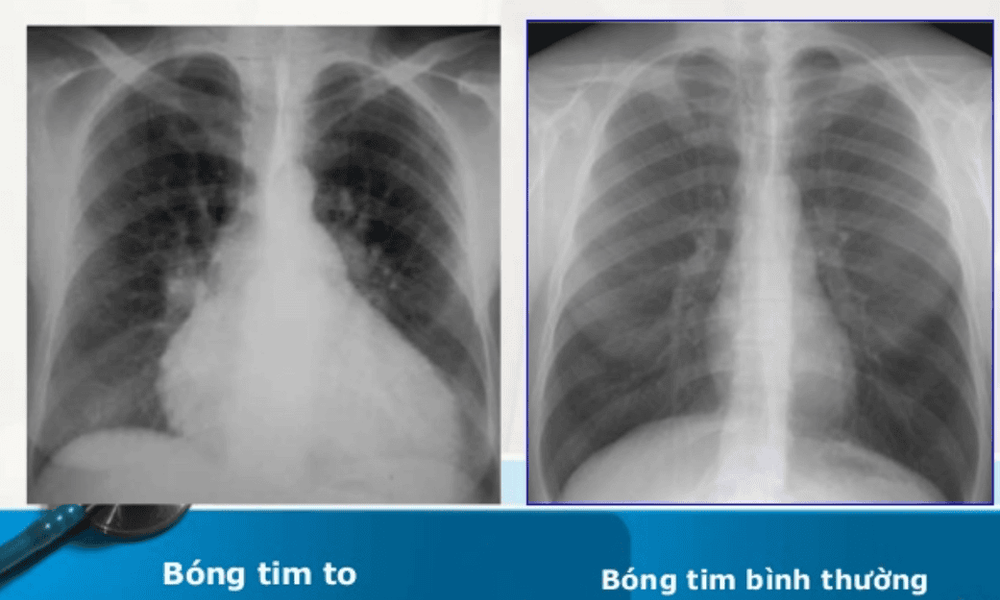
4. How to treat empyema?
The treatment of empyema pericarditis must include drainage of pus in the pericardial cavity combined with systemic antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics should be instituted early, as soon as microbiological culture results are not available, and the antibiotic of initial choice is usually empiric, such as vancomycin, ceftriaxone or imipenem, meropenem or piperacillin-tazobactam plus fluconazole if disease is present. occur in immunocompromised patients. The duration of antibiotic therapy should be maintained for at least 28 days or until the fever is gone and there are no signs of infection above the laboratory criteria.For surgical interventions, the technique will be considered depending on the patient's condition, the patient's condition as well as the availability of necessary facilities and the surgeon's skill. Accordingly, the procedures or surgery to resolve pus in the pericardial cavity include the following ways:
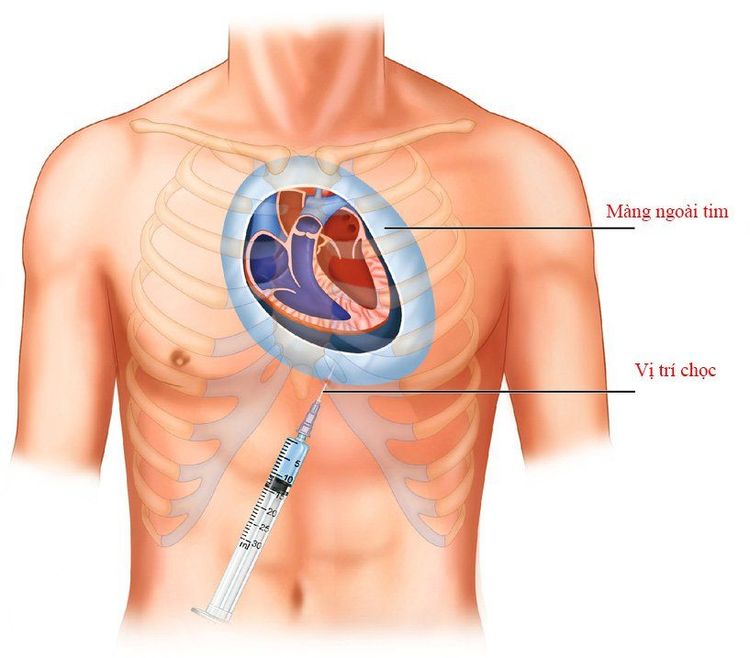
Local pericardial drainage: This is the simplest and fastest method, which can be performed immediately. at the hospital bed, both helping to take samples to find the agent, and allowing decompression of the pericardial cavity. However, this procedure will be difficult when the pericardial fluid is thick pus, contains many thick fibrous fibrin and also has the risk of leading to the development of constrictive pericarditis. In addition, intravenous infusion of fibrinolytic agents may increase the effectiveness of pericardial drainage, which may be appropriate in some cases but the range of recommendations is still under review.
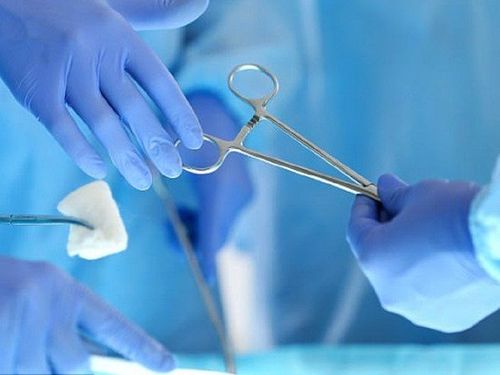
Pericardectomy: Although the mortality rate in this type of intervention can be as high as 8%, it is a radical approach that addresses all situations, even the most complex in empyema of the pericardium such as adhesions, localized pus, or persistent infection unresponsive to antibiotics.
5. Is pericarditis dangerous?
Purulent pericarditis is a serious condition with a poor prognosis even with aggressive treatment. Overall, the mortality rate in patients with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment is not less than 40%, usually due to cardiac tamponade, septic shock or constrictive pericardium. At the same time, this rate will be higher in people with infections caused by the agent S. aureus and in malnourished patients.Early complications of empyema are infection spreading to nearby organs or sepsis. This makes it easy for the patient to fall into septic shock and multi-organ failure. On the other hand, if the choice of antibiotic does not respond, the inflammatory process causes the formation of pus with a rapid rate of regeneration, easily causing acute cardiac tamponade, manifested by rapid pulse, hypotension and circulatory collapse.
The long-term complication of empyema is progression to constrictive pericarditis. At this time, the pericardium loses its elasticity, is no longer able to stretch with each heart beat, and becomes a thick, fibrous capsule. Therefore, indications for pericardectomy should be set at the outset, both to make infection control easier, and to prevent this complication in the long run.

Dr. Nguyen Van Duong has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of internal cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular interventions; Perform other noninvasive functional investigations in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Currently working as a treating doctor at Cardiovascular Center, Vinmec Central Park Hospital since August 2017
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.