This is an automatically translated article.
Hyperinflation is understood as an abnormal increase in lung volume. Excessive lung swelling needs early intervention to avoid adverse effects, threatening the patient's life.
1. What is an overinflated lung?
Normally, the lungs will perform the respiratory function by inflating and contracting, corresponding to the action of inhalation and exhalation.
Pulmonary hyperinflation occurs when the patient begins to inhale, before the exhalation ends. This leads to an amount of air being trapped in the lungs. This amount of gas keeps increasing after each inhalation and exhalation cycle.
In other words, hyperinflation is an abnormal increase in functional residual fluid. Excessive lung swelling causes decreased respiratory function, thoracic movement disorders, increased oxygen consumption, increased risk of increasing CO2 in the blood, leading to shortness of breath. This phenomenon is worse when the patient exerts himself.
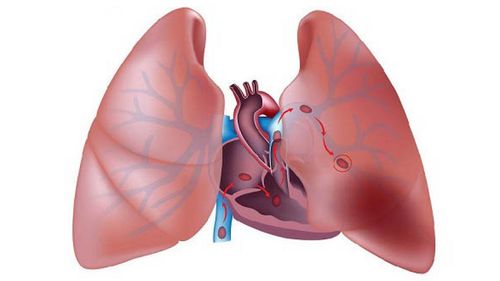
Excessive lung swelling will lead to excessive alveolar dilation, leading to physiological disturbances in ventilation and blood perfusion in the lungs, even changes in the thorax.
Căng phồng phổi kéo theo nhiều biến đổi trong lồng ngực
2. Classification of lung hyperinflation
Pulmonary hyperinflation is divided into 2 types: static overinflated and dynamic overinflated. Patients may have these symptoms individually or at the same time.
2.1 Static hyperinflation In a normal person there is always a balance between the elastic force of the lung and the chest wall. The force of lung elasticity decreases with age, so there will be an increase in the volume when there is excess in the lungs at the end of expiration.
The elastic force of the patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with emphysema is only reduced to 0, this is a static over-inflated phenomenon. This phenomenon occurs quite often and gradually increases in severity.
2.2 Dynamic hyperinflation Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease will have slow alveolar emptying, increased respiratory rate with exertion. The more the patient exerts himself, the greater the expiratory volume at the end of the period. This phenomenon can be corrected through certain types of bronchodilators.

Người bệnh có thể xuất hiện cả hai hiện tượng cùng lúc
3. How dangerous is excessive lung swelling?
3.1 Effect on Lung Volume Slow alveolar emptying resulted in an increase in FRC functional residual volume, increased RV residual gas, and an increase in total lung capacity and RV/TLC ratio. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with rapid shallow breathing will make the over-inflated lungs worse. An increase in FRC will reduce the inspiratory capacity, hindering the body's ventilation response.
3.2 Reduced exercise capacity Excessive lung swelling reduces mobility, reducing the effectiveness of strenuous exercise. Reduces the amount of blood and oxygen supplied to organs in the body.
3.3 Effects on the Cardiovascular System Excessive inflating the lungs causes a reduction in the size of the heart's chambers, even causing problems related to pulmonary hypertension.
4. What are the symptoms of overinflated lungs?
Shortness of breath is a characteristic symptom of overinflated lungs. The degree of shortness of breath gradually increases with exertion. Shortness of breath with dry cough, cough with phlegm.
Khó thở kèm ho khan là đặc trưng của hiện tượng căng phồng phổi quá mức
5. Treatment of Overinflated Lungs
5.1 Principles of treatment Improve exercise capacity Reduce hyperinflation of the lung Dynamically Reduce the volume of the air-filled lung Decrease the work of breathing. 5.2 Drug treatment of overinflation Bronchodilators can help improve static overinflation and dynamic hyperinflation, reduce dyspnea, increase exercise capacity, and improve IC.
Some commonly used bronchodilators such as: indacaterol, tiotropium, glycopyrronium... Dosage, usage, combination of bronchodilators need to be consulted and allowed by the treating doctor.
5.3 Treating hyperinflation without using oxygen reduces the work of breathing. Multi-component respiratory rehabilitation, combined with bronchodilators Lung volume reduction surgery, improved respiration Endoscopic lung volume reduction surgery. When there are symptoms of shortness of breath, especially in patients at high risk for overinflated lungs, patients should go to the hospital for medical examination, diagnosis and timely intervention.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
MORE
How does chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affect the heart? Guidelines for breathing in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Certain congenital malformations of the lungs, trachea, and bronchi