This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II To Van Thai - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. Thai doctor has more than 34 years of experience in the field of anesthesia - emergency resuscitation.Surgical removal of head and neck hemangiomas are often performed in cases of head and neck hemangiomas that affect aesthetics or ulcerative hemangiomas pose a risk of infection. Endotracheal anesthesia is an anesthetic method commonly used in head and neck hemangioma surgery.
1. Surgical removal of hemangiomas in the head and neck region
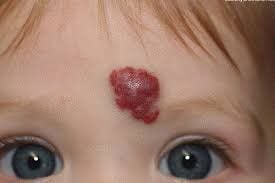
Hemangiomas are benign tumors, formed by the proliferation of blood vessels such as arteries, veins, and capillaries. Hemangiomas have common features such as red or purple color, painless, raised bumps on the skin or mucous membranes; If you squeeze or press it, it will collapse, if you let go, it will swell again. The majority of hemangiomas appear in only one location on the body, about 20% of hemangiomas appear in many different locations. Hemangiomas can appear in any part of the body, but the head and neck area is the most common site. Head and neck hemangiomas account for 60% of hemangiomas.Head and neck hemangiomas usually appear in children in the first weeks after birth and develop during the first years of life. Most hemangiomas do not need treatment, as the tumor will improve over time, the red color of the tumor will gradually decrease, turn gray, and the tumor will become softer and flatter. However, the treatment will be considered for implementation in case the tumor is large, grows quickly and affects the patient's life much such as:
Tumor in the head and neck area causing limited vision, hearing loss, obstructing the airway, ... or seriously affecting aesthetics, affecting the psychology of patients, hemangiomas, ulcers, bleeding, infection.
Endotracheal anesthesia is a technique of general anesthesia with intubation for the purpose of breathing control during surgery and postoperative resuscitation. Endotracheal anaesthesia is the most commonly used anesthetic method during surgical resection of head and neck hemangiomas. This is a routine technique but should not be performed when the patient does not agree or the medical facility does not have enough anesthesia and resuscitation facilities, or the medical staff is not proficient in the technique.
2. Preparation for endotracheal anesthesia for head and neck hemangioma
The person performing endotracheal anesthesia for head and neck hemangioma surgery is a doctor and nurse specializing in anesthesiology and resuscitation.Before performing surgery, the doctor will examine the anesthesia to assess the detection and prevention of risks. The patient will be explained the purpose and steps in the process to cooperate with the doctor in the process. The doctor will prescribe the patient to use sedation from the night before surgery if necessary.
The necessary facilities to perform endotracheal anesthesia include:
Anesthesia machine system with breathing, hand squeeze oxygen source, vital function monitor (ECG indicators, arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2) , breathing rate, temperature), defibrillator, suction machine,...;

3. Endotracheal anesthesia procedure for head and neck hemangioma surgery
3.1. Steps to perform endotracheal anesthesia for head and neck hemangioma surgery
After checking the patient's records and examining the patient, the anesthesia team placed the patient in a supine position, installed a monitor and established an effective transmission line, performed pre-anesthesia if necessary, and administered 100% oxygen to the patient. volume of 3-6 liters/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia, ...Initiating anesthesia with drugs:
Sleeping pills: use one of the drugs such as intravenous anesthetics (propofol, etomidate, thiopental, ketamine). ,...), volatile anesthetics (sevoflurane, Isoflurane,...) Painkillers: fentanyl, sufentanil, morphine,... Muscle relaxants: rocuronium, vecuronium, succinylcholine,... are used if necessary . For intubation, the patient needs deep sleep and adequate muscle relaxation (in most cases). There are two techniques that can be used for intubation: oral intubation and nasal intubation.
Procedure for endotracheal intubation:
The doctor (or anesthesiologist) opens the patient's mouth, inserts the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, moves the tongue to the left, pushes the light deep, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis. Perform rapid induction of anesthesia and Sellick maneuver in case of full stomach (pressing the cricoid cartilage 20-30kg as soon as the patient loses consciousness until the intubation is complete).
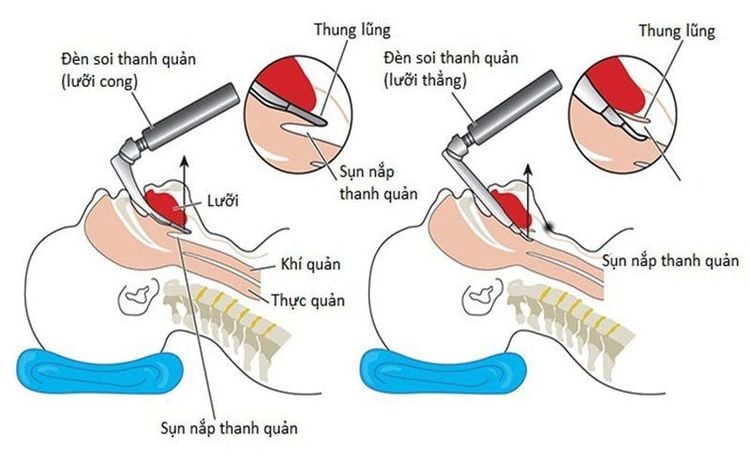
The doctor chooses the side of the nose where the endotracheal tube will be intubated, drops the vasoconstrictor drugs such as naphazolin, otrivine,... Select the endotracheal tube with the appropriate size (endotracheal tube). trachea in a smaller nasal passage than in the mouth), insert an endotracheal tube lubricated with lidocaine ointment through the nostrils. The doctor opens the patient's mouth, inserts the laryngoscope to the right side of the mouth, pushes the patient's tongue to the left, pushes the lamp deeply, and coordinates with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis. If favorable, proceed to gently insert the endotracheal tube through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes 2-3 cm through the vocal cords. If it is difficult, use Magill pliers to guide the tip of the endotracheal tube into the correct glottis, the assistant pushes the endotracheal tube from the outside. Gently withdraw the laryngoscope, then inflate the endotracheal balloon. The doctor listens to the lungs and checks the EtCO2 results to check that the endotracheal tube is in the correct position. If the endotracheal tube is in place, secure the endotracheal tube with tape. The anesthesiologist will switch to a difficult intubation procedure if the two procedures are unsuccessful.
To maintain anesthesia when surgery to remove head and neck hemangiomas takes place, the patient will be given intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if needed). The patient's breathing is controlled by machine or hand squeeze. The depth of anesthesia will be closely monitored based on parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, tearing (PRST); MAC, BIS, Entropy (if any). In addition, must always closely monitor vital signs and prevent the endotracheal tube from being misplaced, flexed, or blocked.

3.2. Criteria for extubation
After surgery to remove head and neck hemangiomas ended, the endotracheal tube was removed when the patient met the following criteria:Patient was awake, able to follow orders, raised his head more than 5 papers, TOF > 0.9 , breathing spontaneously, respiratory rate within normal limits. Stable blood pressure, normal body temperature, No complications of anesthesia and surgery.
4. Possible complications during endotracheal anesthesia during head and neck hemangioma removal surgery
4.1. Reflux of gastric juice into the airway
If detecting that the patient has digestive juices in the oral cavity and airways, the anesthesia team will immediately drain the fluid, let the patient lie down, tilt the head to the side. Place the endotracheal tube quickly and clear the airway. Patients are closely monitored after surgery to prevent lung infections.4.2. Hemodynamic complications
During endotracheal anesthesia for surgery to remove head and neck hemangiomas, patients may experience hemodynamic disturbances such as hypertension, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias such as bradycardia, bradycardia, and bradycardia. tachycardia, arrhythmia. The treatment will depend on the specific symptoms and cause.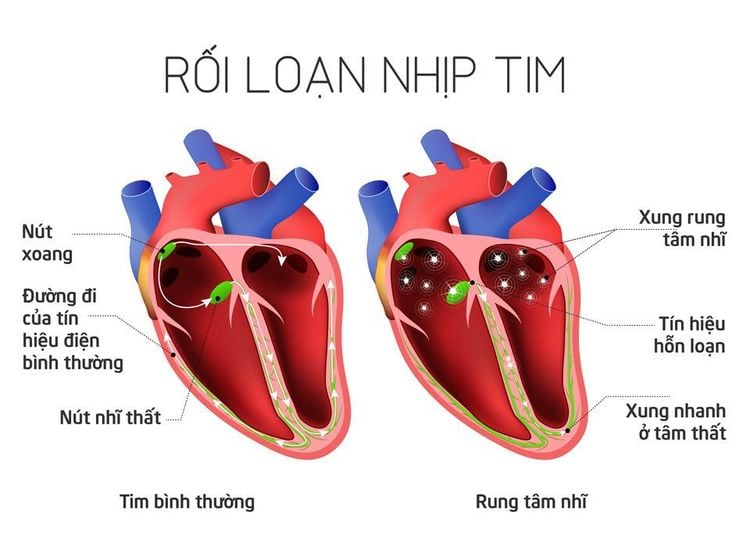
4.3. Complications due to endotracheal intubation
Complications may occur during intubation such as:Failure to intubate: the doctor will switch to a difficult intubation procedure or switch to another method of anesthesia. Misplaced in the stomach: If the endotracheal tube is mistakenly placed in the stomach, there will be no alveolar murmur, no measurement of EtCO2. The anesthesiologist team will re-intubate the endotracheal tube. Vocal-tracheal-bronchospasm: If it is difficult or impossible to ventilate the patient, with crackles or muted lung sounds, the anesthesiology team will provide adequate oxygen, add sleeping pills and muscle relaxants, ensure ventilation and give bronchodilators, corticosteroids. Switch to a difficult intubation procedure if breathing is still not controlled. Injuries that can occur during intubation such as bleeding, broken teeth, damage to the vocal cords, falling foreign bodies into the airways,... Injuries are handled according to each specific injury.
4.4. Respiratory complications
Hypoxia and anthrax will occur if the endotracheal tube is folded, retracted, pushed deep into one lung, collapsed or opened the respiratory system, the oxygen source is exhausted, the soda is ineffective,... Anesthesiology team will immediately ensure ventilation, provide 100% oxygen and actively treat the cause.
4.5. Complications after extubation
After extubation, patients may experience complications such as respiratory failure, upper respiratory tract inflammation, sore throat hoarseness, laryngotracheal spasm, laryngotracheal stenosis, ... The doctor will treat according to the symptoms and causes.To ensure safety as well as limit functional complications after endotracheal anesthesia for endoscopic surgery to remove head and neck hemangiomas, patients need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly applies safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. With a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, along with modern equipment such as nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz difficult airway control system, anesthesia monitoring system GE's comprehensive AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will deliver high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not awake, no residual relaxant muscle after surgery. Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.