This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a Doctor of Hematology - Blood Transfusion - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Thalassemia is a congenital hemolytic disease, inherited in an autosomal recessive manner from parent to child through generations. The main manifestation of the disease is anemia with dangerous complications, affecting ethnic groups. Performing pre-marital tests is extremely necessary to accurately screen for Thalassemia gene, to help identify couples carrying the gene that causes Thalassemia, thereby assessing the risk of Thalassemia in future children. this.
1. What is Thalassemia?
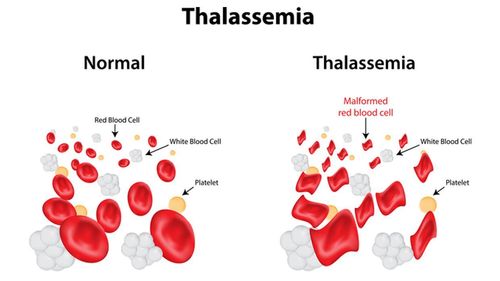
Thalassemia is caused by an abnormal structure of hemoglobin in red blood cells. The quality of red blood cells is reduced, making red blood cells easily broken (hemolysis) leading to chronic anemia. When the disease is severe, the patient often requires a blood transfusion. A lot of blood transfusion can easily lead to iron excess in patients with congenital hemolysis, causing complications on all organs, changing the patient's appearance such as short stature, protruding forehead, flat nose, protruding teeth, impaired heart, liver failure, endocrine failure... can lead to death.There are different types of Thalassemia, the classification depends on the type of gene and the number of mutated genes. In Vietnam, two common types of Thalassemia are Alpha Thalassemia (when the Alpha gene is mutated and loses its function) and Beta Thalassemia (when the Beta gene is mutated to lose function).
2. Why need pre-marital hemolysis test?
Currently, the number of people carrying the congenital hemolytic gene accounts for 7% of the global population, of which 1.1% of couples will have a risk of having a child with the disease or carrying the disease gene.
According to the National Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Vietnam is one of the countries with a high rate of Thalassemia gene carrier in the world with 10% of the population carrying the disease gene. It is estimated that about 8,000 children with the disease are born each year, of which 2,000 have severe disease. Babies born with Thalassemia will face serious health risks such as iron stagnation, enlarged spleen, infections, bone deformities, growth retardation, and cardiovascular diseases such as congestive heart failure. bleeding, arrhythmia.
The main treatment of the disease today is blood transfusion and iron chelation, to maintain life, the child must be treated for life. The cost of treatment is very expensive, besides, parents have to temporarily stop working to take care of their children in the hospital, which is really a great economic and spiritual burden for the patient's family.
Xét nghiệm tiền hôn nhân để xác định bệnh tan máu rất quan trọng vì ngăn ngừa nguy cơ sinh con mắc bệnh Thalassemia
3. Severe consequences from congenital hemolytic disease
Most patients with Thalassemia have facial deformities due to maxillary hyperplasia; Gray discoloration of the skin at the base of the nails, elbows, knees, and ankles. The disease can affect the organs in the body:Enlarged spleen, Thrombocytopenia; Anemia; Pathological fractures; Premature ossification of the lower femoral head. Pituitary: Affects the development of sex organs, adrenal glands, thyroid gland; Parathyroid glands: Decreased blood calcium; Liver: Enlarged liver; Pancreas: Having diabetes; Genital organs: Affects sexual development and function. Patients with the disease must have blood transfusions for life, depending on the blood donation from others to sustain life. The danger is that, but we can completely avoid it thanks to prenatal screening.
4. Pre-marital health check - The only preventive measure
Before the serious consequences of the disease, it is necessary to have accurate and effective diagnostic criteria, treatment methods and screening measures. Based on clinical symptoms, total blood cell analysis, blood chemistry... from there, doctors will recommend appropriate treatment.To avoid the consequences of having a child with Thalassemia, it is recommended that couples do before marriage:
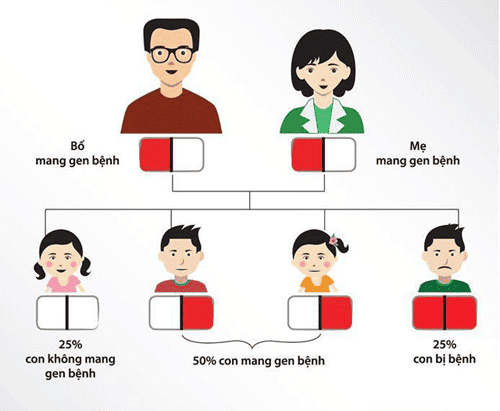
Pre-marital counseling: Married couples should be examined and tested for the disease. Thalassemia before marriage. All relatives of someone with Thalassemia should be screened. If both carriers of the same Thalassemia gene are married, counseling should be sought before planning a pregnancy. If a couple carrying the same Thalassemia gene is pregnant, they should be diagnosed before birth at 12-18 weeks' gestation at specialized medical facilities. Should be consulted by doctors specializing in Hematology, Pediatrics and Genetics about Thalassemia.
5. Pre-marital tests to assess your child's risk of thalassemia
Pre-marital tests help detect healthy people carrying the Thalassemia gene, thereby assessing the risk of Thalassemia, including:5.1. Screening tests
These tests have not yet allowed the diagnosis of healthy gene carriers, but only help to detect people at high risk of carrying disease genes, including:- Peripheral blood cell total analysis is performed on automatic/semi-automatic hematology analyzers: Red blood cell count, Hemoglobin, mean hemoglobin per red blood cell (MCH), mean erythrocyte volume (MCV)... Healthy carriers of the disease gene are MCH in a red blood cell < 27 pg or MCV < 80 fL.
- Evaluation of erythrocyte morphology and size by microscopy: Small red blood cells, hypochromic...
5.2. Definitive diagnostic tests
5.2.1. The test determines the type of hemoglobin and the percentage of each type in the red blood cells
Commonly used test sample is venipuncture or dry blood sample, taken from the child's heel, ear lobe, finger. The percentage of each type of hemoglobin in the blood in normal cases is as follows:
Adults: HbA 95-98%, Hb A2 from 2-3%, Hb F 0.8-2%, Hb C: 0% Children: Newborn HbF is from 50-80%, HbF in babies 6 months old is 8%, HbF in babies over 6 months is 1-2%. To determine the type of hemoglobin and the percentage of each type of hemoglobin to detect healthy carriers, one of the common techniques below can be used:
hemoglobin electrophoresis on gel (gel electrophoresis) or on cellulose acetate paper . Capillary electrophoresis of hemoglobin: this technique is newer than gel electrophoresis, performed on a specialized electrophoresis machine, for automatic results, with high resolution. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): this is a modern method, giving fast and accurate results
5.2.2. Genetic testing
Genetic testing DNA analysis is performed on the principle of detecting gene mutations on alpha and beta genes by sequencing techniques or PCR techniques with specific primers, thereby helping to identify people Thalassemia gene carrier.
Xét nghiệm di truyền phân tích ADN có thể xác định được người mang gen bệnh Thalassemia
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, which provides a basic pre-marital examination package for customers who are about to enter married life, the reproductive health and happiness of the family will be guaranteed safely. the best.
To know more about health care services at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.