This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with a Doctor of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalEpilepsy is a disorder of the central nervous system in which brain activity is altered, causing seizures or behavioral changes, abnormal sensations, and sometimes short-term loss of consciousness. Things to keep in mind when having a seizure in an epileptic patient.
1. What is Epilepsy?
According to the World Health Organization, epilepsy is a chronic disease of various etiologies, typically characterized by repeated seizures. Seizures are short, definite, sudden, cyclical and recurrent seizures caused by sudden excessive discharge from the cerebral cortex or through the cortex of groups of neurons, causing dysfunction of the central nervous system. (motor, sensory, sensory, vegetative, ...), EEG recorded paroxysmal waves. Loss of consciousness is also common during or after a seizure.The most common manifestations are generalized convulsions, foaming at the mouth, unconsciousness due to repeated excessive discharges of brain neurons. In children, there are additional epileptic manifestations.
Causes of epilepsy
Head trauma affecting the brain during childbirth; Vascular malformations in the brain ; Sequelae of inflammatory lesions, parasitic infections of the brain; Brain tumors ; Traumatic brain injury ; Stroke; Structural abnormalities of the brain.

Cơn co giật ở người bệnh động kinh
2. Common types of epilepsy
Epilepsy: Sudden manifestations of unconsciousness, falling, hissing breathing, stiffening limbs, purple lips due to apnea, two clenched teeth easily biting the tongue. Then muscle twitching, difficulty breathing, foaming at the mouth, twitching eyelids, rolling back of the eyeballs. During the attack, the patient may fall into a coma, call to ask if he does not know, but gradually regain consciousness and do not remember the seizure occurred.Absence of consciousness: common in girls, discovered by relatives: suddenly look dull, face pale, drop something you're holding, if you're writing, your handwriting gets worse, making it difficult to read. No falls, but eye twitching may then go away on its own, or progress to a major epileptic seizure or a combination of both.
West syndrome: seen in children under 1 year of age, men more often than women manifest when they wake up suddenly suddenly bowed his head, bent his body, stretched out his arms first and quickly regained consciousness. Attacks occur several times a day. Children often have mental retardation.
3. Notes when having seizures in epilepsy patients
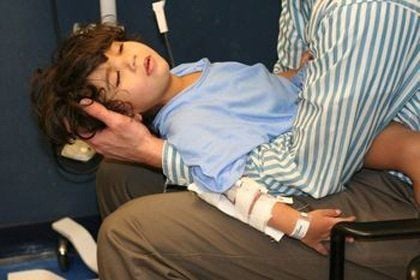
Sơ cứu khi bị cơn co giật ở người bệnh động kinh
Keep the head tilted to one side while loosening the patient's clothes, keeping the patient in a comfortable position, not too tight. Go to the nearest hospital Emergency Department. Do not squeeze a small amount of lemon juice into the patient's mouth because it has no effect on stopping the attack and the lemon juice will flow into the trachea, causing choking and breathing difficulties. Suction, wipe sputum. Continuously monitor the disease, right after the patient comes out of the convulsion because at this time the patient is not fully awake, it is easy to have dangerous unintentional behavior If the convulsion occurs continuously, emergency treatment must be given to the hospital. specialized and fully equipped first aid.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.