This is an automatically translated article.
This article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Duc Hoang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.Placing an emergency laryngeal mask (laryngeal mask) is a method to help control the airway quickly, contributing to improving the patient's chances of survival and reducing the rate of complications in dangerous cases.
1. What is emergency laryngeal mask placement?
The laryngeal mask is a means of opening the upper airway with a structure consisting of a large barrel, the lower end has an elliptical balloon. After the laryngeal mask is placed and inflated, the balloon is closed with low pressure through the larynx entrance – forming a mask-like layer.The classic laryngeal mask was invented by doctor Archie Brain in 1981 and started to be used in 1988. Up to now, the laryngeal mask has been improved many times, there are more types of larynx mask. different on the basis of the classical laryngeal mask.
The laryngeal mask is convenient, has easier airway control properties than intubation, so the laryngeal mask has been included in the emergency regimen for difficult airways, especially in cases where no tube is in place. endotracheal intubation, not ventilation. In addition, the laryngeal mask is also used to control the airway in anesthesia and emergency resuscitation instead of traditional methods such as intubation or using an open mask. Some types of surgery can apply anesthesia with laryngeal mask, including: breast tumor, thyroid cancer, breast cancer, neck tumor or some difficult cases of intubation.
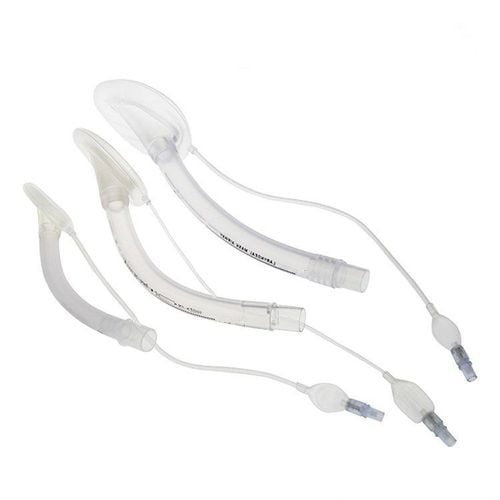

Mask thanh quản còn được sử dụng để kiểm soát đường thở trong gây mê và cấp cứu hồi sức
Easier to place than other supraglottic airway devices; Enables rapid and precise airway control with secure airway control rate in 98.5% of cases; Ensures better oxygen delivery when compared with open mask method; Laryngeal mask is less likely to cause cough reflex as when using endotracheal tube. Laryngeal mask also causes little or no sympathetic reflexes such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure when compared with intubation/extraction; Reduces the need for anesthetic, reduces the incidence of sore throat compared to intubation. Disadvantages of laryngeal mask placement:
Must ensure deeper anesthesia than other methods of airway control; Patients are at risk of regurgitation and aspiration.
2. Indications/contraindications for emergency laryngeal mask placement
2.1 IndicationsSurgery in short and medium time (less than 2 hours); Surgery for patients at high cardiovascular risk; Outpatient surgery; Option for difficult intubation. 2.2 Contraindications
Stomach full; There is a disease in the throat; Cervical spine injury; Need ventilation with inspiratory pressure over 20 cm H2O (in case of bronchospasm, obesity or prone position,...).
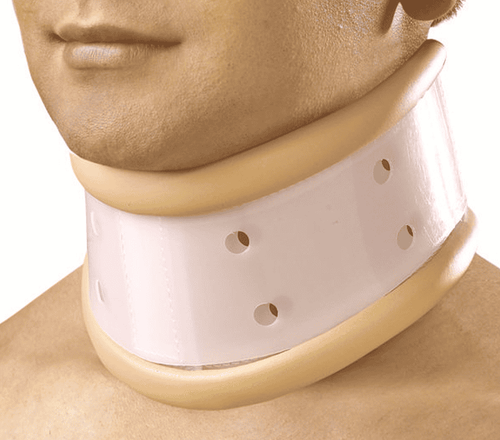
Chống chỉ định đối với người bệnh bị chấn thương cột sống cổ
3. Perform emergency laryngeal mask placement
3.1 PreparationImplementation personnel: Specialist doctors and supporting medical staff;
Patient: To be discussed in advance about the purpose, procedure for performing the procedure (or discussing with family members), preparing the standard posture and necessary procedures before the intervention; Instruments: Tube, balloon, squeeze bulb, laryngoscope, resuscitation medicine, laryngeal mask,... It is necessary to choose the appropriate size of the laryngeal mask, measure the inflated air and check that the balloon is not open. Laryngeal masks are available from size 1 - size 5, for subjects of different weights. 3.2 Implementation procedure
Vacuum deflate, lubricate the back of the larynx mask; Induction of anesthesia sufficiently deep with suitable anesthetic; With the patient's head tilted as much as possible, open the patient's mouth; Thread the larynx mask through the mouth, push the larynx mask deep down the throat to a suitable point, inflate the balloon with enough air in the middle of the tube to keep the mask in place; Hold the tube, check by gently squeezing, chest rising and falling, listening to both lungs,...; Maintain deep enough anesthesia, may allow patient to breathe spontaneously through a mask or mechanical ventilation if the inspiratory pressure is less than 20 cmH2O or a smaller intubation through a mask instead; Withdrawal of the laryngeal mask: When the patient recovers the protective airway reflex (opening the mouth, swallowing on command), aspirate to deflate the balloon and remove the laryngeal mask, the balloon will also drag sputum in the throat. Throat aspiration, balloon removal, or laryngeal mask removal should be avoided when the patient is not awake. Then, insert the gauze roll or Guedel canun next to the tube, tape the tube to the patient's edge and across the nucleus pulposus.
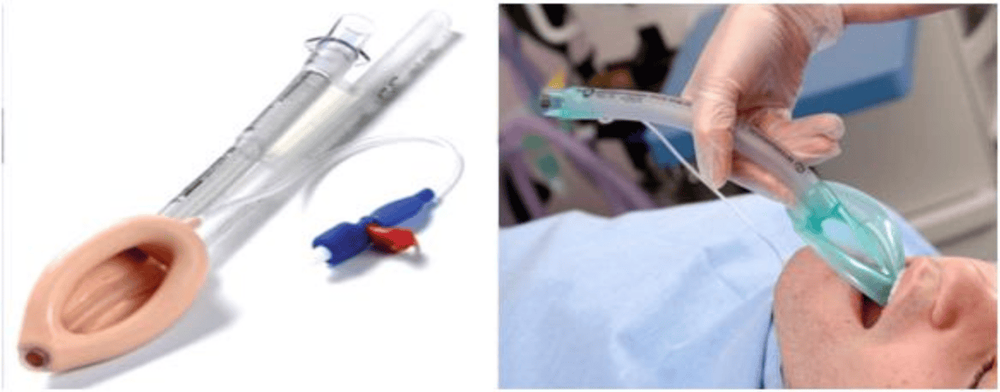
Đặt mặt nạ thanh quản cần được thực hiện đúng kỹ thuật
4. Follow-up after laryngeal mask placement
Make sure the laryngeal mask does not slip: The black line along the tube is always pointing up to the upper lip, listen for air in the neck, measure the exhaled air volume and monitor EtCO2 (if any).5. Some complications and how to handle them
Difficulty placing the laryngeal mask : Do not attempt to push in. The tip of the laryngeal mask should be checked, making sure it is not curled or pressed against the back of the pharynx. Then, with the patient's head tilted to the maximum, push the lower jaw forward and do it again; Deviation, obstruction of the laryngeal mask: Should be pulled out and put back; Surgical awakening and laryngospasm: This complication occurs due to superficial anesthesia, painful surgery or mobility of the laryngeal mask. In this case, the management is 100% oxygen ventilation and rapid induction of deeper anesthesia of the patient; Inhalation of vomit into the lungs: Should be managed by squeezing the 100% oxygen balloon, carefully aspirating the tube, replacing the laryngeal mask tube with an endotracheal tube, bronchoscopy, and breathing PEEP. Placing an emergency laryngeal mask is a simple and quick procedure, but there is still a potential risk of complications, so patients need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions to avoid unwanted problems.Master - Doctor Cao Thanh Tam has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases; Performing transthoracic echocardiography in the field of internal medicine and interventional Cardiology; Perform other non-invasive functional investigations in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Currently working as a cardiologist at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital since November 2015.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
SEE MORE
Things to know when intubation in children Intubation anesthesia cesarean section in patients with preeclampsia Intubation is indicated in what cases?