This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Nhu Thu Truc - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. Doctor has more than 8 years of experience in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology.Placental abruption is a serious disease during pregnancy that can lead to many dangerous complications for both mother and fetus. Depending on the degree of placental detachment and the mother's condition, doctors will consider choosing an appropriate and safe delivery method for both mother and baby.
1. What is a veggie?
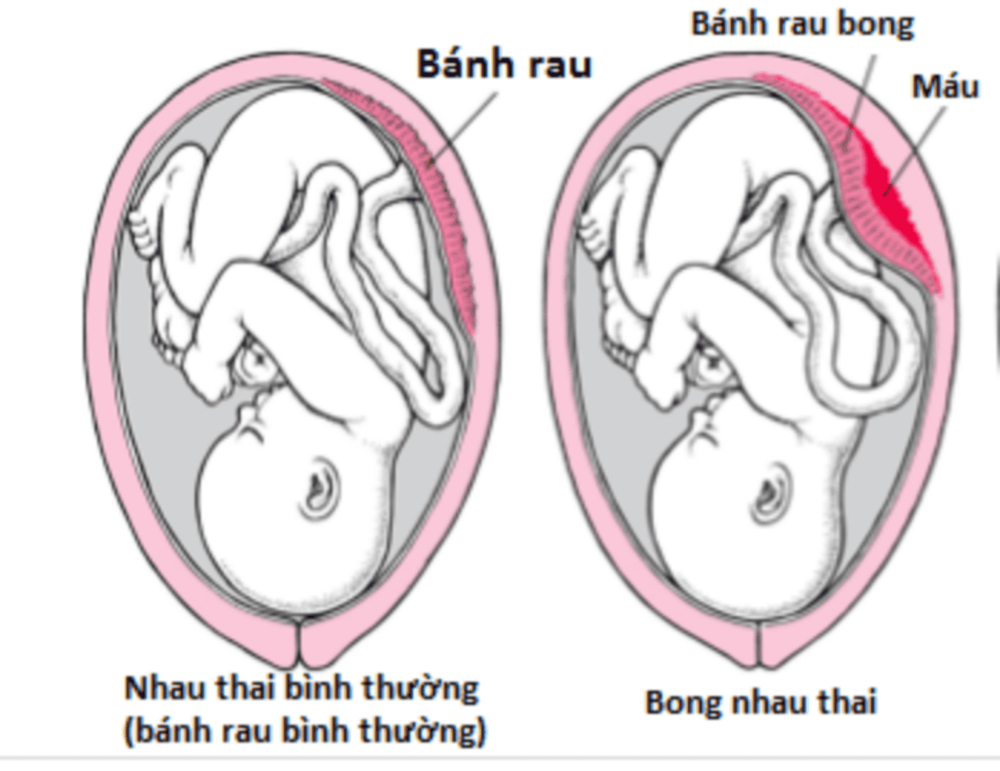
Placental abruption is a condition in which the placenta is shed before the pregnancy is delivered.Macroscopic picture can be seen:
Placenta: posterior hematoma indented into the placenta, with infarct or hemorrhage. Uterus: infarct or bruised uterus, spreading to the broad ligament. Ovarian or elsewhere: bleeding in the ovary, bleeding in the kidney, in the intestines. Microscopic image:
Localized necrosis, red infarct nodules. Capillary inflammation, arteriosclerosis. Thrombosis in the smaller veins behind the placenta. Severe placental abruption can show uterine muscle fibers flooded with blood and serum. Blood separates between the 2 broad ligaments and the pelvic peritoneum.
2. Is the vegetal sprout dangerous?
Placental abruption is a serious disease in pregnancy because the disease occurs suddenly, progresses rapidly to severe form, difficult to predict.In addition, if not treated promptly, the disease can lead to many dangerous complications such as:
Shock due to blood loss. Blood clotting disorder. Anemia in viscera such as liver, kidney, anterior pituitary gland.
3. Causes of placental abruption
Possible causes of placental abruption include:Trauma Pregnancy toxicity Congenital fibrinogenic factor deficiency Smoking Malnutrition Lack of folic acid, vitamin A, calcium Anemia Substance abuse: cocaine, drugs
4. Diagnosis of placental abruption
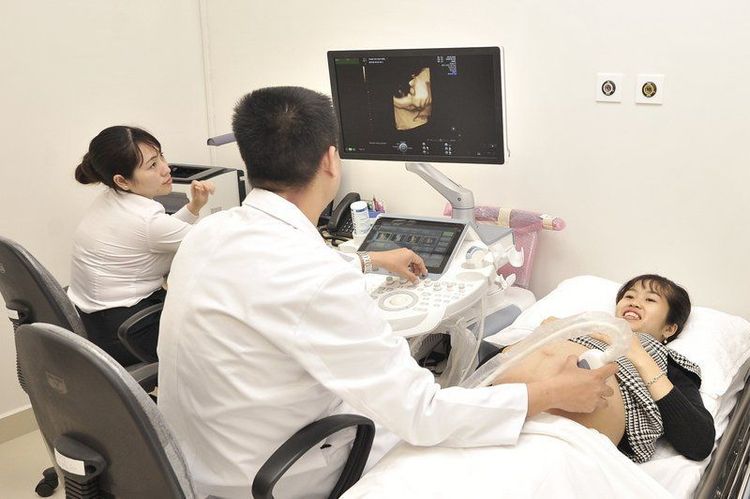
History examination Physical examination Blood tests and other tests Types of placental abruption include:
Latent abruption : difficult to diagnose Abruption Mild body has manifestations such as: Mild pregnancy toxicity. The intensity of uterine contractions is normal, the tone is slightly increased but hardly noticeable. The birth process progressed normally, after birth, examining the placenta showed a hematoma behind the placenta concave into the placenta. Ultrasound is diagnostic. Blood tests showed a slight decrease in fibrinogenic factor. Moderate abruption has the following symptoms: Moderate pregnancy toxicity. Sudden abdominal pain, increasing and lasting pain. Vaginal bleeding that does not clot (thin black blood) Shock: blood pressure is reduced or normal, pulse is rapid. The uterus is hard, ascending and difficult to feel the fetal parts. Fetal heart rate is fast or slow or sporadic. Hard cervix. Amniotic fluid is swollen, if the water breaks, you can see red amniotic fluid with blood. Ultrasound showed a hematoma after the vegetable. Blood tests showed a decrease in fibrinogenic factors. Severe placental abruption: Severe pregnancy toxicity. Blood loss shock. Vaginal bleeding does not clot. The uterus is as hard as wood. No fetal heart Ultrasound showed a posterior placental hematoma. Blood tests showed severe anemia, severely reduced fibrinogenic factor. Differential diagnosis
Veggies striker. Uterine rupture.
5. Should I give birth vaginally or by caesarean section?

However, in most cases the treatment takes place in the hospital and the doctor has to stabilize the pregnant woman first. Patients will receive intravenous fluids, injections to stabilize blood pressure and maintain a stable urine flow.
Latent and mild placental abruption: most term infants with mild placental abruption can be delivered spontaneously vaginally but require special care by an obstetrician and gynecologist. Moderate and severe form: Obstetrics: cesarean section, without amniotomy. If you are eligible for a vaginal delivery, help with forceps delivery. Internal medicine: Resuscitation, anti-shock. Infusion. Blood transfusion. During pregnancy, pregnant women should go for regular check-ups and if they notice symptoms such as vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, etc., they should promptly go to a hospital specializing in obstetrics and gynecology for timely diagnosis and treatment. . Depending on the degree of placental detachment, the doctor will decide to give birth vaginally or need a cesarean section.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.