This is an automatically translated article.
Ventricular dilatation in stroke patients is a surgical emergency requiring intervention as soon as possible. Placement of ventricular drainage plays a vital role in cases of increased intracranial pressure due to acute ventricular dilatation.1. Overview of ventricular drain placement
Ventricular drainage is the procedure of inserting a catheter into the lateral horn of the ventricle to drain CSF and monitor intracranial pressure. However, ventricular drainage can become blocked if there is too much blood in the ventricles.2. Diagnosis of ventricular dilatation
To diagnose ventricular dilatation in stroke patients, we rely on clinical and subclinical symptoms, including:Clinical Headache, vomiting. Consciousness disturbances progressed in the following order: somnolence, lethargy, coma. Acute or gradual ventricular dilation determines how quickly or slowly the disturbance of consciousness develops. Blurred vision, papilledema. Memory disorder. Subclinical Criteria to determine
Temporomandibular horn size > 2mm and Sylvius grooves, sulci are blurred. Temporal horn size > 2mm and FH/ID > 0.5. Suggested criteria
Balloon image of the third ventricle and bilateral frontal horns (Mickey mouse ear) Peripheral ventricular structures Evan FH/BPD score > 0.3 Image of the corpus callosum on middle longitudinal section MRI
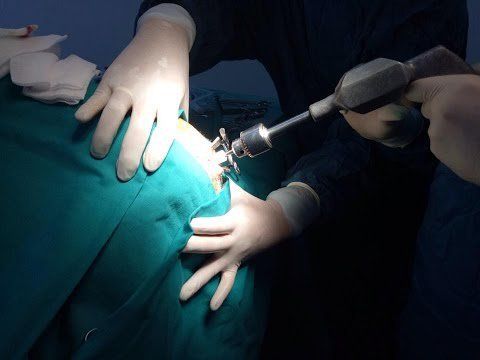
Đặt dẫn lưu não thất là thủ thuật đưa một catheter vào sừng bên của não thất nhằm dẫn lưu dịch não
3. Classification of ventricular drainage
There are 2 forms of ventricular drainage, which are:External ventricular drainage (also known as open ventricular drainage): Applied on stroke patients with large volume of cerebral hemorrhage. Aim to resolve temporary ventricular dilatation. After 7-10 days, the patient will be considered for drainage. If ventricular dilatation persists, the patient will need to have an intra-abdominal ventricular drain. Ventricular drainage: Apply to patients with dilated ventricles due to stroke but little or no blood in the ventricular cavity.
4. Monitoring and treatment of ventricular drainage
The goal of ventricular drainage is to reduce intracranial pressure, maintaining pressure below 25 mmHg with cerebral perfusion pressure above 70 mmHg. Patient position: Lie with head 30 degrees, avoiding neck flexion or side tilt. Limit manipulations that can cause the Valsava reflex, such as suctioning sputum through an endotracheal tube. Mechanical ventilation ensures maintaining SaO2 > 95%, PaCO2 from 35 to 38. Control body temperature from 36.5 to 37.5 degrees C with measures: use antipyretic drugs, cool compresses as much as possible. The patient was sedated with midazolam combined with analgesia with continuous intravenous fentanyl. In case of indications, propofol will be used to easily assess neurological signs when necessary. Maintain blood pressure to ensure cerebral perfusion pressure above 60 mmHg. Cases at risk of seizures based on clinical and CT-scan lesions should be treated with antiepileptic drugs early. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: vnha.org.vn