This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor La Thi Thuy - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Peripheral artery occlusion, a disease that causes many serious consequences and can lead to disability, is not well known.
1. What is peripheral artery occlusion?
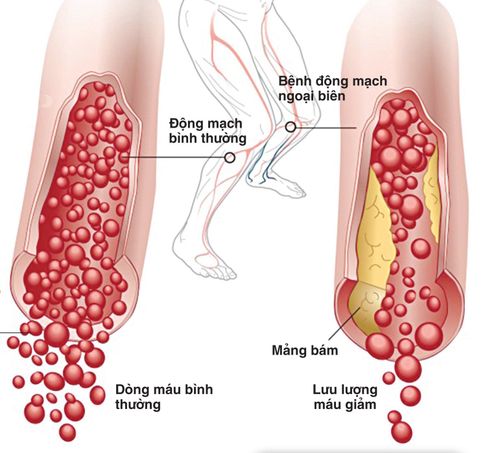
Peripheral artery occlusion is a blockage in the peripheral arteries, caused by plaque and thrombus. The peripheral arteries are the arteries that supply blood to the extremities, excluding the arteries that feed the heart and brain.Peripheral artery occlusion is a disease that belongs to the group of peripheral vascular diseases.
2. Causes of peripheral artery occlusion?
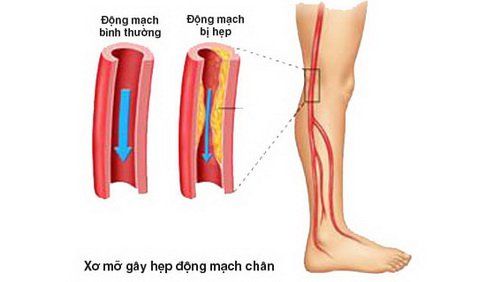
The main cause of peripheral artery occlusion is atherosclerotic plaque. Fat and other substances deposit on the vessel walls, narrowing the lumen. These deposits form plaque on the endothelium of the vessel wall, forming atheroma. Atherosclerotic plaque grows gradually causing narrowing, even completely blocking the lumen.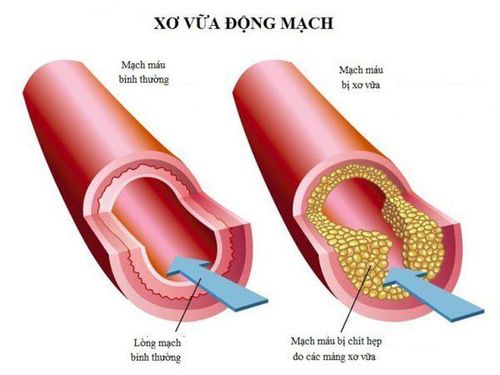
Xơ vữa gây tắc động mạch ngoại biên
3. What factors increase the risk of peripheral artery occlusion?
Peripheral artery occlusion has controllable and nonmodifiable risk factors, including:Unmodifiable risk factors such as: Age: Peripheral artery occlusion tends to increase with the increase of life expectancy; With age > 70 years, about 20% of the population has peripheral artery occlusion. Family history of peripheral artery disease, cardiovascular disease, or stroke. The risk factors can be controlled such as: Smoking: is the main risk of peripheral artery disease; Smokers have an increased risk of peripheral artery occlusion about 10 years earlier than non-smokers. Obesity: Increased risk of excess fat depositing in the walls of blood vessels (atherosclerosis). High cholesterol: Increases the risk of atherosclerosis (due to increased fat deposition in the artery walls). Diabetes: The endothelium is easily damaged, thereby increasing the risk of excess fat deposition in the vessel walls. Hypertension: The pressure in the vessel wall increases, which damages the vessel wall and causes fat deposition in the vessel wall. sedentary
4. Symptoms of peripheral artery occlusion?
Nearly 75% of patients with peripheral artery occlusion have no symptoms, leaving the disease undetected. When infected, patients may appear the following symptoms:The most common symptom is cramps in the thighs, hips and calves, appearing when walking, climbing stairs; This symptom improves or goes away with rest, but continues to cause pain (called claudication). Pain: Leg pain due to peripheral artery occlusion usually occurs in the muscles, not the joints. Usually, the intensity of pain is proportional to the degree of obstruction. Particularly, patients with diabetes may be confused by symptoms of pain, numbness in the feet or thighs due to neurological complications of diabetes. When the patient has the following symptoms, it means that the disease is severe:
Leg pain that does not get better with rest. Wounds in the feet and toes are difficult to heal. Necrosis of feet and toes. The affected side leg is colder than the healthy leg, or colder than the upper extremities.

Đau chân không đỡ khi nghỉ ngơi
5. What is the significance of early detection of peripheral artery occlusion?
Early detection of peripheral artery occlusion is very important. In addition to early resolution of limb ischemia before serious complications such as amputation due to gangrene occur, people with peripheral artery occlusion often have atherosclerosis in other arteries, including the arteries. blood supply to the heart and brain. In fact, patients with peripheral artery occlusion face a six to seven times higher risk of heart attack or stroke than those without the condition. Thus, early detection and timely treatment of peripheral artery occlusion not only avoids the risk of disability, but also helps to protect the patient's life.6. How to treat peripheral artery occlusion?
The goal of treatment for peripheral artery occlusion is to reduce pain and prevent adverse outcomes from the disease. Based on the specific examination of each patient, the doctor will make an appropriate indication. Treatments to slow the progression or reverse symptoms of the disease include lifestyle changes, exercise regimens, and medical treatment. Particularly in severe cases, the patient may need intervention methods such as stenting or surgery to avoid amputation complications.Exercise regimen: exercise is the most effective treatment for peripheral artery occlusion. Based on your specific condition, your doctor will recommend an appropriate exercise regimen. Although the effects appear to be slow, persistent exercise can reduce symptoms after several months, and this is the basic treatment for all patients with peripheral artery occlusion. Patients can exercise and monitor at rehabilitation centers or practice on their own according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. Lifestyle changes: High cholesterol occurs in many patients. In addition to using therapeutic drugs, a diet low in cholesterol and saturated fat is necessary to reduce blood fat and limit atherosclerosis. Quit smoking: Quitting smoking helps slow the progression of the disease as well as limit other heart-related diseases. Treatment with drugs: To achieve the best results, patients need to take the drug exactly as prescribed by the doctor. Methods of intervention and surgery: in some cases, based on the extent and nature of the damage, the doctor will prescribe arterial stenting or surgery. However, after the intervention, the patient needs to be persistent in using the drug according to the indications as well as maintaining exercise and adjusting the diet to be able to achieve the highest efficiency.

Bệnh nhân tắc động mạch ngoại biên cần kiên trì tập luyện
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.