This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. Doctor Tran Quoc Vinh has more than 6 years of experience (starting in 2011) in the field of Emergency Medicine.1. What is acute arterial occlusion of the extremities?
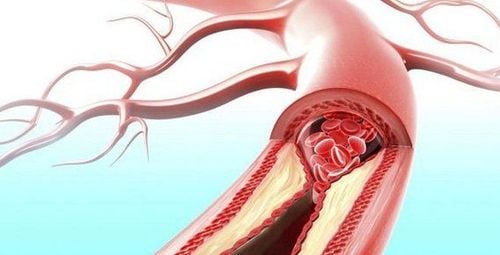
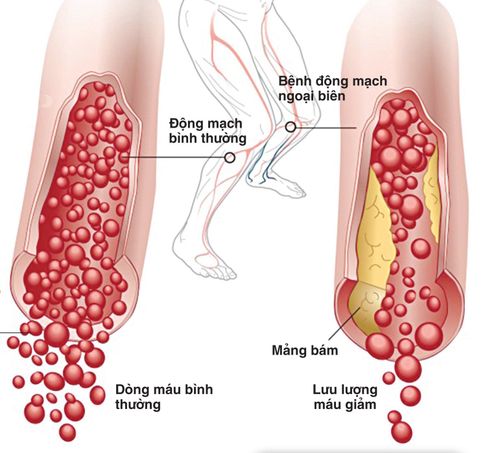
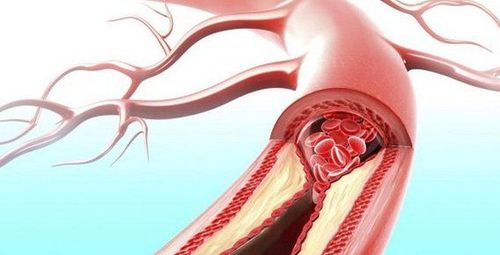
Acute arterial occlusive disease of the extremities is a blockage caused by an obstructing object from elsewhere in the circulatory system or due to the formation of a blood clot at the site of the blockage, causing an embolism resulting in no blood supply. nourish the limb nourished by that artery. Vascular embolism, arterial trauma, and acute thromboembolism are the 3 main causes of acute limb ischemia:1.1 Vascular embolism Is caused by a blood clot traveling from another place to due to an embolism .
Cardiovascular diseases that cause embolism such as: arrhythmia, especially atrial fibrillation, valvular disease, myocardial infarction, prosthetic heart valve, cardiac osler, left atrial mucinous tumor, interventricular septal aneurysm Aneurysm: A common cause of arterial embolism. Among them, abdominal aortic and popliteal artery aneurysms are the most common. Other causes of embolism include: Ulcerative plaque. The most common is atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta in the lower renal segment causing embolism in the lower extremities. 1.2 Acute thromboembolism A thrombus that forms on an ulcerated atherosclerotic plaque and obstructs the arterial lumen.
1.3 Injury to the artery Arterial trauma, contusion to an artery, or injury to the artery from a procedure such as catheterization can all cause acute embolism.
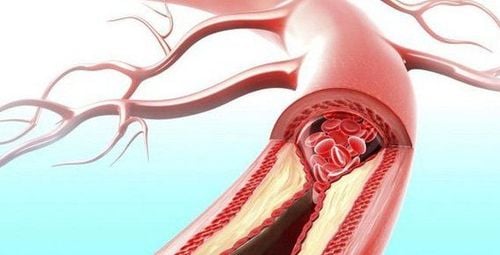
2. Manifestations of acute arterial occlusive disease in extremities
Clinical symptoms:Pain in the limb: Sudden severe pain Paresthesia, numbness, tingling, decreased sensation in the extremities Cold in the affected limb area The blocked limb is paler than the healing disease, spots may appear gradually. purple necrosis Loss of blood vessels in the extremities Decrease or loss of movement Subclinical symptoms:
Mainly based on arterial Doppler ultrasound to evaluate and determine: The location of the artery is blocked, determine the degree of atherosclerosis in the vessel wall , which examines the arterial blood flow below the occlusion through which the spread of the clot can be assessed.
3. Treatment of acute arterial occlusion in the extremities
3.1 Principles of treatment of acute arterial occlusion in the extremities Identify the cause of the occlusion Anti-shock Analgesia Treat symptomatically Care for the ischemic limb until re-establishment of vascular circulation such as warmth, avoidance of friction rubbing Use anticoagulants Indicated surgically when necessary.
Removal of emboli by Fogarty catheter: This is a very simple but effective method, applied in case of acute arterial occlusion without limb necrosis. Intra-arterial dissection: Applied after embolization for patients with acute arterial occlusion in the atherosclerotic limb. Arterial bypass surgery: This surgery will be indicated in the case of arterial thrombosis in the patient's body with atherosclerotic lesions over 10cm long, in case there is soft tissue damage accompanied by an atherosclerotic lesion. followed by a high risk of infection. Surgical removal of the damaged artery: This method is indicated in the case of patients with acute arterial thrombosis due to trauma. Amputation surgery. Indicated in the case of patients with acute arterial occlusion in a limb with limb necrosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.