This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Mai Anh - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Acute cerebral infarction is a condition that requires urgent emergency care within 4-5 hours after a stroke. This is a very dangerous disease with a high risk of death. Therefore, early identification and diagnosis of cerebral infarction is the best way to prevent risks and complications.
1. Overview of cerebral infarction
According to statistics, cerebrovascular accident is one of the top 10 causes of death. Cerebrovascular accident is divided into 2 types:Cerebral infarction (ischemic) caused by a blockage of a blood vessel in the brain, usually caused by a blood clot (a buildup of arterial plaque in atherosclerotic disease). arteries). Due to the rupture of blood vessels in the brain, it causes vasoconstriction, leading to cerebral ischemia. Cerebral hemorrhage Acute ischemic stroke is the most common type of cerebrovascular accident (accounting for 80%), involving the formation of blood clots in the brain that block blood vessels. This injury reduces suddenly or completely stops the supply of blood and oxygen to the brain, nerve cells are damaged, if prolonged damage will cause sequelae such as paralysis, slurred speech, distorted mouth, ulcers due to prolonged lying...
The disease has a high risk in people with high blood pressure, smoking, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, heavy alcohol use.
2. Early symptoms of acute cerebral infarction
Sudden appearance:Distorted mouth. Hard to say. Stiff limbs. Hemiplegia May lose vision. Comatose.

Hôm mê là một trong các triệu chứng sớm của nhồi máu não cấp tính
3. Diagnosis of cerebral infarction
Contrast-free CT scan of the brain: can help rule out intracerebral hemorrhage, but it can be difficult to detect infarction if the lesion is small in size and early in the stage. If there is damage, some patients need more cerebral angiography to determine the blocked blood vessel segment.What is perfusion magnetic resonance imaging?
Cranial magnetic resonance imaging: Basic pulse sequences such as T2W, FLAIR, DWI, ADC... are pulses that detect changes in brain parenchymal signal in the infarct area, helping to detect 80% of infarction in the first 24 hours. Magnetic resonance perfusion (MRI) to evaluate cerebral microcirculation helps determine the viability of brain parenchyma in the affected area. Indication case
Diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction, search for brain parenchymal ischemic but potentially reversible. Brain tumors. Cases of contraindications
Patients bring electronic devices such as: cochlear implants, pacemakers, automatic subcutaneous drug pumps, anti-vibration machines, Neurostimulator... Wear surgical forceps intracranial metal, eye socket, blood vessels less than 6 months (If worn for more than 6 months, consider depending on the patient's condition). Severely ill people need resuscitation equipment next to them
4. Perfusion magnetic resonance imaging procedure
4.1 Preparing the team to perform:Radiology specialist Imaging technician. Means of use:
Resonant angiogram from 1.5 Tesla or more. Movie. Film printer. Dedicated electric pump. Image storage system. Medicines: contrast agents, sedatives, antiseptics for the skin and mucous membranes.
Common supplies
Patient needs to prepare:
In most cases, fasting is not required. Prepare a copy of the clinician's request for a scan, with a clear diagnosis or complete medical record (if necessary). The procedure is explained in advance to work well with the doctor. Sign a commitment to technical implementation. Change the clothes of the MRI room according to the instructions, remove the contraindicated items.
Người bệnh có khối U não cần được chỉ định chụp cộng hưởng từ tưới máu
Patient position
The patient is instructed to lie on his or her back on the table. Select and position the receiver coil. Move the table into the machine bay and position the shooting area. Imaging technique
Place an intravenous line, connect to an electric injection pump. Conduct location capture. Take common cranial pulse sequences: T1, T2, FLAIR, diffuse pulse sequences,... Cerebral perfusion scan: inject bolus of magnetic contrast agent (gadolinium) at a dose of 0.2ml/kg body weight at a rate of 5ml /s followed by expulsion with 20ml physiological saline at the same injection rate. Taken immediately after starting the injection with the T2* pulse sequence, the field of study includes the entire brain parenchyma, repeated continuously for 40-45 seconds. Calculation of perfusion parameters: Time to bolus, time to peak (TTP), mean apparent transit time (MTT), Relative cerebral blood volume (CBV), peak peak (MAX), cerebrovascular index (CBFI). Based on the images and parameters of perfusion magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor will evaluate the brain parenchymal damage (if any), the degree of brain parenchymal diffusion and the recovery ability of the damaged brain parenchyma. , thereby providing professional advice to the patient and the patient's family if required. Note:
During the scan: always monitor blood pressure, pulse, focal neurological signs. After the scan: the patient is asked to wait 15 minutes for further monitoring or transfer to the emergency room.
Hệ thống máy chụp cộng hưởng từ 1,5 Tesla trở lên được sử dụng trong kỹ thuật chụp cộng hưởng từ tưới máu
5. Advantages of perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of acute cerebral infarction
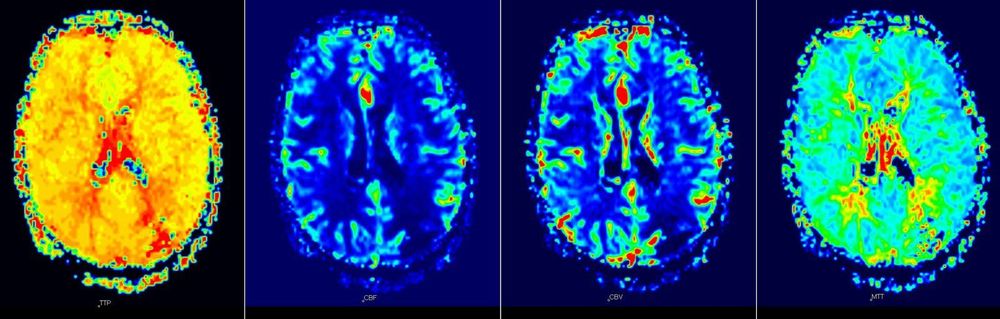
Hình ảnh chụp cộng hưởng từ tưới máu não
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Mai Anh has nearly 10 years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially in imaging breast and thyroid cancer. Received formal training at Thai Binh Medical University and specialized postgraduate training at Hanoi Medical University. Currently, the doctor is a radiologist at Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.