This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging.1. What is a pancreatic pseudocyst?
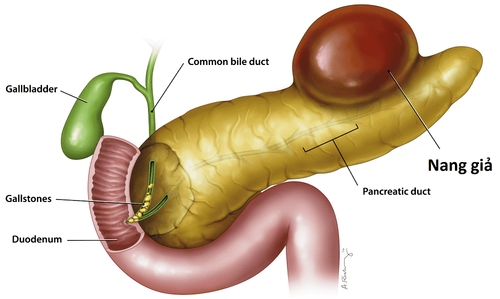
A pseudocyst is a cystic lesion lacking epithelial or endothelial cells. Pseudocysts can form in several places, including the pancreas, abdomen, and adrenal glands. eye. Pancreatic pseudocysts are composed of pancreatic juice surrounded by fibrous tissue or granules. The cause of pancreatic pseudocyst is due to:Pancreatic pseudocyst is formed mostly after acute or chronic pancreatitis. Due to gallstones blocking the pancreatic bile duct and drinking a lot of alcohol causes acute or chronic pancreatitis, thereby forming pancreatic pseudocysts. Trauma and infection of the pancreas Pancreatic tumors, cystic fibrosis or heredity Too high blood calcium levels, blood triglyceride levels Drug damage to the pancreas or autoimmune diseases Pancreatic pseudocysts if left untreated can cause dangerous complications and complications will increase during disease monitoring. Complications of pancreatic pseudocyst can cause include:
Infection: When infected, the patient will have abdominal pain, fever, high white blood cell count. This case needs to be drained to avoid retroperitoneal spread. Obstruction of the duodenum and common bile duct: Caused by a large cyst, it should be inserted into the duodenum or common bile duct Bleeding: This is a very dangerous complication. The cause of bleeding appeared secondary to mucosal necrosis, intestinal leakage into the pseudocyst causing direct damage to the visceral blood vessels. Pancreatic pseudocyst rupture: When the pancreatic pseudocyst is too large, it can burst into the gastrointestinal tract, causing cyst-digestive fistula and reducing pressure and collapsing the pancreatic cyst. Cysts can also rupture into the peritoneal cavity, the pleural cavity.
2. Diagnosis of pancreatic pseudocyst by ultrasound method
Pancreatic pseudocyst ultrasound is a simple test and gives 90% accurate results. The image of pancreatic pseudocyst on ultrasound will show the doctor:Pancreatic pseudocyst on ultrasound is a collection of negative effusion. Next to the umbilical cord, when ultrasound, the pancreatic pseudocyst will show increased light behind. Pancreatic pseudocyst on ultrasound has thick cortical wall, clear border. Pancreatic pseudocysts in the process of formation contain hypoechoic fluid with echogenic fragments or pseudoseptum due to tissue necrosis or bleeding. If ultrasound does not clearly distinguish pancreatic cysts and pancreatic pseudocysts, the following methods can be used:
Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance cholangiography are also effective methods to detect pancreatic pseudocysts because can provide better contrast, helping to clearly visualize fluid and debris, and detect bleeding. Endoscopic ultrasound: This is a secondary test to further evaluate cysts found in other tests and determine if they are pseudocysts; Clinical diagnosis: Symptoms usually appear in large pseudocysts. When the pancreatic pseudocyst is large, the patient will have symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, feeling of fullness, indigestion, infection, hernia or intestinal obstruction. Subclinical: In addition to ultrasound of pancreatic pseudocyst, quantitative tests of pancreatic enzyme levels in blood and urine; Internal metabolic testing is also done to diagnose pancreatic pseudocysts.
3. Method of treatment of pancreatic pseudocyst
3.1. Purpose of treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts Pancreatic pseudocysts with clinical symptoms can only be treated by surgical methods to exclude pseudocysts, internal or external drainage. However, based on the size, location and invasion of other organs will be important factors in choosing the technique for each case as follows:Chronic pancreatic pseudocyst: Need to choose method With immediate drainage, drainage is based on diagnosis and finding the wall of a stable, sutureable cyst for internal drainage. Infectious pseudocyst: Selecting a method of rapid external drainage. Acute pseudocyst: If surgery is performed too early, the wall of the cyst will be broken and cannot be anastomosed. Therefore, 4-6 weeks is a suitable time for the cyst wall to develop stably and perform surgery. 3.2. Treatment Methods External Drainage:
Although the mortality and recurrence rates of external drainage are high compared with other surgical interventions, it is a life-saving surgery and is simple to perform. External drainage is indicated when:
Bleeding pseudocyst Infection of a pancreatic pseudocyst Free rupture of a pseudocyst A soft-walled pseudocyst makes anastomosis impossible. Endoscopic drainage:
Chronic pseudocyst: If a chronic pseudocyst has contact with the stomach or duodenum, it can be drained endoscopically by creating a cystic fistula - digesting the diameter of the drainage hole 1 - 2 cm. Acute pseudocyst: Cannot be performed by this method because it is difficult to determine whether the cyst has attached to the viscera. Therefore, pancreatic drainage is the method used because of lower morbidity and mortality compared to external drainage.
In cases of stable pseudocyst wall, internal drainage is the best surgical approach. Mortality and recurrence rates are low, and the choice of surgical procedure depends on the location of the pseudocyst and the local situation. Specifically as follows:
Cysts attached to the stomach: In case the pancreatic pseudocyst sticks to the stomach, it is necessary to conduct cyst-gastric drainage by endoscopic drainage. Pseudocyst to duodenum: Use this method when the pseudocyst in the head of the pancreas is pressing on the duodenum. Connect the pseudocyst to the jejunum: This method is often chosen. In certain cases, an Omega connection can be made with the addition of a Braun joint. Peripheral pancreatectomy:
Indicated when the pseudocyst of the body and tail of the pancreas are related to the spleen, and not attached to the splenic flexure colon, then the peripheral pancreatectomy is performed. ERCP method helps to determine the resection level, the recurrence rate after surgery is low. In case the main pancreatic duct of the ampulla of Valter and the muscle of Oddi are obstructed, the method of connecting the pseudocyst to the jejunum is chosen to avoid complications of pancreatic fistula. In a nutshell, a pancreatic pseudocyst is a sac that contains pancreatic fluid when it has leaked out. This condition may have no symptoms but can sometimes cause serious problems, sometimes even more than acute pancreatitis, if there is a massive release of pancreatic enzymes into the peritoneum. Therefore, early detection of the presence of pancreatic pseudocysts after acute pancreatitis and proactive intervention is essential to help prevent serious complications later.
If you suspect that you have a pancreatic pseudocyst, you can come to Vinmec International Hospital System to conduct an ultrasound of the pancreas, Vinmec is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country. , using the most modern generation of color ultrasound machines today in examining and treating patients. One of them is GE Healthcarecar's Logig E9 ultrasound machine with full options, HD resolution probes for clear images, accurate assessment of lesions. In addition, a team of experienced doctors and nurses will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs of the body in order to provide timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.