This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Specialist Doctor II Phung Thi Phuong Chi - Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park International Hospital
Clinical examination and use of imaging tools such as breast ultrasound, mammography, breast MRI... can help evaluate tumor and lymph node stage. In the case of advanced breast cancer, PET/CT can be used for staging.
1. What does a diagnosis of breast cancer mean?
Breast cancer, if detected early, the more effective the treatment, the better the prognosis. Currently, screening for the diagnosis of breast cancer plays a very important role. People can diagnose breast cancer by doing a self-exam at home or using modern diagnostic facilities.
Clinical examination and use of imaging tools such as breast ultrasound, mammography, breast MRI... can help assess tumor and lymph node stages in patients.
Indication for screening for distant metastatic breast cancer is done when the patient has signs suggestive of metastasis or advanced disease, by means such as: bone scan, CT scan of abdomen and pelvis, X-ray , CT scan of the chest or MRI of the brain. In the case of advanced breast cancer, PET/CT can be used for staging.
Tumor biomarker CA15.3 has no role in screening, diagnosis and follow-up after treatment for early breast cancer. CA 15.3 combined with clinical examination and imaging is used to assess response in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Increasing CA15.3 suggests treatment failure.
Trắc nghiệm: Những lầm tưởng và sự thật về ung thư vú
Ung thư vú có tỷ lệ tử vong cao nhất ở nữ giới khiến họ rất lo sợ bản thân mắc phải căn bệnh này. Tuy nhiên, không ít chị em có những hiểu biết thái quá về ung thư vú. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau sẽ giúp bạn loại bỏ được những nghi ngờ không đúng về căn bệnh này.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. Mammography to diagnose breast cancer
Mammography is an effective screening tool in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Most malignancies of the breast can be detected by mammogram abnormalities. However, a negative mammogram does not rule out breast cancer. Approximately 10% of palpable lesions are not detected on mammography, especially when breast tissue density is dense.
Common malignancies on mammograms are hyperattenuated mass, nodular, microcalcification, structural disturbance, stellate (dendritic) appearance.
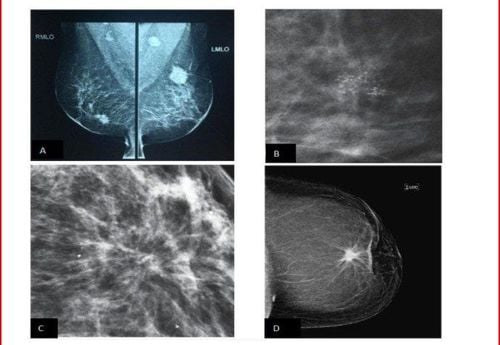
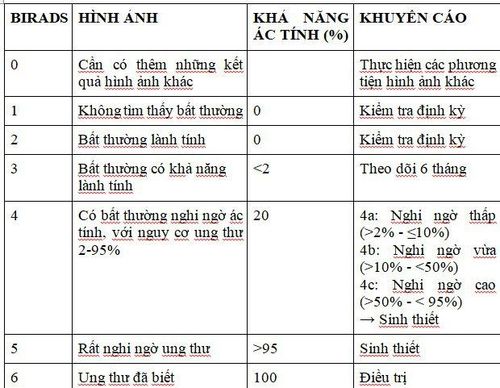
After the scan, the doctor who reads the mammogram will classify it according to the BI RADS (Breast Imaging-Reporting And Data System) system.
Table 1: BIRADS Mammography Rating and Significance according to the American Radiological Society 2013
3. Breast ultrasound in cancer diagnosis
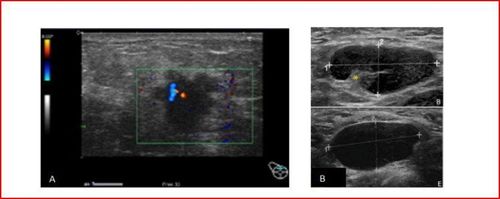
Breast ultrasound is an important imaging tool after mammography. Ultrasound helps to distinguish adipose tissue, breast tissue, and between solid tumors and breast cysts that are palpable or mammographically detected. Ultrasound diagnosis of breast cancer is usually the choice for young patients < 35 years of age.
Characteristic of malignant lesions on ultrasound are usually poor echo mass, vertical axis, unclear boundaries, spicule margins, vascular proliferation, microcalcifications can be detected. In addition, mammography helps detect axillary lymph node metastases and can guide interventional procedures or ultrasound aspiration biopsies. These nodes have thickened cortical areas, enlarged foci in the lymph node cortex region over 2.5mm, or complete loss of the hilum.
4. Breast MRI in cancer diagnosis
Magnetic breast MRI with gadolinium contrast improves the diagnostic accuracy of invasive breast cancer by about 88-100%, depending on tumor vascularity. Some breast cancers can only be seen with an MRI scan. However, gadolinium injection also causes false positive and false negative diagnoses such as fibroadenoma, papillary tumor, atypical ductal and lobular hyperplasia. Diagnosis of false negatives may occur when there is a lack of angiogenesis in mucinous carcinomas, lobular carcinomas, and ductal carcinomas in situ or after chemotherapy.
Disadvantages of breast MRI: High cost, mandatory injection of contrast, false positives on benign lesions, many images, so the survey time is long, the reading time is long and there are 5% of invasive cancers take up less and less drugs, so they are confused with benign lesions.
Currently, to join hands in "Say no to breast cancer", Vinmec International General Hospital has built a breast cancer screening package including: Breast examination with an oncologist or a gynecologist; Mammogram (2 sides); 2D breast ultrasound on both sides.,..
Advantages of breast cancer screening at Vinmec:
Team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA, .. Comprehensive treatment and care, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. There are full range of main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant... Breast cancer screening package at Vinmec for the following subjects:
Female customers, over 40 years old. Customers wishing to be able to screen for breast cancer Customers are at high risk of cancer – especially customers with a family history of breast cancer. Women of reproductive age, perimenopause and menopause. Women who are having symptoms of breast cancer such as: pain in the breast, lump in the breast ...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
REFERENCESHortobagyi GN, Connolly JL, et al. Breast, in AJCC Cancer staging manual, 8th edition 2017: 589-628. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast Cancer, Version 2.221. Jagsi R, King TA, et al. Malignant tumour of the breast, Devita, Hellman, and Rosenberg’s Principles and practice of oncology, 11th edition, 2018, pp:1269-1317. Cardoso F, Kyriakides S, et al. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019 Aug 1:30(8):1194-1220.