This is an automatically translated article.
Craniopharyngioma is a dangerous disease that, if not completely removed, will easily lead to recurrence. Cranial open surgery for craniopharyngioma is an effective method in the treatment of this disease.
1. Learn about craniopharyngioma
Craniopharyngioma is a tumor that develops near the pituitary gland, close to the skull. Craniopharyngioma accounts for 2-4% of all brain tumors. The disease occurs mainly in children and adolescents, sometimes in adults. Craniopharyngioma has 2 types: enamel form (common in children) and papillary form (common in adults). Most craniopharyngeal tumors are slow-growing and benign.The growth site of the craniopharyngeal tumor is just below the thalamus, around the pituitary gland, and the great blood vessels of the brain. This is a particularly dangerous position. At the same time, if the craniopharyngioma is not completely removed, it is easy to recur. Therefore, even though it does not spread, craniopharyngioma is still considered a malignant brain tumor.
In the early stages, craniopharyngeal tumors usually grow slowly. It takes about 1-2 years for the disease to appear symptoms. Symptoms of craniopharyngioma include: Persistent headache, pain medication that doesn't go away, or partial loss of vision. In addition, patients with craniopharyngioma also have some other typical symptoms such as mood swings, mood swings, insomnia, nausea in the morning, difficulty keeping balance, easy falls, urinary incontinence, depression. colds, coma,... Craniopharyngioma can also change hormones, affect vision, make it difficult for children to gain weight,...
2. Methods of treating craniopharyngioma
The most common treatment for craniopharyngioma is surgery. In addition, some cases can choose radiation therapy or radiation therapy combined with minor surgery. After treatment, the patient will have a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to determine if the tumor has been completely removed. If surgery has not removed all of the tumor, the patient will receive radiation therapy to completely remove the remaining tumor.
Details of treatment methods are as follows
Surgery: Aim to remove the maximum tumor, protect the surrounding nerve and blood vessel structure. In children, removing the tumor at the first surgery helps to avoid recurrence and increase the effectiveness of treatment. This method can work for 70-85% of children with the disease. The choice of incision depends on the location, size, nature, growth direction of the tumor and the doctor's experience to bring the highest efficiency and ensure patient safety. There are 3 main surgical techniques for craniopharyngioma: Open frontal or bilateral frontal craniotomy: Applied to craniopharyngeal tumors that develop in the hypothalamus, around the visual interference. Most craniopharyngioma are operated by this incision; Endoscopic surgery through the nose: Apply to children over 8 years old. For patients whose tumor axis grows parallel to the transsphenoidal incision, this technique increases the efficiency of tumor removal in the post-optical-hypothalamus region. When applying the transnasal endoscopic technique, it is necessary to pay attention to patch the skull base carefully to avoid post-operative fistula; Surgery through the corpus callosum, through the cerebral cortex into the ventricles: Indicated for cases of craniopharyngioma growing into the third ventricle; Supportive treatment (endocrine): Craniopharyngioma affects pituitary gland function, so all patients need adjuvant pituitary endocrine therapy. If the tumor or surgery reduces hormone production, the patient should be treated with hormone replacement therapy to maintain normal hormone levels in the body; Radiation therapy: Indicated for recurrent craniopharyngeal tumors that cannot be continued with surgery. This is a method that uses high-intensity X-rays to destroy tumors
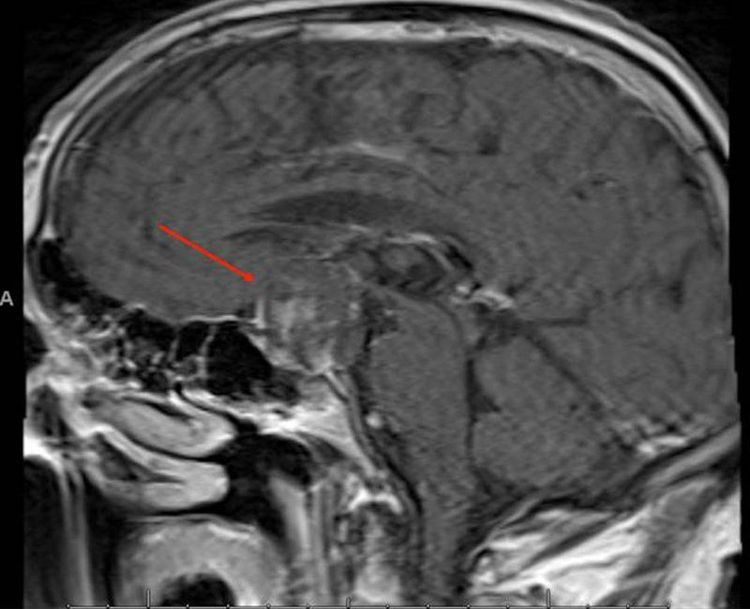
Chụp MRI giúp xác định vị trí, tình trạng khối u
3. Learn the surgical method of craniopharyngioma by opening the skull cap
Craniopharyngioma surgery following the opening of the skull has advantages such as a large surgical field, high customization ability depending on the location of the craniopharyngeal tumor (in the pituitary, suprabasal or third ventricle,...) applicable to most patients.
3.1 Indications and contraindications
Indications: Large craniopharyngeal tumor, growing laterally, posteriorly or into the ventricles; Contraindications: Craniopharyngioma surgery has no absolute contraindications.
3.2 Preparation for surgery
Performers: Surgeon, assistant surgeon, nurse, anesthesiologist; Patients: Have a detailed medical examination, basic tests, eye exams, imaging tests, pre-operative anesthesia; shave hair, wash hair clean, clean the surgical area; Technical facilities: Equipment for endotracheal anesthesia and patient monitoring during and after surgery; operating table with Mayfield head; drilling machine, microsurgery glasses, neural positioning system, ultrasonic suction knife; consumables (gauze, cotton, sutures, skull wax,...); skull pin or maxillofacial screw, closed subcutaneous drainage, Floseal hemostatic material,...; Medical records: Prepare according to regulations.
3.3 Performing surgery
Posture: The patient lies on his back, depending on the tumor position, the head can be slightly tilted to the left or straight, the head is tilted to the maximum, and the head is fixed on the Mayfield frame; Anesthesia: Perform endotracheal anesthesia; Register the patient's neural navigation system; Disinfect large areas of surgery, spread acid; Anesthetize the incision site: right forehead hairline or above the eyebrow; Make skin incision, peel off the muscle fascia; Using a drill to open the skull cap; Open the dura in an arc; Place microsurgery glasses, separate sylvian arachnids, aspirate cerebrospinal fluid to deflate the brain; Identify ipsilateral optic nerve and carotid artery, perform arachnoid dissection toward midline to identify optic interference; Burn and cut the craniopharynx, when the fluid in the tumor flows out, the tumor will shrink. Next, remove the tumor in sections with an ultrasonic aspirator or curette and then peel off the tumor. In parallel, using the positioning system to check the poles; Pay attention to preserving the pituitary stalk; Hold the machine with a bipolar, flopal or surgicel electric knife; Close the sclera with prolene 5.0 sutures; Place epidural and subcutaneous drainage; Using pins or maxillofacial screws to fix the skull cap; Perform incision closure.
3.4 Follow-up after surgery
Patient's pulse, temperature, blood pressure and respiration; Sensation, pupils and urine; Surgical wound bleeding.
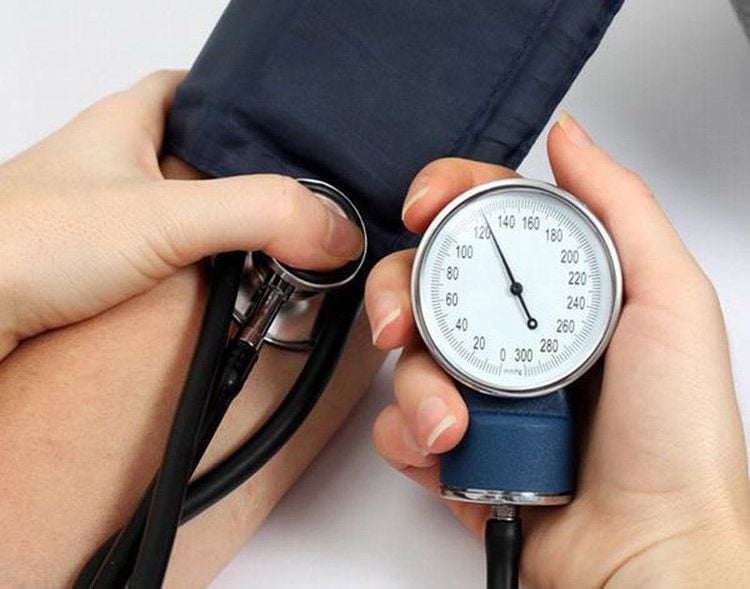
Hậu phẫu thuật bệnh nhân cần được theo dõi về huyết áp, nhiệt độ,...
3.5 Management of complications after surgery
Bleeding: Perform surgery again to collect hematoma and stop bleeding; Diabetes insipidus or adrenal insufficiency : Treatment by taking drugs (using hormone replacement), water-electrolyte replacement; Ventricular dilation due to intraoperative bleeding: Treat by draining the ventricles out or into the abdomen; Cerebrospinal fluid leak: Shoulder lumbar puncture to drain CSF, strengthen the incision and treat with antibiotics. Cranial open surgery to treat craniopharyngioma is a widely indicated method for patients. Patients should follow all instructions given by the doctor during treatment to improve the chances of cure and reduce the risk of complications.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE
Are mediastinal tumors dangerous? Mediastinal tumor removal by open surgery How to treat mediastinal tumor?