This is an automatically translated article.
Open skull trauma is a common surgical condition that causes open skull injuries. It is usually caused by a traumatic brain injury that causes a skull fracture. The principle of treatment is to stabilize the hemodynamic status, resuscitate the patient before surgery and operate the open skull wound as soon as possible.1. What is an open skull wound?
An open skull fracture is an injury that tears the scalp, fractures the skull and tears the dura, causing the subarachnoid space to communicate with the outside environment.The cause of open skull injuries is traumatic brain injury, the most common is trauma from traffic accidents.
2. Classification of open skull wounds
Open skull wounds can be classified according to the agent and anatomical location, but the most commonly used classification is by depth.Penetrating wounds are wounds with only one hole causing lacerations of the skin, skull and dura mater, possibly with a foreign body in the skull. Piercing brain injuries caused by bullets are injuries that penetrate both the skull and the meninges. The mouth of the wound often has blood with cerebrospinal fluid flowing out, fragments of the skull are thrown out of the skin or plugged into the brain parenchyma. Tangential penetrating wounds can be caused by bullets or by machetes, which are wounds that have a tangential path to the skull. The traumatic brain injury communicates with sinuses such as the maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, sphenoid sinus, ethmoid sinus or mastoid sinus. The traumatic brain injury communicates with the superior longitudinal venous sinus or the transverse sinus. This is a serious wound with a high mortality rate before, during and after surgery. Infected open traumatic brain injury due to necrotic wound, protruding brain tissue. The patient may present with meningitis.
3. Risks of open traumatic brain injury
Because of the communication with the outside environment, open skull wounds increase the risk of intracranial infections, mainly meningitis. In some cases of small open skull trauma, the blood cannot flow out completely, creating a hematoma, blocking and possibly compressing the brain, increasing intracranial pressure. Clinically, the patient will have headache, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck and loss of consciousness, coma.If the open skull wound penetrates the brain, damaging many brain parenchymal tissues or the deep wound causes hemorrhage, cerebral edema, causing the patient to fall into a coma, like a closed traumatic brain injury, the mortality rate is high. .
In addition, open skull trauma also carries a risk of wound infection. The degree of infection depends on whether the causative agent of the wound is clean or dirty, the wound is compact or crushed, the location of the wound, the associated lesions, and the age and location of the patient.
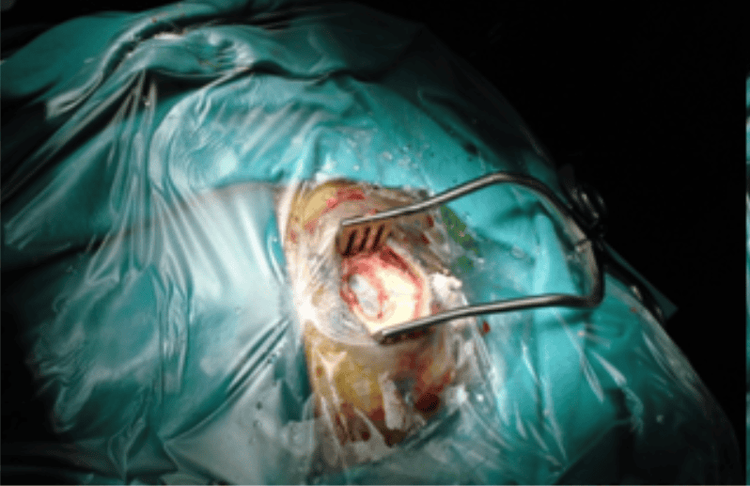
Phẫu thuật vết thương sọ hở là một loại phẫu thuật cấp cứu
4. Open skull wound surgery
When traumatic brain injury is diagnosed early and properly treated, timely surgery will save the patient's life and limit complications. Open skull surgery is an emergency surgery that is required in most cases. Some special cases such as too small clefts, too many openings or open skull wounds with openings from the face, chin, and neck can be delayed.Steps for surgical treatment of open skull wounds are as follows:
Preoperative resuscitation: Including correction of hemodynamic status, respiratory disorders, cardiovascular resuscitation, especially in cases of brain protrusion, The patient was in a deep coma with signs of brain stem damage. Remove all bone fragments, remove foreign bodies if any, but pay attention to avoid damage to the brain and meninges. If the wound is clean, large skull fragments may be left behind after cleaning. Enlarge the meninges to treat the damage inside the brain. Then, depending on whether the wound is clean or dirty, the meninges can be closed or the meninges left open. However, meningeal regurgitation causes the risk of cerebrospinal fluid leakage, fungal infection of the brain - meninges and especially increases the risk of epilepsy after surgery. Remove brain contusion and hematoma with low-pressure suction to avoid further damage to healthy brain tissue, especially functional brain areas. When the traumatic brain injury is located in an important functional area such as sensation, movement, and language, the suction machine should not be used, but water should be pumped to the brain tissue to allow the hematoma to drain. Do not try to remove foreign bodies far or deep in the brain parenchyma because it will damage healthy brain tissue. Open cranial trauma to the ventricles often causes intraventricular bleeding, so during surgery it is necessary to stop the intraventricular bleeding. Ventricular drainage by threading under the skin as far away from the incision as possible helps to avoid ventricular dilatation, increased intracranial pressure and ventricular occlusion due to blood clots. Withdraw ventricular drainage as soon as possible. Administer intravenous high-dose broad-spectrum antibiotics. In summary, open skull trauma is a common surgical condition that causes open skull injuries. The principle of treatment is to stabilize the hemodynamic status, resuscitate the patient before surgery and operate the open skull wound as soon as possible.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.