This is an automatically translated article.
A recent study found that people who are obese are almost twice as likely to develop periodontitis. The main reason is that fat cells increase chemical and hormone signals, affecting metabolism, leading to increased inflammation in the mouth.
1. What is gum disease?
Healthy gums are fundamental to having healthy teeth. Without a solid foundation, nothing can stand forever. While healthy gums are pink and fit snugly around the teeth, rarely bleeding or causing pain, gum disease can cause soft tissue damage and eventually infect the jawbone. Some research shows that if bacteria get into the bloodstream, a tooth infection can lead to a respiratory infection, rheumatoid arthritis, coronary heart disease, or stroke.
Some signs of gum disease include:
Bad breath that persists and doesn't go away when brushing or using mouthwash; Bright red or swollen gums; Gums are soft, painful, or bleed with daily cleaning; Pain when chewing or brushing teeth; Loose or sensitive teeth; Sudden receding gums or teeth appear longer than usual. Although there are different types of gum disease, the three most common are:
Chronic periodontitis: The most common form of gingivitis in adults and children, there is an accumulation of inflammatory fluid on the teeth and can easily Easy to prevent and treat if detected early. Severe periodontitis: A rarer form of gingivitis, often affecting the entire tooth cluster and quickly causing bone damage and even tooth loss. Necrotizing periodontitis: This form of gum disease is most common in immunocompromised patients such as HIV, cancer or those suffering from malnutrition, resulting in death of gum tissue and possibly severe infection. , spread all over the body.
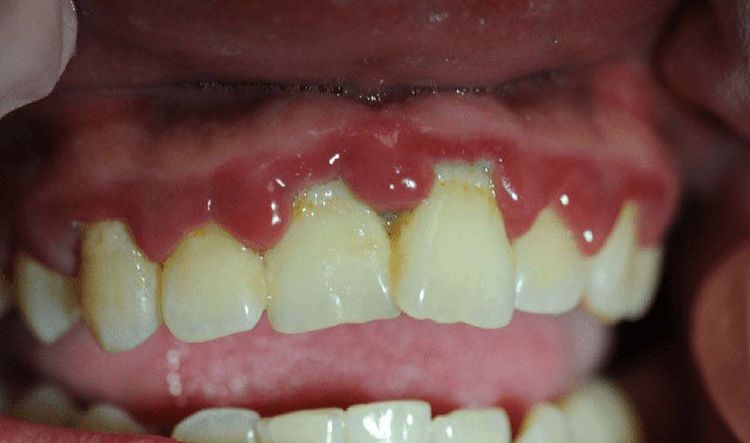
Bệnh nướu răng viêm nha chu gây ảnh hưởng đến hơi thở của người bệnh
2. What is obesity?
Obesity is an abnormal condition that develops over time. Obesity is different from being overweight. While overweight people may have gained weight due to fat, muscle, water weight or bone density, obesity can only occur when there is too much body fat compared to what is considered healthy. height and health, which in turn can increase the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke and arthritis.
3. The link between obesity and gum disease
Gum disease or periodontitis is an inflammatory condition and people who are obese have long been considered at high risk for such diseases. In summary, both obesity and gum disease seem to share a similar condition, chronic inflammation in the body.
A recent study found that people with obesity are almost twice as likely to develop periodontitis, while those with severe obesity are three times more likely than fit people. It is fat cells that increase chemical and hormone signals, which affect metabolism, leading to increased inflammation. Inflammation reduces blood flow to the gums and can accelerate disease progression.
In addition, obesity, along with smoking and poor oral hygiene, is one of the many factors that can influence gum disease and should be considered when looking for ways to prevent and address periodontitis. in these patient populations.
Besides, another basis that is thought to be able to prove a link between obesity and gum disease is that patients regularly consume a diet high in fat and calories. Commonly used foods are from processed sources, are high in sugar and lack nutrients to function, so they easily lead to obesity. It is the same foods that can cause oral health problems including gum disease and bad breath.
So, if people who are overweight think they may be showing symptoms of gum disease, it's important to make an appointment with their dentist as soon as possible. Accordingly, gum disease is a common disease in obese people as well as normal people, but it is completely preventable. Furthermore, symptoms can be relieved quickly with simple lifestyle changes as well as proper oral hygiene.

Người bệnh béo phì thường tiêu thụ thức ăn giàu chất béo có thể liên quan đến bệnh nướu răng
4. Measures to keep your ideal weight while also bringing good oral health
Here are some ways to keep your ideal weight and improve your oral health:
Control your portion sizes at each meal and consume fewer calories; Reduce sugar intake; Increase consumption of fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains in daily meals; Drink water instead of soft drinks, fruit juices; Avoid candy, cookies, cakes and chips; Limit your choice of junk food and fast food; Do not use food as a reward or a goal to strive for; Regularly participate in sports and physical activities every day; Quit smoking; Brush properly twice a day and floss every night after brushing; Visit your dentist once every 6 months. In summary, obesity can be viewed as a complex disease. The relationship of obesity with gum disease has been demonstrated. Accordingly, dental practitioners need to be aware of the growing number of obese people and the importance of obesity as a syndrome of multiple risk factors for overall oral and general health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: lanap.com, furumotodentistry.com, webmd.com, colgate.com, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov