This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Hong Hai - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.The spleen is an important organ in the body that produces antibodies to protect the human body. Diseases of the spleen if not detected early will cause many dangerous complications. Splenic ultrasound is the fastest way to detect abnormalities in the diagnosis of splenic disease.
1. What is a spleen?
The spleen, also known as the spleen, is brown in color and is located on the left side of the stomach, in the cell below the left diaphragm. The adult spleen is 7-14 cm long and weighs about 100-200 grams.The spleen has a pyramidal structure consisting of three faces, three banks, one base and one apex.
2. The role of the spleen
The spleen has an extremely important function for the human body. They have the function of destroying old blood cells to retain protein, iron and other substances needed to create new blood cells.
Lách giúp phá hủy các tế bào máu già cỗi và tái tạo tế bào máu mới
3. When does the doctor order an ultrasound of the spleen?
Splenic ultrasound is often more difficult to perform than other ultrasounds because the location of the spleen is quite obscured and covered by the ribs. The methods of splenic CT scan and splenic magnetic resonance imaging are more appreciated, but splenic ultrasound also has certain advantages such as ease of implementation, non-invasiveness, low cost and can be performed directly at the bedside. illness for emergencies.In the following cases, the doctor will appoint the patient to perform an ultrasound of the spleen:
The patient has signs of splenomegaly and needs to be re-checked Monitoring the progress of treatment for some diseases of the spleen Detecting the spleen loud with uniform, diffuse or regional echogenicity Cases of hematoma in the spleen or traumatic rupture of the spleen due to traffic accidents, work accidents or other accidents Cases of pain in the upper quadrant Left upper quadrant of abdomen of unknown etiology Signs suggestive of a bacterial or fungal splenic infection Spleen cancer is suspected.
Bệnh nhân có dấu hiệu bất thường về lách đều được chỉ định siêu âm
4. Steps to conduct an ultrasound of the spleen
The steps to conduct a spleen ultrasound take place quickly and simply, the patient needs to coordinate with the doctor to take the most favorable steps.The ultrasound scan of the spleen does not cause any pain and the patient does not need to prepare in advance at home. Before conducting an ultrasound, the doctor will perform a general examination of the patient with the aim of more closely assessing the patient's health.
The steps to conduct a spleen ultrasound are quick and simple, the patient needs to coordinate with the doctor to take the most favorable steps:
For the clearest ultrasound image, the patient should fast. 6 hours before the ultrasound, drink plenty of water and practice breathing during the ultrasound. The transducer performed during splenic ultrasound is 3.5 MHz for adults and 5 MHz for children. The patient exposed the area to be ultrasound and was given a gel before performing the ultrasound. The patient's position during the scan can be supine, right, left side or sitting depending on the doctor's instructions. The splenic ultrasound takes place with transverse, longitudinal and transverse slices performed continuously and approaches the spleen in anterior, superior and posterior directions... The patient breathes according to the doctor's instructions.
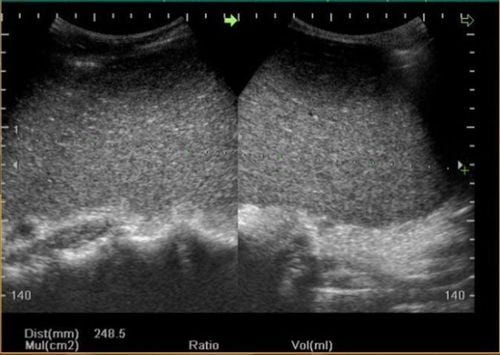
Kết quả hình ảnh siêu âm lách
5. Ultrasound image of spleen
5.1 Normal splenic ultrasound image A normal splenic ultrasound image will show the doctor a truncated semi-conical shape, concave on the inner surface and convex on the outside surface. The standard size of a healthy spleen is:In adults: length (L) less than or equal to 12 cm. In children: the length in children from 0-3 years old is less than 6cm, the way to calculate spleen length in children: L = 5.7+0.31x age (in years). The thickness of the spleen (T) is less than or equal to 7cm. The width of the spleen (W) is less than or equal to 5cm. The spleen index is calculated using the formula: L x T x W and it is usually less than 480. The weight of the spleen (SW) is calculated by the formula: spleen index x 0.55. Normally, spleen weight at birth is about 15g, adult spleen weight ranges from 100-265g. The border of the spleen is sharp and regular, the splenic medial surface may be concave with echogenic lines running into the splenic parenchyma.
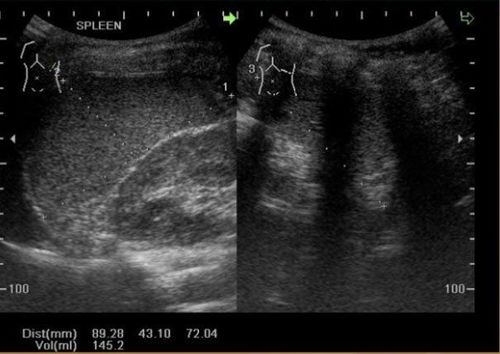
5.2 Abnormal image of the spleen Abnormal images of the spleen after ultrasound show that the patient is suffering from some disease. The survey of these abnormal images helps the doctor diagnose some of the diseases that the patient may have:
Hình ảnh siêu âm lách to bất thường
The accessory spleen is usually round or oval in shape with a mildly hyperechoic border, and the acoustic structure is completely similar to the splenic parenchyma structure.
The size of the accessory spleen is usually 1-3cm. The accessory spleen is often enlarged if splenectomy is performed.
5.2.2 Abnormal spleen position This case is also called ectopic spleen because the splenic stalk is long, so there is a risk of torsion. If the spleen is twisted, the spleen will lose its crescent shape and the spleen parenchyma will be irregular.
5.2.3 Enlarged spleen From the ultrasound image of the spleen, the doctor can investigate the condition of splenomegaly based on weight such as splenomegaly less than 500g, medium to larger than 500g and less than 2000g, splenomegaly. greater than 2000g.
Common in blood diseases such as Thalassemia, dengue fever, or in infectious diseases....
5.2.4 Localized, diffuse lesions in the spleen Ultrasound images help detect the Hyperechoic, hypoechoic, drum-sound or mixed-sound lesions are found in some diseases such as splenic cyst, splenic abscess, splenic hemangioma, splenic lymphoma, .....
Also evaluate spleen damage in trauma such as: parenchymal tear lines, intraparenchymal hematoma, subcapsular hematoma, etc., to help classify splenic injuries.
Master, Doctor Nguyen Hong Hai graduated with a Master's degree in Diagnostic Imaging at Hanoi Medical University with strengths in diagnosing breast and thyroid cancer. Currently, Dr. Hai is working at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Classification of 5 degrees of splenic rupture in blunt abdominal trauma Spleen rupture: How is it treated? Enlarged spleen: Causes, symptoms and treatment