This is an automatically translated article.
Non-gonococcal urethritis is an infection of the urethra that is usually caused by the bacterium Chlamydia Trachomatis. Non-gonococcal urethritis can be transmitted through unsafe sex, so it is necessary to take measures to prevent and detect and treat promptly to prevent dangerous complications.
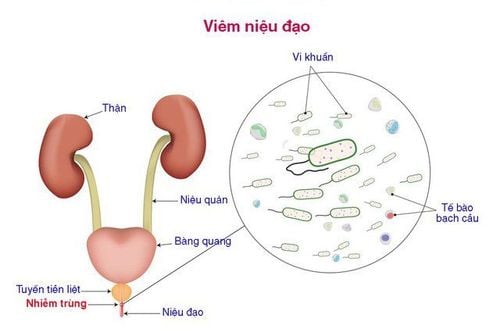
1. Urethritis not due to gonorrhea
Nongonococcal urethritis is an infection of the urethra not caused by gonorrhea but by some other bacteria. The most common is Chlamydia Trachomatis, which can be caused by bacteria Ureaplasma Urealyticum, Trichomonas Vaginalis, HSV or Mycoplasma Genitalium. The disease usually appears in the young age and usually on those who have had sexual intercourse. Chlamydia Trachomatis infection can be spread when an infected person has unprotected sex, without using a condom. In addition, people with weak immune systems or immunocompromised diseases such as HIV/AIDS are at high risk of non-gonococcal urethritis.
Some common symptoms in non-gonococcal urethritis are as follows:
Urinating painfully, urinating many times, each time the amount of urine is very little, when urinating, the patient feels itchy and burning, the urine is cloudy. . During sexual intercourse, the patient may experience genital pain. Fever may cause blood in the urine.

Cảm giác đau khi quan hệ
These symptoms usually appear about 1-5 weeks after infection with bacteria, but there are many cases of non-gonococcal urethritis without clinical symptoms, so it is difficult to diagnose. guess. If a pregnant woman has these symptoms and is diagnosed with Chlamydia Trachomatis, she should tell her obstetrician because the bacteria can be passed to the baby during labor and delivery. If the disease is not found early and treated appropriately, it will leave a number of complications affecting health such as reactivated arthritis, eye conjunctivitis, upstream infection causing upper genital tract inflammation...
2. Test for urethritis fluid
One of the high-value specimen tests in the diagnosis of non-gonococcal urethritis is the urethritis fluid test. Some of the testing techniques performed include:
Cell testing EIA enzyme immunoassay Using unamplified DNA probes DFA direct fluorescent antibody testing Bacterial culture in culture medium The method has the highest specificity, helping to identify bacteria so that a suitable treatment regimen can be given. Nucleic Acid NAAT amplification technique. Blood tests are done if urethritis is severe, with complications from sepsis occurring. Note that it is possible for a patient to have both syphilis and several types of bacteria at the same time, so testing for syphilis should also be done to treat the disease according to the most accurate cause.
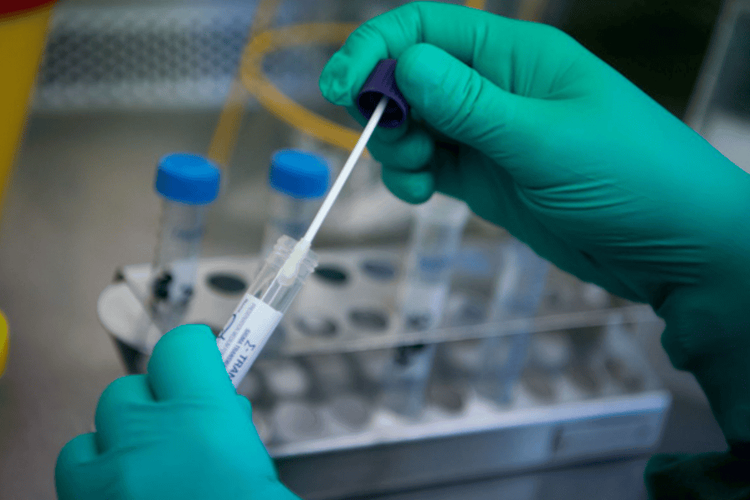
Xét nghiệm dịch viêm niệu đạo
3. Treatment of non-gonococcal urethritis
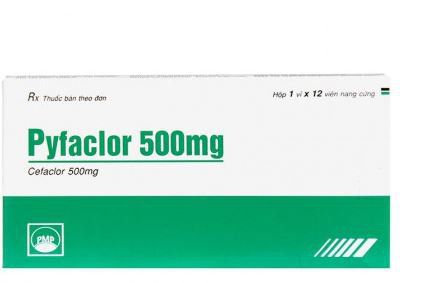
When treating non-gonococcal urethritis, both sex partners must participate in the treatment. The first treatment regimen may be Azithromycin 1g, taken as a single dose or Doxycycline 100mg orally twice a day for 7 days. In addition, some other drugs can be used including: Erythromycin base 500mg, taken 4 times a day for 7 days Or Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate 800mg, taken 4 times a day for 7 days Or Levofloxacin 500mg, taken 1 time a day for 7 days Or Ofloxacin 300mg, orally twice a day for 7 days. Patients can also use some pain relievers such as Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen in cases of need. To help the treatment process be effective as well as to be able to end the disease, the patient should strictly adhere to the following notes:
Sử dụng thuốc điều trị viêm niệu đạo không lậu
Strictly follow the treatment regimen given by the doctor. Do not have sex during treatment, if any, use a condom to prevent the infection from spreading. If the disease is detected, notify the person who has had sex at risk of contracting the disease to protect public health. Timely follow-up so that doctors can closely monitor the progress of the disease, how effective the treatment is as well as perform tests to check whether the patient has fully recovered or not, whether it is necessary to change to a new regimen. or not... Do not arbitrarily quit treatment without the appointment of a treating doctor. If there are any abnormal signs, it is necessary to immediately notify the treating doctor for timely treatment. The community also joins hands in educating and propagating about safe sex, avoiding the spread of infectious diseases.

Quan hệ tình dục an toàn giúp phòng bệnh
Non-gonococcal urethritis is not a life-threatening disease, but if not detected early, it can spread the infection to nearby organs as well as cause some dangerous complications. other. When there are suspicious signs, the patient should immediately go to a medical facility to examine and test the urethral fluid along with some other necessary tests to diagnose non-gonococcal urethritis promptly. take appropriate treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
Recommended video:
Health check recurring at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
READ MORE
Urethral discharge syndrome in men What is the function of the urethra? Signs and treatment of urinary tract infections in women