This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalStress comes in different forms, there is mental or psychological stress and there is also physical stress. Certain types of stress may be more likely to affect different types of ulcers.
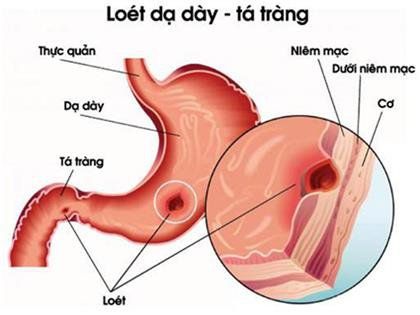
The relationship between stress and ulcers
The type of ulcer commonly known as a stress ulcer is believed to be caused by physical stress. Physical stress can occur in some of the following forms:
Serious long-term illness Surgical procedures Injuries to the brain or body Serious burns Central nervous system damage With other sores, such as such as mouth ulcers and stomach ulcers may not be directly caused by stress. However, there is some evidence that emotional stress can make them worse.
Mouth ulcers can be particularly stressful and anxiety-provoking due to the pain and its effect on speaking, chewing, eating and drinking. This social stress adds to any emotional stress you may be experiencing. Stomach ulcers can be stressful due to the symptoms they can cause. They can also make you anxious and can make your condition more uncomfortable. Stress is believed to be able to limit the function of the immune system, and managing stress will also help your overall. You should talk to your doctor about some of the treatment options for your stress.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:
Antonangeli F, et al. (2017). How mucosal epithelia deal with stress: Role of NKG2D/NKG2D ligands during inflammation. Carabotti M, et al. (2015). The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. (2005). Levenstein S, et al. (2015). Psychological stress increased risk for peptic ulcer, regardless of Helicobacter pylori infection or use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Mayo Clinic Staff. (2016). Peptic ulcer. Mohebbi L, et al. (2009). Stress ulcer prophylaxis in the intensive care unit.