This is an automatically translated article.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune-related neuromuscular disease. Current treatment methods are still only treating symptoms, inhibiting the progression of the disease, but cannot cure the root of the disease.
1. What is myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that leads to conduction disturbances at the neuromuscular junctions, reducing the function of the muscle system. Normally, impulses from the nervous system to the muscles that ensure muscle function are due to neurotransmitters. However, in people with myasthenia gravis, the body produces an autoantibody against acetylcholine, which reduces the amount of this substance and reduces the response of acetylcholine receptors. As a result, there is a decrease or loss of nerve impulse conduction, so there is muscle weakness and paralysis.
Another cause of myasthenia gravis is the presence of autoantibodies against muscle-specific enzymes. Acetylcholine will not be able to differentiate and form in the absence of the enzyme kinase, which results in a reduced number of acetylcholine receptors. At the same time, because the thymus gland develops too strongly, it produces antibodies against acetylcholine and the body is hypersensitive to thymic tumors.
Myasthenia gravis can occur at any age, but treatment is often delayed, leading to respiratory failure and death. Signs of myasthenia gravis include:
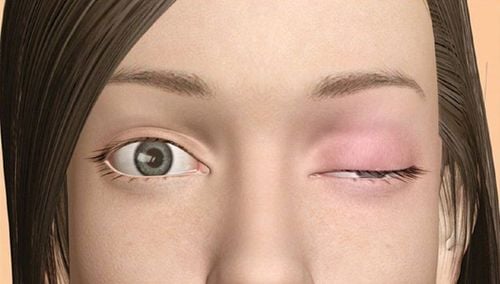
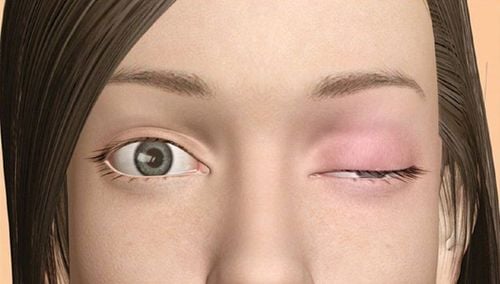
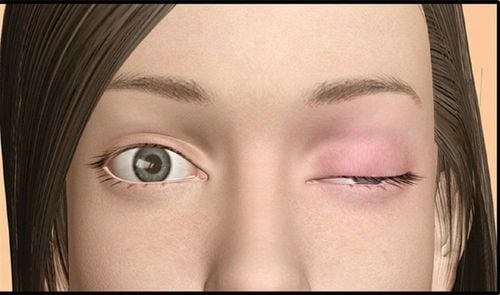
Initial symptoms are transient, myasthenia gravis may arise after a period of stress or infection, pregnancy, anesthesia. The characteristic sign of the disease is muscle weakness, which at first may be weak in one muscle or all of the muscles in the body. The disease usually affects the eye muscles, facial muscles, chewing muscles, and neck muscles. When it comes to the final stage, all muscles in the body will be damaged, leading to drooping of one eyelid with the other eye opening wide or drooping both eyes. Some patients have diplopia. When the muscles are damaged, the patient feels that chewing is very difficult, the throat feels difficult to swallow, and has to swallow many times to finish a piece. When talking, the voice becomes more difficult to hear, the neck can droop. In the later stages, all muscles are weak and weakened (respiratory muscles such as diaphragm, intercostal muscles, abdominal wall muscles). Weakness in muscle condition.

Bệnh nhược cơ có thể xảy ra ở bất kỳ lứa tuổi nào
2. Dangerous complications of myasthenia gravis
Specific manifestation of myasthenia gravis is that the patient often has progressive drooping of the eyelids, paralysis of the motor muscles of the eyeball, causing symptoms of double vision, strabismus; paralysis of the chewing muscles, pharyngeal muscles, and hand motor muscles, causing the patient to become tired of chewing quickly, swallowing hard, speaking difficult, working quickly tired, walking poorly, and the degree increases when the intensity of exercise is heavier and continuity. However, the most ominous and dangerous symptom of myasthenia gravis is respiratory failure due to weakness or paralysis of the respiratory muscles (diaphragm, intercostal muscles, sternocleidomastoid, trapezius). In many cases, complete paralysis of the respiratory muscles will cause the patient to die quickly if not treated promptly. Poor swallowing and coughing are also causes of aspiration, and pneumonia contributes to worsening respiratory failure. In addition, myasthenia gravis also makes patients always tired, eat poorly, reduce or lose the ability to concentrate, difficult to integrate into society.
3. How to treat myasthenia gravis?
In the treatment of myasthenia gravis, doctors often combine medical and surgical methods, depending on the severity of the patient's condition.
The treatment is only treating the symptoms, relieving the symptoms, inhibiting the progression of the disease, but not curing the root of the disease. The following are the main methods commonly used today to treat myasthenia gravis:
Initial treatment: Acetylcholinesterase is a class of inhibitors used in the initial treatment of myasthenia gravis. The drug inhibits the destruction of acetylcholinesterase receptors by antibodies. Thus, there is no reduction in the number of neuromuscular postsynaptic receptors. However, the drug is only effective in the initial treatment of patients with mild myasthenia gravis or newly diagnosed myasthenia gravis. Immunosuppression: This is a method of using immunosuppressive drugs to suppress autoimmune activity at the neuromuscular synaptic cleft. Corticosteroids or non-steroidal drugs are the drugs used in this case. However, the side effects of corticosteroids if used for a long time are very dangerous. Thymus surgery: As mentioned above, up to 85% of patients with myasthenia gravis have thymic abnormalities, so surgical removal of the thymus is also a cure for myasthenia gravis. The results of the treatment of myasthenia gravis by this method are relatively positive, but the postoperative treatment is very difficult, so the surgery needs to be performed in the centers with good experience and resuscitation. After surgery, patients with myasthenia gravis continued to be treated with medium-dose prednisolone. Plasmapheresis: This method of treatment is intended to remove anti-receptor antibodies as well as complement components in the plasma of patients with myasthenia gravis, severe symptoms of myasthenia gravis will be relieved. In a sense, this can also be considered an immunosuppressive method. Other short-term treatment methods: In addition to the above methods, doctors can also use short-term treatment methods such as immunoglobulin infusion or plasma exchange (for patients with worsening myasthenia gravis, severe myasthenia gravis. and patients with myasthenia gravis before thymic surgery) when myasthenic symptoms are not well controlled. These two short-term treatments give very good results but no long-term effects.

Biểu hiện cụ thể của nhược cơ là bệnh nhân thường bị sụp hai mi mắt tăng dần, liệt các cơ vận động nhãn cầu
4. Prevention of myasthenia gravis
With myasthenia gravis, special attention must be paid to factors that may contribute to worsening myasthenia gravis. Firstly, you must ensure adequate nutrition, eat enough nutrients and have enough potassium from bananas and papayas because potassium deficiency also causes severe muscle paralysis. Second, to prevent infections (oral, pharynx...) while using immunosuppressive drugs. Patients should also not arbitrarily use drugs that can cause muscle weakness such as sedatives, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants...
Absolutely do not quit smoking while being monitored. Treatment because the fact that most cases of severe myasthenia gravis rapidly progressing to the emergency room is because the patient feels stable, so he stops taking the drug or switches to unknown Eastern medicine. source. Patients should also avoid mental stress, too hot, too cold temperatures as well as should not exercise, work with too high intensity and continuously. When symptoms of myasthenia gravis progress, should immediately go to the nearest specialized medical facility for monitoring and treatment advice.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment of myasthenia gravis at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE
Mechanism of formation of myasthenia gravis (myasthenia gravis) How dangerous is myasthenia gravis in children? Dangerous complications of myasthenia gravis