This is an automatically translated article.
Myasthenia gravis is one of the more common autoimmune neuromuscular diseases in women. When suffering from this disease, the patient will have the problem of reducing the number of acetylcholine receptors in the motor plates due to the attack of autoimmune antibodies on these receptors. Myasthenia gravis if not treated promptly, the risk of dangerous complications will be very high.1. What is myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis, also known as Myasthenia gravis, is an autoimmune disease that leads to conduction disturbances at the neuromuscular junctions in patients and reduces the function of the muscle system. It is characterized by fatigue and skeletal muscle weakness, which increases with exertion and decreases with rest.When suffering from myasthenia gravis, the patient has a phenomenon that the body produces an anti-Achr antibody, thereby reducing the amount of this substance, and at the same time reducing the response of Achr receptors at the postsynaptic membrane, causing The body is reduced or lost the transmission of nerve impulses from nerve endings to the neuromuscular postsynaptic membrane and leads to muscle weakness and paralysis.
According to statistics, the prevalence of myasthenia gravis in the population is 0.5-5/100,000. This disease can occur at any age, but is most common in women under the age of 40.
Depending on the condition and severity, myasthenia gravis is classified as follows:
Group I: Myasthenia gravis localized in the eyes; Group IIA: Mild systemic myasthenia gravis and no respiratory or swallowing disorders; Group IIB: Moderate generalized myasthenia gravis, beginning with swallowing and speaking disorders but no respiratory disorders; Group III: Severe, acute generalized myasthenia gravis, with disturbances in speech, swallowing and breathing; Group IV: Myasthenia gravis is as severe as in Group III and persists for many years.
2. Signs of myasthenia gravis
Bị nhược cơ chân, cơ tay, không thể làm việc, thậm chí không đi lại được là dấu hiệu của bênh nhược cơ
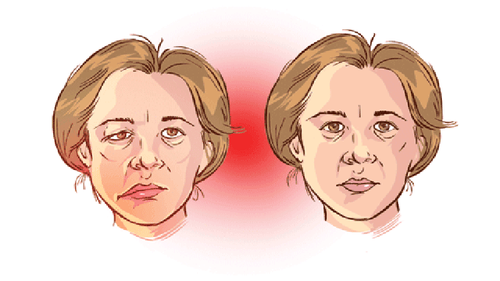
Feeling of muscle weakness and feeling of change during the day, at rest and when exercising; Eyelid drooping or can be combined with double vision, strabismus. Weakness in the muscles of the legs and arms, unable to work or even walk; Having myasthenia gravis of the larynx, the patient suddenly becomes livid, has difficulty speaking, and has difficulty swallowing; Having respiratory muscle weakness, feeling short of breath, if severe, it will be respiratory failure and life-threatening.
3. Who is susceptible to myasthenia gravis?
Anyone is at risk of developing myasthenia gravis, but the most susceptible are women under 40 and men over 50. In addition, some factors can increase the risk of this pathology including:Patients being treated for cardiovascular disease and hypertension; Genetic factors, having a parent with myasthenia gravis; Patients with thymic tumors; Suffer from infectious diseases.

Bệnh nhân tim mạch có nguy cơ mắc nhược cơ cao hơn bình thường
4. Diagnosis of myasthenia gravis
To diagnose myasthenia gravis accurately, doctors will rely on clinical symptoms and tests on the patient's body. Along with the neurological assessment and general examination, the doctor will ask some questions for the patient such as:Does muscle weakness worsen with heavy activity or in the afternoon? Does the patient have a condition where the eyes open wide when they wake up, then gradually droop, accompanied by squinting? Do you have difficulty swallowing, choking, or speaking? If the patient is an infant, is there any fussiness or poor feeding in the first few hours after birth? Does anyone in your family have myasthenia gravis? After asking the patient's medical history, the doctor made a diagnosis of myasthenia gravis by clinical examination:
Find signs of drooping eyelids on one or both sides, ophthalmoplegia; Weakness in limbs; Examination of tendon reflexes; Look for signs of respiratory distress in the patient. In addition, some tests to help diagnose myasthenia gravis include:
Prostigmin test: The patient will be injected with an anti-cholinesterase drug to slow the destruction of Achr molecules and thus make the muscles work. Okay. The test will be positive when the symptoms of myasthenia gravis are markedly reduced; Electromechanical recording; Plain X-ray and mediastinal air pump; CT scan and MRI; Mediastinoscopy and biopsy to determine the nature of the thymic lesion; Test for anti-Achr autoantibodies: A very valuable test in the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis as well as monitoring and prognosis of the disease. Once you have myasthenia gravis, you can live with the disease for many years. Therefore, to ensure health, the patient should not be too dependent and dependent on the doctor's treatment plan, but need to have a suitable labor, eating and living regimen, proactively scheduled visits. and when abnormality occurs.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently has modern methods of diagnosing myasthenia gravis, performed by a team of highly qualified and experienced medical doctors, with a complete and advanced medical equipment system that will for accurate diagnosis of myasthenia gravis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.