This is an automatically translated article.
To limit the spread of the disease, patients with mumps should be isolated for a minimum of 7 days and a maximum of 14 days from the time of diagnosis. At the same time, people who come into contact with sick people must make a list and follow up to promptly detect if infected; Limit gatherings in crowded places in areas where people are sick with a follow-up time of about 2 weeks or 3 weeks.
1. Clinical forms of mumps
Based on the locality of the virus causing the disease, the clinical forms of mumps include inflammation of the parotid salivary glands commonly called mumps, submandibular, sublingual; inflammation of the testicles, ovaries; pancreatitis, meningitis, encephalitis-meningitis... Each type of inflammation has typical and hidden forms.
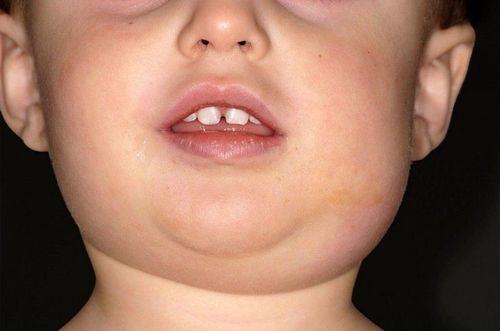
Typical parotid gland inflammation:
Incubation period: 15 - 21 days, average 18 days. The disease occurs insidious, the clinical signs are not clear. Period of onset: Acute with symptoms of high fever 38 - 39 degrees Celsius or more accompanied by headache, fatigue, joint pain, poor sleep. Full-blown period: Causes parotid salivary gland inflammation and swelling, patients with mumps experience a natural sharp pain in the corner of the jaw, see the angle of the jaw bulge, the skin is tight and smooth but not hot, not red; Patients often have inflammation on both sides, separated by 1-3 days, only 1/3 of cases have inflammation on one side. Accompanied by inflammation of the oral mucosa, edema, and redness around the salivary duct opening of the parotid gland. Remission period: With signs of fever disappearing after 4-5 days, symptoms of swelling gradually decrease, pain subsides, and then return to normal after 8-10 days from the date of illness. Inflammation of the gonads:
In male patients: Most common is orchitis (accounting for about 20 - 30% of mumps cases in adults) with symptoms of swollen testicles, fever again worse with high fever 39 - 40 degrees Celsius, chills all over, fatigue, sharp pain in the testicles spreading to the groin, thighs, lower cysts, especially when walking and can cause vomiting. In female patients: Ovarian inflammation, mastitis, and mucinous lymphadenitis are common (accounting for a low rate of about 2-5% of mumps cases).

Viêm tinh hoàn là biến chứng thường gặp trong bệnh quai bị
Acute pancreatitis:
Common in adults (accounting for a fairly high rate of about 10% of cases of mumps), only biochemical changes are shown by test results. Illness usually occurs in the second week between days 4 and 10 when the symptoms of salivary gland inflammation have subsided. The patient has fever again, acute epigastric pain, vomiting, abdominal bloating, diarrhea, loss of appetite. Meningitis - encephalitis:
In adults: The patient has a sudden increase in temperature accompanied by chills, and symptoms of headache, vomiting, stiff neck, positive Kernig's sign, lethargic sleep all the time. day. Tests showed cerebrospinal fluid changes of a viral meningitis; Meningococcal disease may appear about 3-10 days after mumps infection. In children: Rarely, common symptoms are sudden increase in temperature, chills, extreme fatigue, headache. , insomnia, delirium, nutritional and mental disorders, sometimes coma, convulsions; the course of the disease is usually benign and the disease usually resolves after a few weeks; However, in fact, it can also leave sequelae and serious complications. Inflammation of some other organs:
Some other pathological manifestations of the rare disease form when mumps is transmitted are: mastitis, prostatitis, acute and subacute thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid gland. myocarditis, pericarditis, pleural effusion, atypical pneumonia, nephritis, polyarthritis, acute myelitis, polyneuritis,...
2. How long should sick people be isolated to avoid spreading?

Để hạn chế lây lan bệnh, bệnh nhân bị quai bị cần được cách ly tối thiểu là 7 ngày và tối đa là 14 ngày kể từ khi phát hiện bệnh
For patients with mumps, in addition to timely treatment, how long should mumps be isolated to limit the transmission of the disease to people around and limit the possibility of the disease spreading into a large-scale epidemic? what the patient needs to know.
Accordingly, to limit the spread of the disease, patients with mumps should be isolated for a minimum of 7 days and a maximum of 14 days from the time of diagnosis. At the same time, people who come into contact with sick people must make a list and follow up to promptly detect if infected; Limit gatherings in crowded places in areas where people are sick with a follow-up time of about 2 weeks or 3 weeks.
Patients need to perform mumps isolation as follows:
For mild disease, patients can take care and isolate mumps at home. During the period of suspected illness, the patient is not allowed to go to crowded places such as schools, workplaces, ... within 7 - 9 days from the date of illness. Must minimize contact with other people and must wear a mask often. Personal items, nasopharyngeal waste and medical instruments related to the patient need to be disinfected with essential solutions. After the disease is over, disinfection of the air and tools associated with the patient must be carried out.
3. Prevention of mumps
Regularly wash your hands with soap, ensure the hygiene of the house, classroom, clean personal hygiene, especially the respiratory tract, regularly wear a mask to avoid infections that cause mumps.
Vaccinate against mumps. Starting at 12 months of age, you can get the mumps vaccine to keep your body immune to mumps for a long time or possibly for life. If starting vaccination at 9 months old, then inject 3 times, 1st time at 9 months old, 2nd time after 1st time 6 months, 3rd time when children are 4-12 years old. If starting injection from 12 months old, then inject 2 times, the first time at 12 months old and the second time from 4-12 years old.
For those who have been in contact with a patient with mumps but have not been vaccinated against the disease, it is necessary to receive the mumps vaccine immediately to be able to protect themselves from infection.
When someone is sick, they must stay at home to isolate the mumps (minimum 7 days and maximum 14 days after detecting the disease), to avoid spreading to others.
When someone is sick or suspected of being ill, they must immediately go to a medical facility for timely examination, advice and treatment, especially in cases of difficulty swallowing, breathing difficulties, orchitis.
To prevent mumps, young children over 12 months old, women who are about to become pregnant, men who have not been vaccinated against mumps... can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for treatment. counseling, scheduling and vaccination against mumps - measles - rubella, in order to prevent the disease in the safest and most effective way.
All biological products and vaccines at Vinmec are of clear origin; preserved on the cold chain according to strict standards of the Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization. Customers are examined and screened before injection, and their health is monitored after injection to ensure the highest safety and effectiveness of vaccination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.