This is an automatically translated article.
The mumps test is a test that identifies the genetic strain of the virus or determines the body's immunity to the mumps virus through specific antibodies. The mumps test is performed with the goal of diagnosing whether a person has ever been infected with mumps, diagnosing whether the patient is infected with the virus that causes the disease, determining the body's immunity to the mumps virus and following Monitor the progression of the disease to find the right treatment.
1. Overview of mumps disease
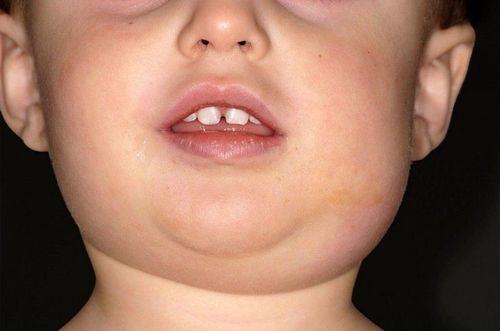
Mumps, also known as eczema, is a contagious viral infection that causes swelling of the salivary glands and causes pain. The time from when a person is infected with the virus and becomes sick lasts from 12 to 24 days.
Mumps is transmitted through the respiratory tract. The virus is present in saliva particles or nasopharyngeal secretions that are released into the air when the patient coughs, sneezes, spits, talks, etc., and the healthy person inhales it directly or through contaminated utensils. discharged by the patient will be at risk of disease. People with mumps are usually most contagious from two days before symptoms appear to six days after symptoms end.
This is quite common in children and usually presents with a high fever, around 39.4°C, followed by swelling of the salivary glands over the next few days. The glands will continue to swell and hurt for 1-3 days. At this point, the child's cheeks should be swollen. Your child will also feel pain when swallowing, speaking, chewing, or drinking acidic water.
Common mumps symptoms include:
Pain in the face or cheeks; Pain when chewing or swallowing; Fever; headache; Sore throat; swelling of the jaw or swelling of the parotid glands; Testicular pain, swelling of the scrotum; If mumps is not diagnosed early and treated properly, it can lead to complications. However, these complications are rare. Besides causing inflammation of the sweat glands, mumps can also cause inflammation in other parts of the body, such as the brain and reproductive organs. , eczema.

Đau mặt hoặc 2 bên má là triệu chứng điển hình của quai bị
2. Tests to diagnose mumps
2.1. Antibody test This test can be used to confirm immunity, diagnose mumps, or monitor a patient's condition. Mumps antibodies are specific proteins produced by the immune system to protect the body against attack by the virus that causes the disease. Two types of antibodies are produced:
IgM antibodies:
IgM antibodies will first appear in the blood after the body is exposed to the mumps virus or after vaccination. IgM antibodies rise within a few days to a maximum level and then begin to decline gradually over the following weeks. If IgM antibodies are present in an unvaccinated person, it is likely that the person has been infected with mumps. However, if both IgM and IgG antibodies are present, the person has mumps. IgG antibodies:
This antibody appears later but is very effective in protecting the body against infection. When IgG antibodies are present in a person who has been vaccinated and/or is currently free of the disease, the person is immune to the virus that causes mumps. If a person does not have both IgM and IgG antibodies, they are not considered immune to the mumps virus. Because the results can be because the person has not been exposed to the viruses, because the IgG is late, or because the person does not have a normal antibody response.
2.2. Virus culture or viral genetic material tests This test includes viral cultures or tests of viral genetic material and can be performed on a wide range of samples. However, these methods only identify the disease state and cannot confirm immunity.
Virus genetic material test (RT-PCR):
Helps detect and identify genetic strains of the virus. Tests that directly detect the virus can sometimes be done to determine the cause of serious complications related to mumps. People with weakened immune systems may not have typical immune antibody responses, so testing for viral genetic material will be done to confirm the diagnosis of measles or measles, especially when the Antibody test results are inconsistent with clinical study results.
Viral culture test:
A positive mumps or measles virus culture test or a positive viral genetic material test means the person is currently infected with the virus that causes the disease.
If the mumps virus culture or mumps virus genetic material test is negative, the person is not infected, the signs and symptoms are suspected to be due to another cause.
2.3. Blood tests In blood tests, white blood cells are reduced, neutrophils are decreased for viral causes and increased for bacterial causes; Urinalysis and blood amylase both increased.
Besides, some other testing methods such as: cerebrospinal fluid test, erythrocyte agglutination inhibitor (HI), complement fixation (CI), necrosis neutralization (NT), urine test, saliva test.
Trong xét nghiệm máu, bạch cầu giảm, bạch cầu đa nhân trung tính giảm đối với nguyên nhân do vi rút và tăng đối với nguyên nhân vi khuẩn
3. Treatment and prevention of mumps
Treatment of mumps:
For all patients, it is necessary to isolate the patient for 2 weeks from the time of diagnosis; Oral hygiene, eating foods that are easy to digest, relieve local pain by warming the swollen area, relieve body pain and reduce fever with paracetamol. Drink more water (avoid acidic drinks). Avoid wind and cold water as this will make the mumps swell and cause pain. In the case of orchitis, the patient wears underwear to lift the testicle to relieve pain, rest is the main thing, and limit movement. Use the right dose of corticosteroids, most importantly, start with a large dose (60mg of Prednisolone), then gradually decrease over 7-10 days. Surgery to decompress when the testicle is very compressed. Indications for medication and surgery are prescribed by a specialist doctor depending on each patient and each stage of the disease. Prevention of mumps :
The best way to prevent mumps today is to get vaccinated. The mumps vaccine works by stimulating children to produce antibodies to fight the disease. If starting vaccination at 9 months old, then inject 3 times, 1st time at 9 months old, 2nd time after 1st time 6 months, 3rd time when children are 4-12 years old. If starting injection from 12 months old, then inject 2 times, the first time at 12 months old and the second time from 4-12 years old. Urgent immunization is indicated for children from 12 months of age, adolescents and adults if they have been in contact with a mumps patient but have had mumps once and have not been vaccinated according to the mumps schedule. bag. In the absence of contraindications, the vaccine should be administered no later than 72 hours after contact with the patient. Passive prevention of mumps with immune globulin, used for people exposed to mumps virus who have not been vaccinated before. Isolate the patient at home for about 9 - 10 days until the disease is cured and is no longer contagious. To prevent mumps, young children over 12 months old, women who are about to become pregnant, and men who have not been vaccinated against mumps... can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for advice. consultation, scheduling and vaccination against mumps - measles - rubella, in order to prevent the disease in the safest and most effective way.
All biological products and vaccines at Vinmec are of clear origin; preserved on the cold chain according to strict standards of the Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization. Customers are examined and screened before injection, and their health is monitored after injection to ensure the highest safety and effectiveness of vaccination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.