This is an automatically translated article.
Minimal pleurectomy with Trocar aims to free the pleural cavity from the pressure of fluid and air to return the pleura to a normal state. This is an easy method to perform with high efficiency for patients.
1. Learn about minimal pleural effusion with Trocar
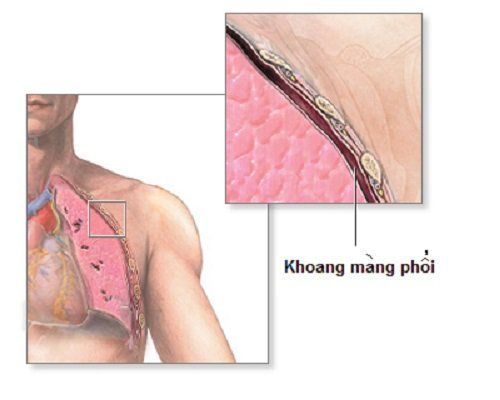
Normally the pleural space is a virtual space with negative pressure between the chest wall and the lungs. This cavity has a small amount of fluid to help with the lubrication process. When there is fluid, gas, blood, pus, ... in the pleural cavity, it changes pleural pressure, affecting respiratory function, causing clinical shortness of breath.
Depending on the difficulty of breathing, the degree of blood gas effusion, the X-ray image, there are different treatment attitudes. Mild degree can be treated medically, moderate severity consider pleural drainage in order to free the pleural space from the pressure of air or fluid to bring the pleura back to its original position.
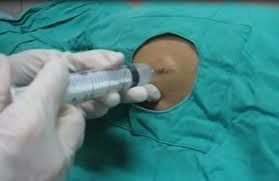
Minimal pleural dilatation through the foramen of Trocar is the procedure of placing a flexible and hollow tube into the pleural space through a trocar hole. Pleural effusion should at least ensure 4 principles: Closed, sterile, one-way and continuous with controlled pressure.
This is a minimally invasive method that can be performed in the operating room, the patient is under local anesthesia to reduce pain, the patient does not have to perform major surgery, the procedure is simple and easy to perform. does not cause pleural irritation, bringing great benefits to patients.

Mở màng phổi tối thiểu qua lỗ Trocar là thủ thuật đặt 1 ống dẻo và rỗng lòng vào khoang màng phổi thông qua 1 lỗ trocar
2. Indications and contraindications for minimally thoracentesis with Trocar
Traumatic pneumothorax, recurrent pneumothorax, tension pneumothorax, physician-induced pneumothorax Hemothorax pleural effusion due to malignancies, multiple degrees, disease patients with severe dyspnea. Empyema pleural effusion Chilli pleural effusion Causing pleural adhesions through drain tube Contraindications:
There are no absolute contraindications. Note in the following cases: Coagulation disorders, hemostasis, prothrombin ratio < 50%, platelets less than 50g/l Hemodynamic disorders Skin lesions at the puncture site

Chỉ định mở màng phổi tối thiểu bằng Trocar cho bệnh nhân tràn khí màng phổi do chấn thương, tràn khí màng phổi tái phát
3. Minimal pleural effusion with Trocar
Preparation:
Medical staff: 1 doctor, 1 nurse, prescribed medical clothing (blouse, hat, mask), hand hygiene, surgical gloves Patient needs to be explained purpose of pleural effusion and possible complications, commit to consent to thoracentesis. The patient has a full range of tests such as basic coagulation, complete blood count, liver and kidney function, electrolytes, chest X-ray, chest computed tomography. Equipment and tools: open kit pleural effusion according to regulations of anesthetics, syringes, drainage tubes, other tools... Steps to perform minimal trocar pleural technique:
Step 1: Prepare drainage puncture site: Confirm locate drainage, disinfect, stretch, numb at the pleural opening site (anesthetize the chest wall in layers, avoid injecting Lidocaine into the vessel)
Step 2: Make a small incision in the skin, insert the tube drain into the pleural space
Make skin incisions and scales along the intercostal space, following the superior border of the ribs to avoid the intercostal nerve bundle. Do not make an incision too wide, just equal to the diameter of the drain by 0.5cm. Using surgical forceps to separate the chest wall muscle layer by layer along the muscle fiber, avoid breaking the muscle, and separate the pleural wall. Using surgical forceps to puncture the pleural cavity Insert the drain tube into the pleural cavity through the opening, withdraw the iron barrel of the drain tube for specialized catheters. For pneumothorax, the direction of the drainage tube is anterior and upward, and for pleural effusion, the direction of the drainage tube is posterior and downward Step 3: Fix the drain, connect the drain with negative pressure aspirator
Fix the drain at 8-10cm (5cm from the last side hole of the drain) Connect the other end of the drain hose connected to the aspirator with suction pressure - 20cm H2O in case pneumothorax Follow up after pleurectomy
Patient's condition: M, temperature, blood pressure, breathing rate, SpO2 Monitor complications after pleurectomy, monitor drainage for the number of colors Change the leg bandages Daily drainage to avoid infection
4. Possible complications
Some possible complications include:
Bleeding Visceral perforation Injury to the intercostal nerve bundles Drainage obstruction Subcutaneous pneumothorax Acute pulmonary edema Incisional infection or empyema
Biến chứng có thể gặp sau mở màng phổi tối thiểu bằng trocar
5. When to withdraw drainage?
Pneumothorax: Drainage of the pleural cavity is cleared of air within 24 hours, chest X-ray is well expanded, clamp the tube for 24 hours, clamp the drain, chest X-ray does not recur, remove the drain Pneumothorax: Withdrawal: pleural drainage when the amount of fluid is less than 100ml/24 hours, the chest X-ray expands well, the patient relieves shortness of breath, Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and team Experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured that they will be examined and treated at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
Emergency pleurisy technique Minimal drainage of the pleural cavity Placing a pleural drain in a breathing patient