This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Pharmacist Nguyen Huy Khiem - Clinical Pharmacist, Faculty of Pharmacy - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Metronidazol is an antibiotic of the nitroimidazol group, the active ingredient in some common brand names such as Flagyl®, Rodogyl®,... Here are some information to keep in mind when using Metronidazol.
1. Spectrum of effects and indications
Metronidazol has a good bactericidal effect on anaerobic bacteria (growing in the absence of oxygen). Anaerobic bacteria are present in many locations in the human body, in which are concentrated in the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract,...
In addition, metronidazole also exhibits effects on some protozoal microorganisms. such as vaginal flagella (T. vaginalis), amoebic dysentery (E. histolytica), Giardia lamblia,...
Therefore, the antibiotic metronidazol is often indicated to treat infections with pathogens that can cause infections. can be from anaerobic bacteria or protozoa such as oral infections, abdominal infections, gynecological infections,...
Metronidazol also works on Helicobacter pylori bacteria - the causative agent of peptic ulcers; Therefore, it can be an option in a combination regimen to eradicate HP bacteria.
Because the drug can be used for a wide range of infections, the daily dose of metronidazole is also quite diverse, changing depending on the indication.
2. Brand name drug containing metronidazol and dosage form
Intravenous infusion: Moretel® 500 mg,... Oral: Flagyl® 250 mg, Rodogyl® (Spiramicin 750,000 UI + Metronidazol 125 mg), ... Vaginal route: Neo Tergynan® (Metronidazol + Neomycin + Nystatin), ... Dental gel: Metrogyl Denta® (Metronidazol + Chlorhexidin),...
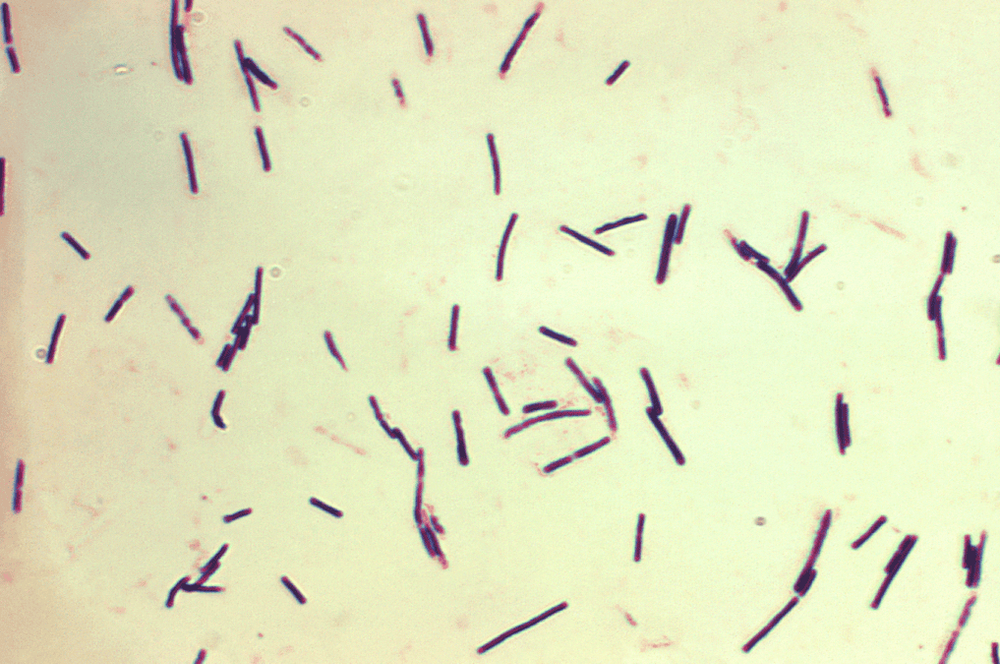
Metronidazol có tác dụng diệt khuẩn trên các vi khuẩn kỵ khí
3. Precautions when using metronidazol
Use caution when using the drug for pregnant women because metronidazole can cross the placental barrier. However, the drug can still be used if it is appropriately prescribed by the treating doctor. Lactation: Metronidazole concentrations in breast milk are equivalent to those in blood after systemic administration (oral, infusion). To limit the amount of metronidazole that a nursing child may be exposed to, breast-feeding should not be done while the mother is taking the drug. After the last dose of metronidazole has been administered 24 hours, breastfeeding can be resumed. Common side effects of metronidazol are mainly on the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, digestive disorders,... Metallic taste in the mouth is also a fairly common symptom. Patients can take the drug after eating to limit the undesirable effects mentioned above in the gastrointestinal tract. Do not consume alcoholic beverages (beer, wine) while taking metronidazole because of the risk of a serious disulfiram-type reaction, which can be fatal. Common symptoms of a disulfiram-type reaction include hot flushes, tachycardia, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, etc. The urine of patients taking metronidazole may be dark red brown. This is normal and will disappear when the medication is stopped. Customers can directly go to Vinmec health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.