This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, one of the most common and leading causes of death in the world is renal cell carcinoma. Like most cancers, kidney cancer cells can spread to other organs or locations, a condition known as metastatic renal cell carcinoma.1. What is metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Renal cell carcinoma, also known as kidney cancer, usually occurs when cancer cells form in the renal tubules. The renal tubules are small tubes that help filter waste from the blood to form urine.Conditions such as high blood pressure, smoking, hepatitis C, and obesity can all increase the risk of renal cell carcinoma. This type of cancer becomes metastatic renal cell carcinoma when it spreads beyond the kidney to other parts of the body, such as the bones and lymphatic system.
2. How does renal cell carcinoma spread?
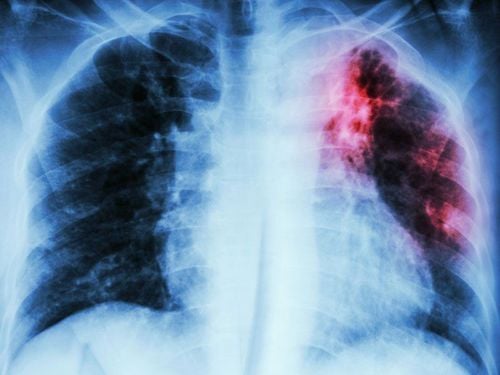
As the tumor grows, it will spread into the fat or major blood vessels around the kidney. It can also creep into the adrenal glands located just above the kidneys. From here, the tumor begins to spread further through the following routes:Blood: Cancer cells enter blood vessels and travel to many parts of the body through arteries and veins. Lymphatic system: This is a network that runs throughout the body, similar to your blood vessels, helping the body fight disease. However, cancer cells can enter this network and travel to other organs. Renal cell carcinoma often metastasizes to the lungs and bones, and sometimes to the brain, ovaries, liver, and testicles. Because renal cell carcinoma has no early symptoms, it can metastasize before the disease is discovered. Even if kidney cancer is found early, treatment does not eliminate all of the cancer cells, and it can also return to the kidney or elsewhere in the body.
3. What are the symptoms of metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
When renal cell carcinoma is in its early stages, patients may not experience obvious symptoms. If noticeable signs and symptoms are present, this usually indicates metastatic renal cell carcinoma.The following are common symptoms of metastatic renal cell carcinoma, including:
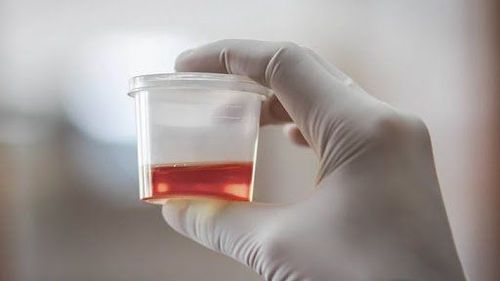
Hematuria Pain on one side of the lower back area Fatigue Weight loss Mass appearance in the abdomen Fever Swelling ankles night sweat

Tiểu máu là một trong các triệu chứng thường gặp của ung thư biểu mô tế bào thận di căn
4. Diagnostic methods for metastatic renal cell carcinoma
To diagnose metastatic renal cell carcinoma, your doctor will do a physical exam and review your medical history, then recommend some of the following cancer diagnosis methods:Blood and urine tests : Although a urine test cannot confirm kidney cancer, it can reveal your kidney health. In certain cases, the results of a urinalysis may show that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Another type of laboratory test useful for diagnosing metastatic renal cell carcinoma is the complete blood count. If the test results show abnormalities in the number of white blood cells and red blood cells, this could be a sign of cancer. Imaging tests: Doctors may use imaging tests to find the location and size of a tumor. In addition, screening also helps to check if the cancer has spread. MRI and CT scans are especially helpful in diagnosing kidney cancer. In addition, patients may also have chest X-rays and bone scans to determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
5. Main stages of renal cell carcinoma
To determine the appropriate treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma, we need to first consider the stage of kidney cancer. Stages of kidney cancer include:Stages 1 and 2: Cancer is only present in the kidney. Stage 3: Cancer has spread to a lymph node near the kidney, fatty tissue around the kidney, or the kidney's main blood vessel. Stage 4 (metastatic renal cell carcinoma): The cancer has spread to other organs or other tissues and lymph nodes.
6. How is metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated?
Treatment options for metastatic kidney cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.Kidney cancer surgery Kidney cancer surgery is usually indicated for stage 1 or 2. Stage 3 cancer can also be operated on, but it depends on how far the cancer has spread.
In some cases, metastatic renal cell carcinoma can be surgically removed to remove the cancerous mass, which includes drug treatment. For some patients, only a single surgery may be needed to remove tumors from the kidney and metastases from other sites in the body.
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy In addition to surgery, there are two other common treatments for metastatic renal cell carcinoma, including chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
In immunotherapy, the doctor will give the patient drugs to strengthen the immune system, helping to fight cancer. On the other hand, chemotherapy usually involves the use of injections or oral drugs to kill cancer cells. However, chemotherapy can have some side effects and often requires additional treatment with surgery.

Tế bào ung thư thận lan sang những vị trí khác gọi là ung thư biểu mô tế bào thận di căn
7. Measures to prevent metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma usually affects the elderly, however, the proportion of young people with this disease tends to increase significantly.To prevent renal cell carcinoma, young people need to adopt a healthy lifestyle as early as possible. Smoking is considered the leading risk factor for kidney cancer. If you don't smoke or give up smoking early, you will increase your chances of preventing metastatic renal cell carcinoma. In addition, you should also control your weight and blood pressure to maintain kidney health.
8. Survival rates of metastatic renal cell carcinoma
The 5-year survival rate of renal cell carcinoma varies widely at the stage at which it is diagnosed. According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for kidney cancer would include:Stage 1: 81% Stage 2: 74% Stage 3: 53% Stage 4 (cancer) metastatic renal cell carcinoma): 8% In summary, early-stage renal cell carcinoma often has no obvious symptoms. If noticeable signs and symptoms are present, this usually indicates metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Currently, early cancer screening is considered the perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce treatment costs and especially reduce the rate of cancer metastasis and death in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live well to help with gene testing, imaging, testing of biomarkers to detect tumors you early.
Choosing the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind at Vinmec, customers will get:
Only one gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women ( lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer,...). Early detection of early signs of cancer through imaging, endoscopy and ultrasound. The operation is simple, careful and accurate. A team of well-trained specialists, especially in oncology, are capable of handling cancer cases. With a system of facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience, it will help the examination and treatment process of patients at Vinmec become faster with High efficiency, save cost and time.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: webmd.com, msdmanuals.com, healthline.com