This is an automatically translated article.
Blood in the urine is a common symptom in many common diseases, due to many different causes. Blood in the urine is not an emergency, but it can be a sign of a serious medical condition. Therefore, when having symptoms of blood in urine, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility to find out the cause and take timely intervention measures.
1. Blood in the urine
Blood in the urine is an obvious symptom of a specific medical condition. Normally the urine is light yellow in color and there are no large molecules in the blood. Due to certain abnormalities, possibly from the kidneys or urinary tract, blood cells pass through the glomerulus into the urine.
There are two types of blood in the urine:
Gross hematuria: When blood in the urine is visible to the naked eye. People may detect blood clots or notice red or brown urine. Microscopic hematuria: The presence of molecules in the blood, and only visible under the microscope through laboratory tests.

Màu sắc nước tiểu phản ánh một số bệnh lý
2. Causes of blood in the urine
There are many causes of blood in the urine symptoms, mainly due to a specific medical condition:
2.1 Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection affecting the kidneys and causing back pain in the hips. A common cause of urinary tract infections is bacteria entering the urethra, resulting in blood in the urine.
In addition, there are symptoms of a urinary tract infection, including:
Feeling the need to urinate right after urinating. Pain or burning in the urethra Cloudy, smelly urine Very few cases of UTIs can affect the kidneys. However, if this is the case, the infection tends to be more serious and can cause symptoms such as:
Pain in the back, sides and pelvis. Nausea, vomiting Fever and chills

Nhiễm trùng đường tiết niệu gây đau lưng 2 bên
2.2 Kidney and bladder stones
Normally, small kidney stones can pass through the urine stream and leave no symptoms. However, in the case of larger stones, they can become lodged in the kidneys, bladder or elsewhere in the urinary tract causing symptoms such as:
Blood in the urine Pain in the lower back and sides Nausea or vomiting Occasional fever and chills Cloudy or foul-smelling urine 2.3 Post-exercise hematuria
Post-exercise hematuria is a condition in which blood is present in the urine, occurring after exercise or activity exertion with great intensity. People who do not properly rehydrate during exercise may also have an increased risk of hematuria. However, experts say the condition usually clears up on its own within three days. If blood in the urine persists for more than 2 weeks, you should go to a medical facility for examination.

Thể dục và hoạt động gắng sức
2.4 Enlargement of the Prostate
The prostate is a small gland about 10-20 grams in size, and only found in men. The prostate gland is located close to the bladder muscle surrounding the urethra, where it connects to the bladder neck, whose main function is to produce fluid that helps the male reproductive process. In addition, the prostate keeps toxins, bacteria, and chemicals out of the urinary tract.
An enlarged prostate can put pressure on the urethra, making it more difficult to urinate. At this point, the bladder can compensate by contracting more to release urine. From there, it can lead to damage and bleeding. Prostate enlargement affects about 50% of adult men between the ages of 51-60 and about 90% of those over the age of 80.
Symptoms of prostate enlargement include:
Urinating many times a day, especially at night, causing insomnia, sudden urge to urinate, not being able to hold urine for more than a few minutes. Difficulty urinating, interrupting, having to push to urinate, weak urine stream, after urinating, there are still a few drops of urine leaking out to wet pants. After urinating, it still feels uncomfortable to urinate. The interval between two consecutive urinations is shortened. Urinary retention: Sudden inability to urinate despite pushing hard, causing discomfort in the lower abdomen, requiring immediate hospitalization. Blood in the urine
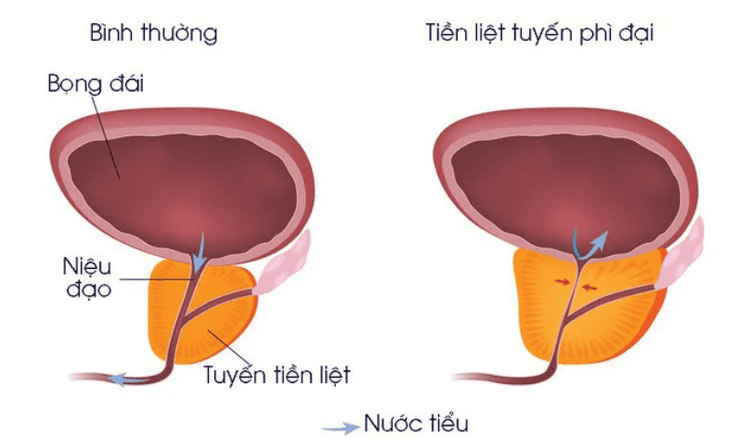
Phì đại tiền liệt tuyến
2.5 Catheterization
Some patients may experience difficulty urinating or abdominal pain due to surgery, trauma, or disease. Therefore, the patient has a urinary catheter placed in the bladder to help circulate urine out. Normally, the tube that carries urine will stay in the bladder for a few days or weeks.
All types of urinary catheters can allow bacteria to enter the urethra, if not sterile will lead to urinary tract infections related to urinary catheters.
2.6 Kidney damage
Platelets are small structures in the kidneys that filter and clean the blood. In people with glomerulonephritis, the damaged kidney is unable to remove waste from the body. If left untreated, glomerulonephritis can lead to kidney failure.
Acute glomerulonephritis comes on suddenly and can cause the following symptoms:
Swelling of the face in the morning Blood in the urine Decreased urine output Difficulty breathing Cough High blood pressure

Tổn thương thận gây tăng huyết áp
Chronic glomerulonephritis progresses slowly. In some cases, there are often no typical symptoms in the early years of the disease. Signs and symptoms in later stages include:
Blood in the urine Protein in the urine Swelling of the face or ankles Frequent urination at night Foaming urine 2.7 Medicines
Some of the following medicines can cause blood in urine :
Anticoagulants: These drugs help prevent blood clots, but some can cause blood in the urine side effects such as warfarin and aspirin. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs: Long-term abuse can cause kidney failure and cause blood to appear in the urine. However, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are unlikely to directly cause blood in the urine. Cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide: These are chemotherapy drugs that can cause hemorrhagic cystitis, which manifests as the sudden appearance of blood in the urine, urinary tract irritation, and bladder pain. Senna: Long-term use of this laxative may lead to hematuria.

Một số loại thuốc có thể gây ảnh hưởng đến chức năng của thận
If it is suspected that blood in the urine is caused by drug use, the patient should consult a doctor about changing to a different drug or reducing the side effects of the drug.
2.8 Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer if diagnosed and treated early can often be curable. However, in the early stages of the disease, there are usually very few symptoms. Symptoms of prostate cancer are often similar to those of prostate cancer.
In addition to blood in the urine, other symptoms of prostate cancer include:
Dull pain in the pelvis Pain in the lower back, hips or upper thighs. Pain during ejaculation. Blood in semen Loss of appetite Unexplained weight loss. Bone pain 2.9 Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is characterized by unexplained weight loss, along with a change in urine color and urination habits. In the early stages of bladder cancer, there are often no typical symptoms. Blood in the urine is often the earliest sign.
A patient may notice a change in urine color. For others, streaks of blood in the urine may only be detected when a urinalysis is performed. In addition, bladder cancer has symptoms such as:
Frequent urination, especially at night Difficulty urinating, weak urine stream Pain or burning when urinating
Tình trạng ung thư bàng quang
3. Treatment of blood in the urine
The treatment for blood in the urine depends on the cause. Treatments for blood in the urine may include:
Antibiotic treatment for an infection Surgery to remove kidney stones Hormone inhibitors, muscle relaxants, and surgery to treat prostate problems. Medicines to treat or dialysis for glomerulonephritis or kidney failure. Surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy to prevent the growth of benign tumors and treat cancer In short, blood in the urine is a symptom of a medical condition. An abnormality of the kidneys or urinary tract causes blood cells to pass into the urine. While blood in the urine is not an emergency symptom, it is a sign of a serious medical condition. Therefore, when you see blood in the urine, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility to do tests to find out the cause, and take appropriate treatment.

Người bệnh nên đến cơ sở y tế uy tín để được điều trị kịp thời
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register for an online examination HERE
MORE
What is proteinuria, yes What is the significance in the diagnosis of urinary kidney disease? Importance of tests to evaluate kidney function Meaning of creatinine test index in the diagnosis of kidney failure