Prolonged menstrual bleeding refers to menstruation lasting longer than a week, sometimes extending to an entire month. This condition has various causes, ranging from benign factors like hormonal imbalances to more severe ones such as cancer. Therefore, early medical consultation is necessary when prolonged bleeding occurs.
1. What is menorrhagia?
Generally, a woman's menstrual period lasts from three to seven days. If bleeding extends beyond seven days, it is considered prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia). A doctor may diagnose prolonged bleeding if your period lasts longer than a week. You might also be diagnosed with heavy menstrual bleeding if the blood loss is unusually excessive. Prolonged bleeding could signal underlying health conditions such as:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Uterine abnormalities
- Cancer
It is crucial to see a doctor if you experience prolonged bleeding. The doctor will examine you to determine the cause and rule out any serious abnormalities.
Menorrhagia can cause discomfort during your period, disrupt daily routines, and negatively impact your quality of life and health.
2. Causes of prolonged menstrual bleeding
Prolonged bleeding may result from a variety of benign or malignant causes.
2.1. Hormonal changes and ovulation
Hormonal fluctuations or ovulation processes can cause prolonged menstrual bleeding. Symptoms of hormonal changes may occur during your first period in adolescence or during perimenopause. Hormonal imbalances may also result from medical conditions such as thyroid disorders or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
If your hormonal levels are high or if ovulation does not occur during your menstrual cycle, the uterine lining may not shed and instead becomes very thick. This thickened lining can eventually shed, causing longer-than-normal bleeding.
2.2. Medication use
Prolonged menstrual bleeding may result from medications, such as:
- Contraceptive methods like intrauterine devices, extended-use birth control pills, or contraceptive implants
- Aspirin and other blood-thinning medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
2.3. Prolonged menstrual bleeding due to pregnancy
Although technically not menstruation, prolonged bleeding can indicate pregnancy complications such as ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.
You may also experience prolonged vaginal bleeding during pregnancy if conditions like placenta previa occur. If you test positive for pregnancy and experience vaginal bleeding, visit a medical facility equipped for proper diagnosis.
2.4. Uterine fibroids or polyps
Uterine fibroids and polyps can cause prolonged and sometimes heavy bleeding. Fibroids develop when fibrous tissue forms in the uterine wall. Uterine polyps result from irregular tissue growth in the uterus, leading to small tumor development.
2.5. Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus or within its walls, typically on other pelvic organs or in the abdominal cavity. Endometrial growths can swell and bleed, much like the uterine lining, causing internal bleeding and pelvic pain during menstruation. This condition can lead to prolonged menstrual bleeding.
2.6. Thyroid condition
Prolonged menstrual bleeding may occur if your thyroid is underactive, a condition known as hypothyroidism.
2.7. Coagulation disorders
Clotting disorders refer to conditions where blood does not clot as it should due to a deficiency in clotting factors. Normally, platelets bind together with clotting factors to form blood clots that stop bleeding. If you have a blood disorder, it may cause prolonged menstruation.
2.8. Obesity
Excess weight can contribute to prolonged bleeding. This is because fat tissues can lead to increased estrogen production in the body. Excess estrogen may cause hormonal imbalances, altering your menstrual cycle.
2.9. Pelvic inflammatory disease
PID occurs when bacteria infect reproductive organs such as the uterus and adnexa. Besides menstrual cycle changes, PID can also result in abnormal vaginal discharge.
2.10. Cancer
Prolonged menstrual bleeding may indicate cancer of the uterus or cervix. For some women, this could be one of the earliest symptoms of these types of cancer.
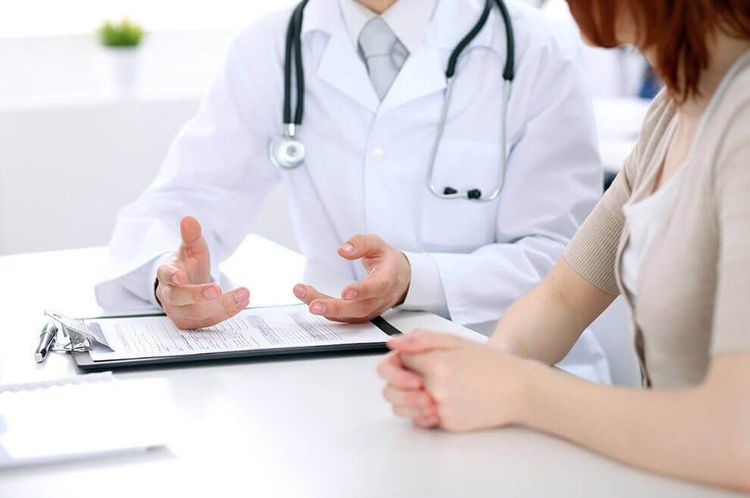
3. When should you see a doctor?
If you experience prolonged menstrual bleeding, it is essential to consult a doctor to discuss the issue. Since there are many possible causes, the doctor may ask you several questions, including:
- When your menstrual cycle began
- How many pads or tampons you used in the past day
- Your sexual activity
- Other symptoms you are experiencing
- Your past and family medical history
The doctor may recommend a gynecological health examination, including vaginal and pelvic exams, as well as additional tests to accurately diagnose your condition:
- Blood tests to check hormone levels and signs of iron deficiency
- Pap smear/LiquiPrep/ThinPrep
- Biopsy
- Abdominal or transvaginal ultrasound
- Hysteroscopy

4. Treatment for prolonged menstrual bleeding
Treatment options for prolonged bleeding can vary. Your doctor will focus on addressing the underlying cause. They may also suggest treatments to reduce current blood flow, regulate your menstrual cycle, or alleviate discomfort.
Hormonal birth control can help regulate your menstrual cycle and shorten it in the future.
Your doctor may also recommend pain relief medications, such as over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Advil or Motrin.
In some cases, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure to reduce prolonged bleeding:
Dilation and curettage (D&C): This procedure can thin the uterine lining and decrease blood flow during menstruation.
If you no longer plan to have children, options such as endometrial ablation or hysterectomy may be recommended. These procedures can reduce or eliminate prolonged bleeding but also prevent future pregnancies.
5. Complications can occur if menorrhagia lasts longer than 1 month.
- Delaying diagnosis may require more invasive procedures or intensive treatments for the underlying cause.
- Additionally, if prolonged menstrual cycles result in excessive blood loss, you may be at risk of anemia, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Prolonged bleeding can also cause pain and negatively impact your health and quality of life.
There are many reasons why your menstrual period may last longer than usual. Prolonged bleeding can disrupt your normal life and may indicate an underlying health condition requiring treatment.
See a doctor to identify the cause of prolonged bleeding and begin treatment. Delaying treatment could result in complications and necessitate more invasive procedures in the future.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.