This is an automatically translated article.
Each antibiotic will have an effect on a site for the composition or a link in the biological reactions of the bacterial cell. Therefore, it can be said that the antibiotic is bacteriostatic because it can stop the growth and growth of bacterial cells. However, in some cases, it is necessary to combine antibiotics to improve the effectiveness of treatment.
1. Mechanism of action of antibiotics
Antibiotics, after entering the bacterial cell, will be delivered to the target to affect the four basic structural components of the cell to inhibit the growth as well as kill bacteria with the following mechanism:
Antibiotics inhibit bacterial cell wall biosynthesis: Specifically, antibiotics of the vancomycin, beta-lactam and fosfomycin groups will prevent the peptidoglycan layer from synthesizing, from which the wall will not be formed. Therefore, the daughter cells that multiply without walls will not be able to reproduce and are killed or lysed, so the mechanism of action of this group of antibiotics is to kill bacteria with growing cells. Antibiotics cause cytoplasmic membrane dysfunction: The cytoplasmic membrane has an important function of selective osmosis. If the membrane function is disturbed, the components (ions) inside the cell will cause the bacteria to die. Mechanism of action of antibiotics is to inhibit protein biosynthesis: The process of protein biosynthesis includes ribosomes and transport and messenger RNAs. The effect is on the bacterial 70S ribosome or at the 50S subunit. From there, causing protein molecules to not be synthesized and formed. The mechanism of action of antibiotics is to inhibit nucleic acid biosynthesis: This synthesis inhibition consists of 3 levels, that is, it prevents the replication of mother DNA to create daughter DNA, prevents RNA biosynthesis, and inhibits RNA synthesis. biosynthesis of metabolites necessary for the cell.

Thuốc kháng sinh ức chế sinh tổng hợp vách tế bào vi khuẩn
It can be understood that each antibiotic will have an impact on a position in the composition or a link in the biological reactions of bacterial cells. Therefore, it can be said that the antibiotic is bacteriostatic because it can stop the growth and growth of bacterial cells.
In case the bacteria is not lysed or can't be killed after using antibiotics, the bacteria will recover again and only one bacterial cell will survive its reproduction after several hours. countable. What's more dangerous is that the surviving bacterial cells are resistant to the antibiotic.
Antibiotic resistance is very dangerous, because it can make bacteria resistant to the effectiveness of antibiotics, thereby changing or partially reducing the effectiveness of the drug, making the disease worse and recurring. frequent, long recovery time, high treatment methods and costs.
2. The right combination of antibiotics
The combination of antibiotics is aimed at improving the effectiveness of treatment, so in really necessary cases, it is imperative to combine antibiotics. That combination has the following specific purposes:
Combination of antibiotics to reduce the possibility of emergence of resistant strains of bacteria: Due to the resistance of mutations, the need to combine antibiotics will be an important factor in reducing the probability of a double mutation. Usually, the combination of antibiotics is mainly in the treatment of tuberculosis, leprosy or in some people with long-term treatment. Combination of antibiotics to treat infections caused by many bacteria: Some diseases are often caused by many types of bacteria, each antibiotic will have a mechanism of action to kill one type of bacteria. Therefore, the combination will help bacteriostatic antibiotics be more effective. The result of an antibiotic combination will be less or more undesirable effects. Antibiotics often cause side effects (mild or severe depending on the drug, the patient's mechanism), so in some cases, when combining antibiotics, this side effect will also increase.
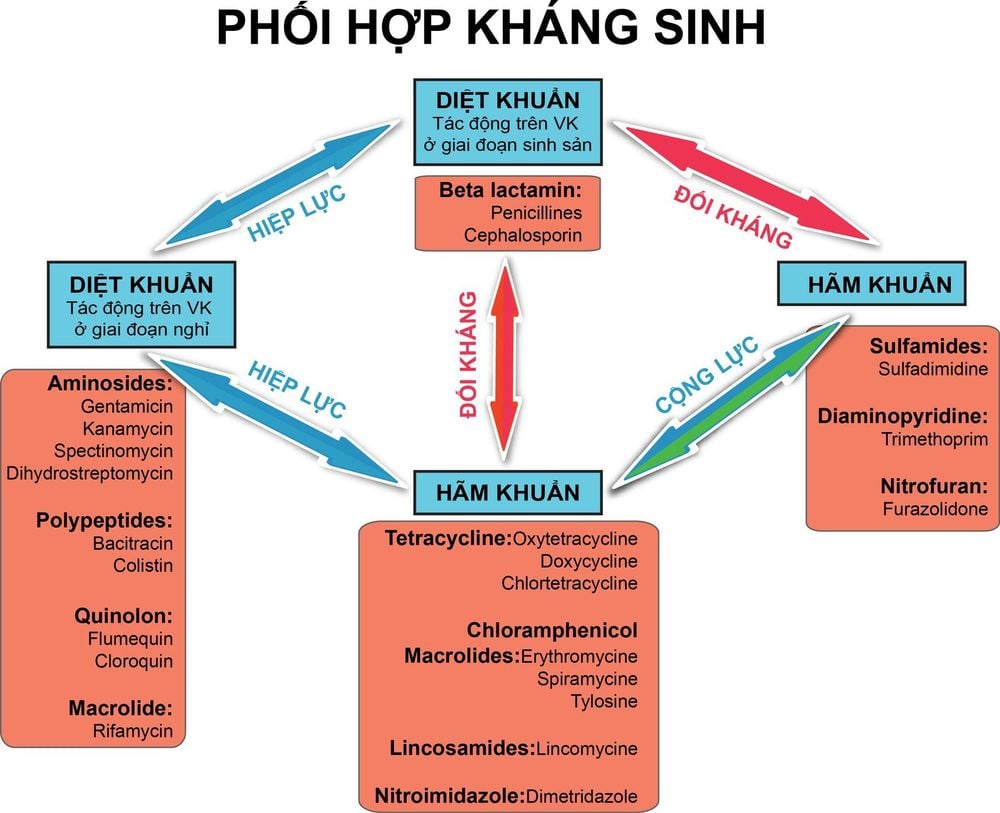
Besides, the combination of antibiotics will not lower the dose of each drug because the bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics, which is very dangerous for the patient if there is no new drug suitable for the disease. Besides, this combination of antibiotics may result in additive and synergistic effects. antagonistic effects or will remain unchanged compared with a single antibiotic. Specifically:
Antagonistic effect: This means that the combination of antibiotics with the same target will lead to antagonism, because the principle is that they repel each other from the target. For example, the combination of tetracycline antibiotics with penicillins can lead to an antagonistic effect, because penicillins have an effective effect on multiplying cells, while tetracyclines inhibit them. proliferation of these cells, which in turn leads to an antagonistic effect. Synergistic effect: This can mean that the combination of antibiotics can double the effectiveness. For example, when the antibiotic Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazol are combined, it will lead to inhibiting 2 different stages on the same pathway of coenzyme - folic acid synthesis, which is necessary for bacteria to multiply, so these two antibiotics will be effective. synergistically, which in turn is combined into a product (Co-trimoxazol). Besides, the combination of an aminoglycoside with a beta-lactam will give synergistic results, because beta-lactams have a mechanism of action that causes wall loss, thereby facilitating aminoglycosides easily penetrate. enter cells to inhibit and destroy disease-causing bacteria.
Sự phối hợp kháng sinh là nhằm mục đích nâng cao hiệu quả điều trị
3. Note when combining antibiotics
The combination of antibiotics is necessary in necessary cases such as treatment of leprosy, endocarditis, tuberculosis or treatment of Brucellosis. Some cases of severe disease but no microbiological diagnosis, waiting for test results, people whose resistance starts to decline or patients infected by many different bacteria need to combine antibiotics. born. However, when combining antibiotics, it is necessary to note some basic things as follows:
Need to use the right dose when combining antibiotics to treat the disease; It is best to choose antibiotics with similar pharmacokinetic properties or with synergistic effects; When there are results of anaerobic bacterial infection, use the antibiotic metronidazole in combination to treat peritonitis or intra-abdominal infections; In case of suspected anaerobic infections in the head and respiratory tract, use clindamycin. Because this antibiotic is highly effective against anaerobic bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria. In summary, most of the time, when a combination of antibiotics is required, the treatment results will usually not be different from the use of one antibiotic, while the side effects of antibiotics caused by this combination will often be the same. more frequent and more severe. Therefore, when using antibiotics, especially combination antibiotics, it is necessary to be cautious and closely monitor the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.













