This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by resident Doctor Nguyen Quynh Giang - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital. Dr. Giang has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially in the field of multi-segment computed tomography, magnetic resonance.Head trauma occurs as a result of trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain and can be classified as closed (no cuts in the skin) or penetrating (broken skin or skull bones). Symptoms of a head injury can occur immediately after the injury or develop slowly over time.
1. What is a head injury?
Head trauma occurs as a result of trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain. Head injuries are classified as closed, without cuts or lacerations in the skin, or penetrating, in which the skin or bones of the skull are broken. Traumatic brain injuries range in severity from mild (called mild traumatic brain injury) to severe.2. Symptoms of head injury
Symptoms of a head injury may occur immediately after the injury, or they may develop slowly over several hours or days. Specific types and symptoms of head injury include:2.1 Mild Traumatic Brain Injury This includes brain injury resulting from a blow to the head or body, a fall, or another injury that causes the brain to shrink or vibrate to the side of the brain. in the skull. People with a concussion may not always show symptoms that are obvious to others. Symptoms of concussion and mild traumatic brain injury include:
Loss of consciousness for seconds to minutes Confusion; problems with memory and/or concentration Dizziness Headaches Loss of memory (loss of memory) of events before or shortly after Nausea and vomiting 2.2 Bleeding A bruise of tissue The brain is often associated with swelling (edema) and increased pressure within the skull, known as intracranial pressure (ICP). Symptoms of increased pressure in the brain and skull include: dilated pupils, high blood pressure, low heart rate, and irregular breathing.
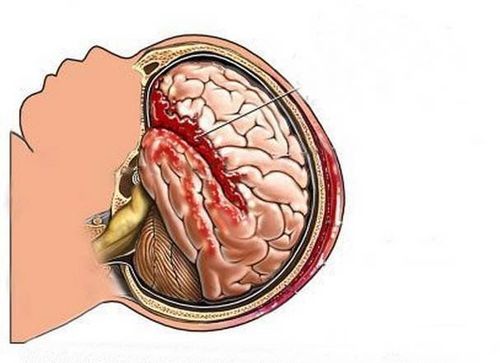
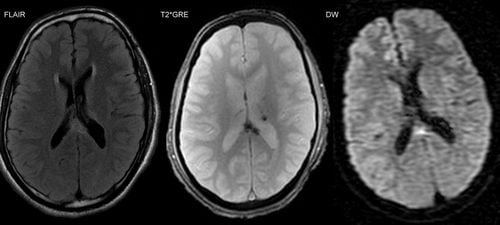
2.4 Cutaneous trauma (also called diffuse axial trauma) This type of injury occurs when the brain is hit hard inside the skull. Nerve fibers extending from the center of the nerve cell are stretched or torn, permanently damaging brain cells and causing other complications in the nervous system. The main symptom of a cut injury is a prolonged loss of consciousness.
3. How is head injury assessed?
The treatment of a head injury depends on the type of injury and the patient's condition. To assess the severity of a head injury, a doctor may perform a physical and neurological exam as well as imaging tests such as:3.1 Head CT scan Computerized tomography (CT) with equipment Special X-rays with sophisticated computers to create multiple images or pictures of the head and brain. Doctors use CT of the head to detect bleeding, swelling, traumatic brain injury, and skull fractures.
3.2 Head Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses strong magnetic fields, radiofrequency pulses, and computers to create detailed images of organs, soft tissues, bones, and virtually everything all other internal body structures.
3.3 Head X-ray An X-ray involves exposing a part of the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation to create an image of the inside of the body.
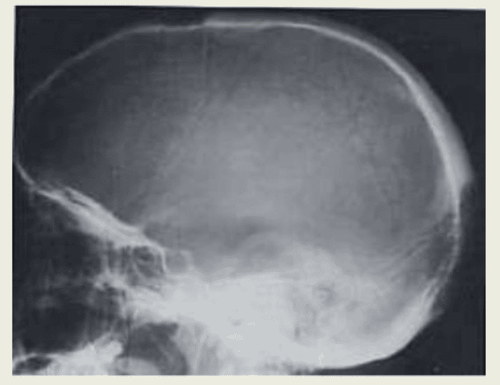
4. How are head injuries treated?
Consider seeking immediate medical attention with any form of head injury because the consequences of an undetected or inappropriately treated head injury can be practically dire.Patients with minor head trauma will be observed and symptomatic treatment, including headache relief and medication to control nausea and vomiting. If you have symptoms of a simple concussion, you should avoid overexertion. Your doctor will advise you when you can return to your normal sports and daily activities.
More seriously, a traumatic brain injury will require personalized and frequent emergency care, such as surgery to remove the blood clot and relieve pressure on the brain.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading medical facilities for diagnosing and treating traumatic brain injury today:
The hospital is fully equipped with modern machinery and medical equipment, and imaging facilities that support the most advanced diagnosis and treatment such as: G.E 3.0 MRI (MRI) scanner, Toshiba 640 slices CT SCAN, cerebral angiogram, MRA and CTA... for clear image quality easy diagnosis and treatment of brain and spine diseases of both medical and surgical pathology (brain tumor, brain degeneration, white matter degeneration, congenital pathology of brain structure, traumatic brain injury) brain, spinal cord injury, cerebrovascular diseases: aneurysms and cerebrovascular malformations...) Being examined and treated by a team of qualified and experienced medical doctors to assist in the treatment process. effective treatment of traumatic brain injury, minimizing the sequelae. Patients are treated and recovered in modern wards, fully equipped with international standards, helping patients feel comfortable, providing maximum support for the treatment process. For more information, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org
SEE MORE
Common types of headaches that make you uncomfortable - The effects of headaches How dangerous are frequent, prolonged migraines? Distinguish between migraine and vestibular disorders