This is an automatically translated article.
Respiratory damage is the most common measles complication, usually occurring within 30 days after the rash appears. Measles with pneumonia is the main cause of death from measles in developing countries.
1. Measles overview
Measles is an acute infectious disease caused by a virus, common in young children. Measles virus usually enters the body of an infected person through the nose, throat and eyes. The disease usually resolves on its own, but serious complications can still occur, especially respiratory and central nervous system complications.
Most of the infected cases have not been vaccinated against measles or vaccinated but have not completed the prescribed dose. The number of measles cases mainly falls among children under 12 years of age.
Measles can cause an epidemic, so in the face of the current complicated situation of cases, everyone needs to be careful and recognize early signs of the disease to support treatment and prevent the spread of the disease. orchid.
2. Signs to recognize measles
Incubation period when infected with measles virus is from 10 to 12 days, then symptoms such as: red eyes, sore eyes when looking at light, low fever, dry cough, cough without phlegm that lasts continuously, runny nose... Inside the mouth, near the cheekbones, the first signs appear are white spots.
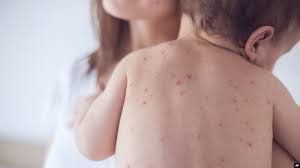
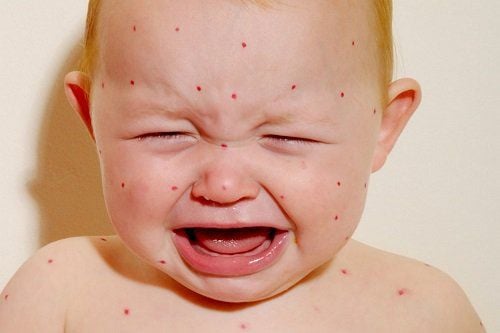
To the stage of rash: The patient appears red on the skin. The rash grows from behind the ears, spreads to the face and back, after 2-3 days will spread to the whole body, gradually spreading down the legs. Patients with high fever continuously accompanied by symptoms: much fatigue, poor appetite, body aches and pains, dry cough, conjunctival congestion, eye rust, ..
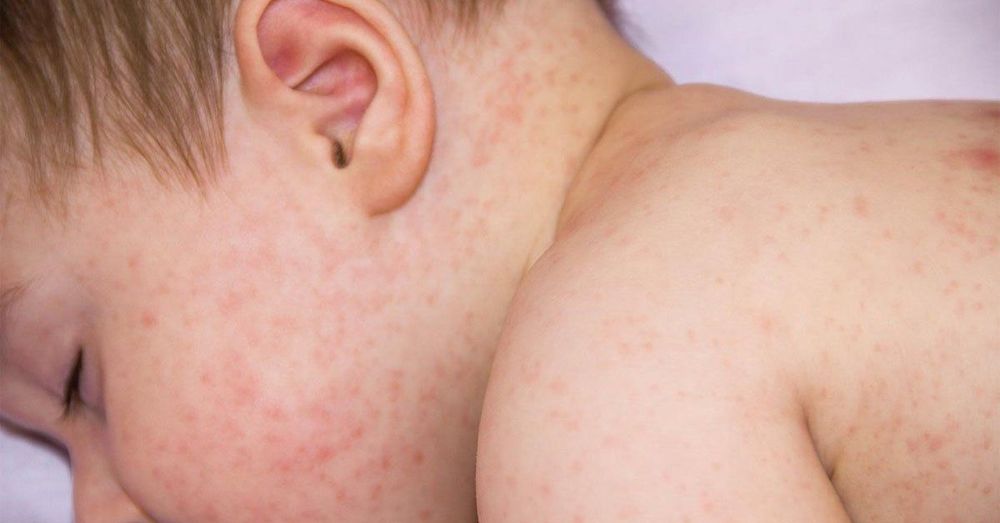
Đến giai đoạn phát ban, các nốt ban đỏ mọc và lan ra toàn thân
3. Who are susceptible to complications from measles?
Children at higher risk for measles:
People who have not had measles or have not been vaccinated against measles or are not fully vaccinated are more likely to be attacked by the measles virus. Cases prone to complications when contracting measles are usually infants under 9 months old, malnourished children, obese children, People suffering from other diseases such as congenital heart disease, influenza, diabetes, etc. Caused by an HIV-infected mother: Babies born to HIV-infected mothers are more susceptible to measles at a younger age than babies born to uninfected mothers. Children with vitamin A deficiency: Children with clinical or subclinical vitamin A deficiency have an increased risk of death from measles. Measles is associated with decreased retinol/blood levels and can lead to marked vitamin A deficiency. WHO also recommends vitamin A supplementation for children with measles in this case, especially in countries with high measles mortality rates. Malnourished children: Children with severe malnutrition are often more susceptible to immunodeficiency in various forms: longer viral shedding time, higher mortality from measles. Measles contributes to malnutrition through protein loss due to enteropathy, increased metabolic requirements, and reduced dietary availability. Tuberculosis: Deficiency of cell-mediated immunity due to measles favors TB infection. Moreover, tuberculosis will also be more severe if the patient is infected with measles.
4. Measles complications

Viêm tai giữa cấp do sởi là biến chứng thường gặp đối với trẻ em dưới 5 tuổi
4.1. Respiratory complications in measles Acute otitis media This is a common complication, especially for children under 5 years old. Inflammation of the Eustachian tubercle epithelium causes obstruction and secondary infection.
Laryngitis Acute laryngitis may appear early due to the measles virus, often precedes the rash, is benign. However, it can also appear late in the subglottis and become severe due to superinfection.
Measles croup is a major cause of death in children with measles, especially children under 2 years of age. Tracheal aspiration culture is positive for bacteria, evidence of tracheobronchitis secondary to otitis media, pneumonia, or both.
Bronchitis Usually appears during the period of inflammation of the respiratory tract, can be aggravated by a rash. Some children have a clinical presentation of bronchiolitis. However, because viral culture is not common, the possibility of co-infection with measles and other respiratory viruses cannot be excluded.
Pneumonia Pneumonia is the most common serious complication, which is present in most deaths from measles.
Among children hospitalized with measles, up to 55% of children have X-ray findings of bronchiolitis, lobar pneumonia or other infiltrates. 77% of severely ill children and 41% of mildly ill children had pulmonary lesions visible on chest X-ray.
Pneumonia caused by measles virus can also be caused by a viral infection, or a secondary bacterial infection, Giant cell interstitial pneumonia (malignant pulmonary measles).
Pulmonary staphylococci - pleurisy Poor physical condition and immunosuppression due to measles are favorable factors making the disease easy to develop complications.
Patients with pulmonary staphylococci - pleurisy often have high fever, gastrointestinal symptoms. Lung signs are often more subtle.
Giant cell interstitial pneumonia (Malignant pulmonary measles) Giant cell interstitial pneumonia is common in immunocompromised/severely malnourished children but can also occur in normal adults and children.
Usually occurs during the rash phase. The disease causes severe respiratory failure, gradually progressing to treatment-resistant hypoxia, with a poor prognosis.

Viêm phổi là biến chứng nặng thường gặp nhất, thường có trong hầu hết các ca tử vong vì sởi
4.2. Immune Deficiency in Measles Immunodeficiency is promoted by the measles virus, leading to opportunistic infections. Immunodeficiency persists for weeks after apparently recovering from measles.
Measles virus often weakens the immune system very quickly, if the sick person comes into contact with other people who have the flu, it will make the disease worse. Therefore, it is necessary to limit contact with patients. Pregnant women who get measles are at increased risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, premature birth, or low birth weight.
4.3. Secondary infection in measles Superinfection complications are common in young children, with poor hygiene.
Acute otitis media: HI, PNE. Bacterial laryngitis. Bronchopneumonia: appears at the end of the rash stage. Pulmonary-pleural staphylococci: typical, severe, present during the rash phase. 4.4. Other complications Pulmonary collapse Emphysema Emphysema Pneumomediastinum: rare. When you suspect symptoms of measles, you must go to the nearest medical facility for diagnosis and treatment, to prevent possible complications. Children who are sick or suspected to have measles must be isolated, absent from school and not in crowded places to avoid spreading in the community.
To prevent disease, for children who have not yet reached the age of vaccination, should avoid contact with people suspected of having measles. Children should be vaccinated against measles as soon as possible (when full 9 months old) and booster shots.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, before vaccination, all children are screened before vaccination with pediatricians - vaccines to help children ensure the best health when vaccinated. The doctor will advise the family on the best preventive vaccines for each age group according to the latest recommendations of the Ministry of Health & World Health Organization as well as how to monitor the reaction after vaccination.
A team of experienced and professional pediatric doctors and nurses, understand children's psychology and apply effective pain relief methods for children during the vaccination process. 100% of vaccinated children are monitored and re-evaluated before leaving. Post-vaccination monitoring room is fully equipped with emergency facilities; the team of doctors - nurses are trained in anaphylaxis emergency management to ensure timely and correct treatment when an incident occurs. The vaccination room is airy, with a play area, helping children feel comfortable as if they are walking and have a good mentality before and after vaccination. Customers can directly go to Vinmec health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
MORE
Is measles contagious? How is measles transmitted? Does the measles vaccine cause a lot of fever?