This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Mr. Dr. Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Previously, brain tumor biopsies were performed via craniotomy in the operating room. Today, to minimize the invasiveness and risks of opening, other closed brain biopsy methods have been born, including manual biopsy under the guidance of computed tomography (Free-hand brain). biopsy).
1. What is a brain tumor?
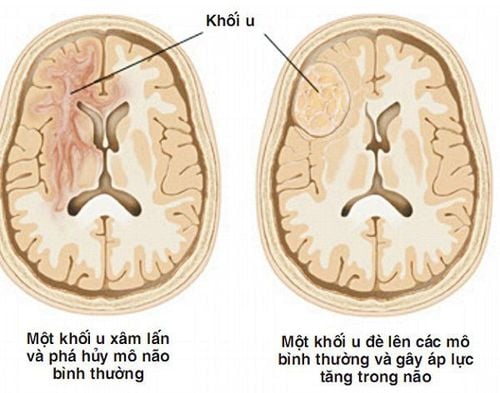
A brain tumor is an overgrowth of cells in the brain parenchyma, which may originate from neurons or cells of structures located in the brain (meninges, blood vessel cells, etc.). ..) or secondary (metastasized) from elsewhere to the brain.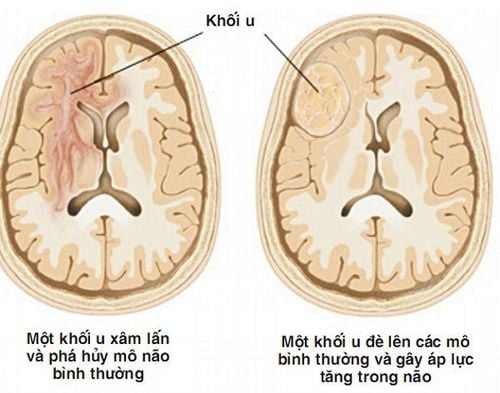
2. Diagnosis of brain tumor
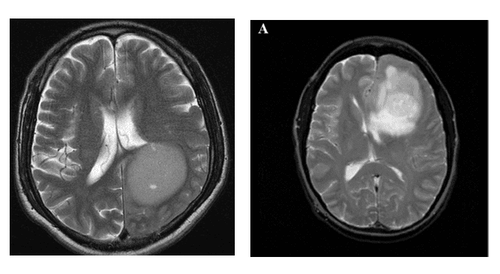
The advent of Computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance (MRI) made a great step forward in the diagnosis of cranial pathologies in general and brain tumors in particular, helping to visually assess the location and quantity. , size, nature of the lesion as well as the relationship of the lesion to other structures. However, in many cases, it is difficult to determine the nature of the brain tumor or to make the differential diagnosis even with a combination of clinical, laboratory, and imaging studies. In this case, a brain tumor biopsy was ordered to determine the nature of the lesion to help determine the treatment attitude.
3. Brain Tumor Biopsy
Previously, brain tumor biopsies were performed via craniotomy in the operating room. Today, to minimize the invasiveness and risks of opening, other closed brain biopsy methods have been developed, including manual biopsy under the guidance of CT (Free-hand brain biopsy).Currently, Vinmec Times City Hospital is one of the few medical facilities across the country that can perform this technique. The technique is deployed at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging.
Compared with open brain biopsies, closed biopsies under CT are much less invasive (several comparisons are shown in the table), are more cost-effective, and the patient time to plan for biopsy is significantly shorter. tell. The risk of nerve damage during and after the intervention is also less and, if present, often milder.
| Đặc điểm | Sinh thiết mở | Sinh thiết kín |
| Phương pháp gây mê | Gây mê | Gây tê tại chỗ |
| Cửa sổ mở xương | Rộng | Bé |
| Đường dài rạch da | Dài | Rất ngắn |
| Số mũi khâu da | Nhiều | Ít |
| Lượng máu mất | Nhiều | Ít |
| Bệnh phẩm | Lấy rộng | Chọn lọc vùng tổn thương |
| Thời gian hồi tỉnh | Sau gây mê nội khí quản | Không gây mê |
| Đau tại chỗ mở sọ | Có + rộng | Ít, lỗ mở sọ rất bé |
| Triệu chứng thần kinh khu trú | Tỷ lệ cao hơn do diện lấy bệnh phẩm rộng | Ít hơn do diện lấy bệnh phẩm chỉ chọn lọc vào u |
| Thời gian nằm viện | Dài hơn | Thường ngắn hơn đáng kể |
Manual brain biopsy procedure under CT can be summarized through the following steps
Patient preparation: The patient has complete medical records and tests baseline testing including baseline coagulation, HIV, and HBsAg. Explain the biopsy procedure to the patient and family. Prepare equipment: Sterile tools and medicine needed for the procedure. Conduct a biopsy: make a hole in the skull 🡪 insert the needle under the guidance of CT into the right lesion 🡪 Take the specimen Post-procedural examination: Post-procedure examination to control bleeding complications blood, gas accumulation, the patient rests in place for 5-10 minutes for monitoring. The doctor sends the specimen to the Department of Pathology.
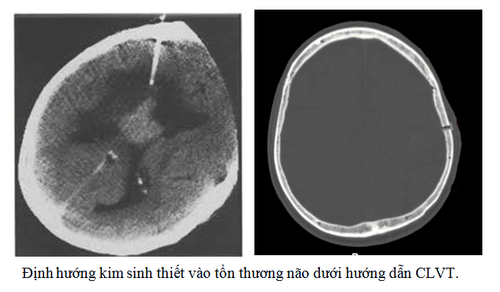
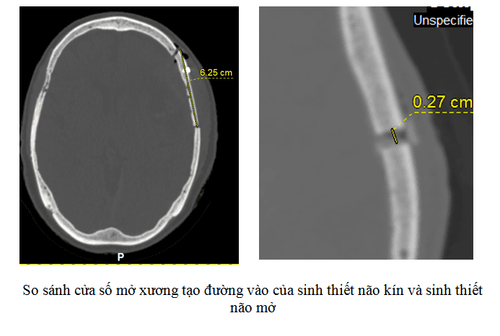
Complications during and after the procedure
There are a number of complications that can occur during and after the brain biopsy procedure. However, the complications that occur are all non-serious complications that do not affect the patient's life or function. During follow-up, the patients with these complications all had a stable development after the biopsy, no new focal neurological signs appeared, and had a normal CT image after 2-7 days.
| Biến chứng cấp tính |
Chảy máu (trong u, trong nhu mô não, dưới nhện, theo chân kim chọc, tụ máu ngoài/ dưới màng cứng) Tụ khí nội sọ (thường không gây ra triệu chứng) Mất ý thức hay dấu hiệu thần kinh khu trú đột ngột |
| Biến chứng muộn |
Viêm màng não Viêm xương tại vị trí chọc |
In the study of Vu Thi Thanh 2016, out of 25 patients who had biopsies, 19 patients finished the procedure safely, without complications (accounting for 76%). There were 6 patients with complications after the procedure (24%). The complications encountered were: bleeding around the needle pin (with 4 patients); pleural bleeding (1 patient) and intracranial gas accumulation (1 patient).
Conclusion: Manual brain biopsy under computed tomography at Vinmec Times City International General Hospital is a minimally invasive procedure with imaging guidance, which has many advantages over open brain biopsies. Traditionally, it saves time and costs of hospitalization, as well as minimizes the risks and complications that may arise from craniotomy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.