This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Mr. Trinh Van Dong - Doctor of Radiology, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.The advantage of magnetic resonance imaging technique is that it can detect early and accurately pathologies of the fetus and placenta that are not detected or suspected by ultrasound. Magnetic resonance accurately assesses the degree of placental disease.
1. Explain the concept/definition (what is this technique)?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a subclinical diagnostic imaging technique based on the principle of imaging not using X-rays but using magnetic fields and radio waves. Magnetic resonance imaging technique is applied to diagnose most diseases in the body such as skull, neck, abdomen, musculoskeletal diseases, software... In obstetrics, in addition to evaluation pathologies of the uterus such as cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, intramuscular and ectopic endometriosis, uterine malformations, pelvic pathologies, assessment of intrauterine fetal malformations In cases where ultrasound is difficult to evaluate such as oligohydramnios, obese mothers..., magnetic resonance imaging also evaluates placental diseases very well, especially in placental diseases.2. What is the purpose/meaning of the technique?
Placental disease (AIP) is an abnormal or invasive attachment of the placenta to the uterine muscle, which may involve part or all of the placenta. This is a rare disease and easy to miss in clinical, they increase obstetric complications and maternal mortality. The cause is because the uterine lining is damaged or not thick enough that the placenta will grow into the muscular layer of the uterus, common in patients with a history of surgery such as fibroid removal, cesarean section. , multiple abortions or patients with placenta previa (pathology where the placenta attaches through the hole in the cervix). The purpose of the placental magnetic resonance imaging technique is to confirm the diagnosis and accurately assess the extent of invasion of the placenta into the uterine muscle or into adjacent structures, thereby helping the obstetrician to guide the follow-up and follow-up treatment. Levels of placenta accreta are accurately diagnosed on magnetic resonance: + Accreta: placenta attaches and partially invades the uterine muscle layer (mild level).
+ Increta: placenta penetrates deeper into the muscular layer of the uterus (moderate).
+ Percreta: the placenta penetrates the muscle layer and serosa of the uterus, possibly reaching the adjacent organs (severe).
In addition to assessing placental disease, magnetic resonance also evaluates early fetal malformations.
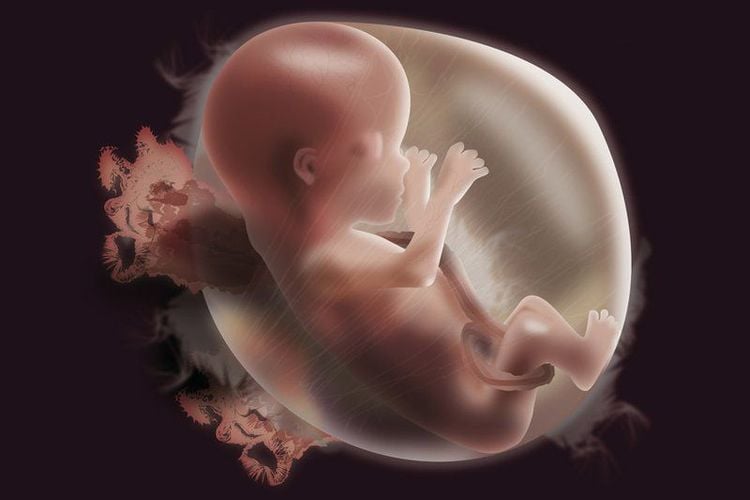
Chụp cộng hưởng từ bánh rau giúp xác định các dị tật thai nhi sớm
3. Indications/contraindications?
3.1 Designation
+ Patients with suspicion of placenta accreta on ultrasound, or with ultrasound with diagnosis directed at placenta accreta, want to further assess the extent of the disease.
+ Patients with risk factors: placenta previa, patients with a history of previous surgery: cesarean section, cesarean section, or a history of hysterectomy.
+ Older mother > 35 years old.
3.2 Contraindications
+ All cases with contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging in general have contraindications to placental magnetic resonance imaging: The patient has a pacemaker; patients with magnetic objects such as surgical forceps, artificial heart valves, intramedullary nails, artificial hip joints, metal screw braces...
+ Relative contraindications: agitated patients, claustrophobia In a closed cage, the patient is unable to lie still.
+ However, it is best not to take magnetic resonance imaging in the first 3 months, because it is in the process of forming fetal organs, it can be considered if necessary.
4. How to do it?
Place the patient in a strong magnetic field of 0.2 - 3 Tesla (T). Broadcast radio to the patient. Then turning off the radio waves makes the protons no longer excited, gradually returning to their original state. After rendering the image using the recorded signal, the computer will reconstruct the image of the sections based on the recorded parameters. In the placental magnetic resonance imaging, pulse sequences are performed: T2 in the horizontal, horizontal, and vertical planes; T1 and the diffuse pulse sequence (DWI) in the vertical plane. About the injection of magnetic contrast agent (gadolinium): usually the magnetic contrast agent used in placental-fetal magnetic resonance imaging has little or no effect on the fetus, but the radiologist and clinician will consider between benefits and risks for the final indication. In cases where it is necessary to use contrast agents, side effects are less common.
5. Pros/cons?
5.1 Advantages
+ Magnetic resonance is a modern diagnostic technique that does not affect the health of the mother and the development of the fetus.
+ Can detect early and accurately fetal and placental diseases that are not detected by ultrasound or are suspected by ultrasound. Magnetic resonance accurately assesses the degree of placental disease. Many fetal lesions are not detected by ultrasound, but on magnetic resonance, they can accurately detect lesions such as lesions in the central nervous system, intra-abdominal viscera...
Chụp cộng hưởng từ là kĩ thuật hiện đại, tiên tiến
5.2 Cons
+ Cannot be performed in patients with contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging (as described above).
+ Not recommended for pregnancy in the first 3 months.
+ Some cases are allergic to contrast agents, but usually mild reactions.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.