This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Dang Manh Cuong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
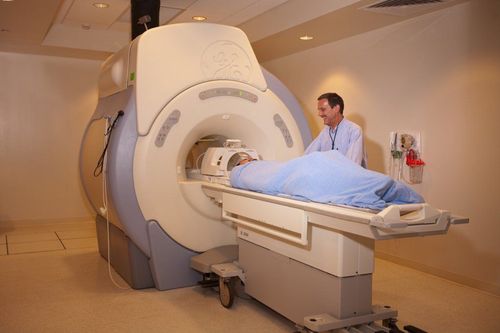
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to diagnose many different diseases. An MRI uses a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of structures inside the body. An MRI does not use radiation (X-rays).
1. What is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee joint?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee joint uses strong magnetic fields, radio waves and computers to create detailed images of structures in the knee joint such as cartilage, bone, tendons, ligaments, muscles, vessels blood. It is commonly used to diagnose or evaluate pain, weakness, edema, or bleeding in and around a joint. An MRI of the knee joint can help determine if you need surgery.
2. In what cases is MRI of the knee joint indicated?
Combined with conventional X-ray imaging, MRI is the best choice to evaluate joints in the body including the knee joint.
MRI of the knee joint to diagnose or evaluate:
Knee pain, knee weakness, swelling or bleeding in the tissues in and around the knee joint Destruction of the hyaline cartilage, meniscus, ligaments or tendons Injury Sports-related knee injuries (such as sprains and tears of ligaments, cartilage, or tendons) Fractures that may not be visible on radiographs and other imaging methods Arthritis Knee effusion Infection (such as osteomyelitis) ) Tumor (primary and metastatic tumor) involving bones and joints Dead bones Decreased range of knee flexion and extension Knee injury or pain Complications related to implanted surgical device Pain or injury after knee surgery Your doctor may also order an MRI to determine if you need arthroscopy or another surgery, and to monitor progress after knee surgery.
A special MRI called MR arthrogram, which injects magnetic contrast material into the joint so that the radiologist can get a better look at the inner structure of the knee joint.
3. Does the patient need to prepare anything? How to prepare?
You may need to wear a hospital gown or you may be able to wear your own if it's loose and doesn't have metal fasteners.
You are given specific instructions about what to eat and drink by your doctor before the MRI scan.
When magnetic contrast injections are indicated, you may be asked if you have asthma or are allergic to iodinated contrast agents, drugs, foods or the environment? Because in contrast agents, there is a contrast agent called gadolinium. Gadolinium may be used in patients with an iodine contrast allergy. Patients are less likely to be allergic to gadolinium contrast than to iodinated contrast. However, even if the patient is known to be allergic to gadolinium, it can be used after notifying the doctor for consideration.
Tell the technician or radiologist if you have any serious health problems or have had recent surgery. Certain conditions, such as severe kidney disease, may require the use of special gadolinium contrast agents that are considered safe for patients with kidney disease. You may need kidney function tests to determine if your kidneys are working properly.
Women should always tell doctors and technicians if they are pregnant. MRI has been used since the 1980s with no reports of any adverse effects on pregnant women or their unborn babies. However, the baby will be in a strong magnetic field, so pregnant women should not have an MRI during the first trimester unless the benefits of the scan clearly outweigh the potential risks. Pregnant women should not have gadolinium contrast injections unless absolutely necessary.
If you have claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces) or anxiety, you can ask your doctor to prescribe a mild sedative before your exam.
Infants and young children often require sedation or anesthesia to complete an MRI without mobility. This depends on the child's age, intellectual development and type of shooting. A specialist in pediatric sedation or anesthesiology will be present during the scan for your child's safety. You will be told how to prepare your child.
Leave all jewelry and other accessories at home or remove them before the MRI. Metal and electronic items can interfere with the magnetic field of the MRI machine and they are not allowed in the imaging room. They can cause burns or become harmful in the MRI machine room. These include:
Jewelry, watches, credit cards and hearing aids => all can damage Pins, hairpins, metal zippers and similar metal objects, can do distortion distortion of the MRI image. Removable dentures Pens, pocket knives and eyeglasses Body piercings Cell phones, electronic watches and tracking devices. In most cases, an MRI is safe for patients with metal implants, with some exceptions. People with the following implants may not be screened and should not enter the MRI area without first being evaluated for safety:
Certain cochlear implants Certain types of clips are used for aneurysms brain Some types of metal coils are placed in blood vessels Some older defibrillators and pacemakers Tell the technician if you have medical or electronic equipment in your body. These devices may interfere with the shooting process or pose a risk. Many implantable devices will have a brochure explaining the MRI risks for that particular device. If you have a pamphlet, bring it to your doctor before the scan is done. MRI cannot be performed without confirmation and documentation of implant type and compatibility with MRI.
X-ray can detect and identify any metal object. Metal objects used in orthopedic surgery usually pose no risks in an MRI. However, a recently placed artificial joint may require the use of a different imaging technique.
Tell the technician or radiologist about any shrapnel, bullets, or other metal that may be in your body. Foreign objects near and especially in the eye are important because they can move or heat up during the scan and cause blindness. The dye (tattoo ink) used in tattoos may contain iron and can heat up during the MRI scan and cause burns. This is rare.
Dental fillings, braces, eyeshadows and other cosmetics are generally unaffected by magnetic fields. However, they can distort images of the face or brain area. Tell the radiologist about them.
4. How is the process done?
This technique can be performed on outpatients as well.
You will be positioned on a movable table. Straps and washers can be used to help you stay still and stabilize your position. The knee joint is placed in a device called a coil that contains coils of coils that send and receive radio frequency pulses to pick up the signal that creates an image. If magnetic contrast is used, your doctor, nurse, or technician will place an intravenous catheter into a vein in your arm to be used to inject the contrast material. You will be placed inside the magnetic block of the MRI machine. The technician will perform the scan with a computer station outside the MRI room. Once the scan is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist re-checks the scans for satisfactory results. The intravenous line will be withdrawn when the scan is over. The whole shooting process takes about 30-40 minutes. If your child needs to be sedated for an MRI scan, you may need to arrive early to have your child's doctor examined for evaluation before sedation. Your child may need to stay longer to be monitored as the sedation wears off. In patients who require intra-articular contrast injection, the contrast agent is injected into the joint and an MRI is performed to visualize the joint structures in more detail.
5. How will you feel during and after the MRI?
Most MRI exams are painless. However, there are some patients who are uncomfortable for the following reasons:
Feeling claustrophobic in the MRI scanner (clautrophobic syndrome). So some anxious patients may need to be sedated Feeling noisy when the MRI machine pulses The area you lie down may feel a little hot, but that's normal. If that bothers you, notify the radiologist or technician. It is important that you remain completely still during the shoot. You'll know when the image is being recorded because you'll hear and feel the loud knocking as the coils that generate the radio frequency pulses are activated. Some centers provide earplugs, while others use headphones to reduce the intensity of the sound produced by the MRI machine. You should be able to relax between pulse bursts, but still have to stay in your position without moving as much as possible.
You will usually be alone in the MRI room. However, the technician can still see, hear and talk to you at all times using the two-way intercom. If you are concerned about needing a loved one by your side, you can request that as long as they are also checked for safety before entering the MRI room.
Children will be fitted with properly sized earplugs or headphones during the search. Music can be played through headphones to help you get through long periods of shooting.
If you have an indication for an intravenous contrast scan, it is normal to feel a hot flush for a minute or two after the injection.
The intravenous needle may cause you some discomfort when it is inserted and removed, you may experience some bruising. There is also very little chance of irritating your skin at the site of the IV placement.
If you are not under anesthesia, there is no need for follow-up time after the scan. You can resume your normal activities and diet right after the scan.
Some patients experience side effects from the contrast agent, including nausea and focal pain. Very rarely, the patient is allergic to the contrast agent and develops urticaria, itchy eyes, or other allergic reactions. If you experience symptoms of an allergy, a radiologist or other doctor will be ready to take action right away.
6. What are the benefits and risks of this approach?
Benefits:
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique with no radiation exposure. MRI has been shown to be valuable in the diagnosis of joint conditions, including tendons, ligaments, muscles, cartilage, and bone abnormalities that cannot be seen on radiographs or CT scans. An MRI can help identify which patients with knee injuries require surgery. MRI can help diagnose fractures when x-rays and methods are inconclusive. MRI provides a non-invasive alternative to X-ray, angiography and CT scanner for the diagnosis of vascular diseases. Risks:
An MRI scan poses almost no risk to the patient if appropriate safety guidelines are followed. Although strong magnetic fields are not harmful by themselves, implanted medical devices that contain metal can be damaged or cause image distortions during an MRI scan. Systemic renal fibrosis is a recognized but rare complication associated with gadolinium contrast injection. It usually occurs in patients with severe renal failure. Your doctor will evaluate your kidney function tests before considering contrast injection. You may have an allergic reaction if you take the contrast medicine. Such reactions are usually mild and controlled with medication. If you have an allergic reaction, your doctor will be available to assist immediately. The manufacturer of the contrast agent says that mothers should not breastfeed for 24-48 hours after taking the contrast agent. However, recent guidelines from the American College of Radiology (ACR) research show that the absorption of magnetic contrast material by infants during breastfeeding is very low.
7. Limitations of knee MRI
For high quality, shake-free images, you must lie still while the image is being recorded. If you are in pain or anxious, it is difficult to lie still and the image will be blurred. People who are too heavy may not be suitable for some common MRI machines. There is a weight limit on the scanner Implants and other metal objects can make images less clear. Patient movements can be of a similar nature. In some cases, metal artifact reduction is performed in patients with metal surgical implants in the knee. Although there is no evidence that MRI harms an unborn baby, pregnant women should not have an MRI exam during the first trimester unless medically necessary. MRI is usually more expensive and takes longer to scan than other imaging methods. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with a 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging system with modern Silent technology from GE Healthcare (USA) with many outstanding advantages compared to MRI machines. usually, common, normal.
Silent technology is especially beneficial for patients who are children, the elderly, weak health patients and patients undergoing surgery. Limiting noise, creating comfort and reducing stress for customers during the shooting process, helping to capture better quality images and shorten the shooting time. Magnetic resonance imaging technology is the technology applied in the most popular and safest imaging method today because of its accuracy, non-invasiveness and non-X-ray. Customers please make an appointment at the website or contact Vinmec medical system nationwide for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org
MORE:
Application of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in diagnosing knee injuries Southeast Asia, Vinmec uses Silent technology magnetic resonance imaging machine