This is an automatically translated article.
The liver is an important organ in the body that plays a role in metabolism, detoxification, protein synthesis, etc. When this organ is damaged by various causes, these functions will be affected. To improve and restore the liver, the patient may be indicated to remove the necrotic liver tissue.
1. What is the surgical removal of necrotic liver tissue?
In case the patient has damaged liver function due to injury, disease or liver abscess causing liver necrosis, surgery to remove the liver parenchyma is required. Because of the fact, these necrotic parts also have no function, it can even spread to affect the entire liver.
When performing liver parenchymal resection, the doctor will completely remove the pathological organization but also ensure the maximum saving of the removed healthy liver tissue.
Patients are assigned to apply this method in one of the following cases:
The patient has liver injury that cannot be treated to preserve this liver organization and needs immediate emergency care. Hepatic parenchymal resection will be performed at the liver tissue that is not able to recover (loss of vascular pedicle) or ablation to reveal clearly the vascular damage (liver veins, hepatic artery ...) hemostasis is good. The patient had a liver abscess but failed medical treatment and aspiration of the abscess. This method is contraindicated in patients with malignant liver lesions.
2. Liver parenchymal removal procedure
2.1. Preparation Before conducting surgery to remove necrotic liver tissue, it is necessary to prepare:
On the side of the hospital, a surgeon specializing in gastroenterology - hepatobiliary medicine is required. These are doctors with at least 5 years of experience in hepatobiliary surgery or hepatectomy. In addition, more nurses and equipment are needed to support the process of cutting necrotic liver tissue.
A number of mandatory medical tools and equipment include: Chain valve frame pulling the abdominal wall; Conventional gastrointestinal surgery set; Sutures 2.0 or higher to suture parenchymal bleeding...
On the patient's side, it is necessary to prepare psychologically before entering surgery. Patients and family members will be thoroughly explained by the doctor about the pathology, surgical steps and possible risks.
Before surgery, the patient is instructed to clean the body, remove pubic hair, and prepare the colon. In case of emergency surgery, the patient needs to be placed in an intravenous vein to meet the best blood and fluid requirements. According to experts, emergency liver injury needs to prepare a central intravenous line.
2.2. Steps to perform Step 1:
The patient is brought into the sterile operating room, lying on his back, with his arms perpendicular to the body. Perform anaesthesia by techniques of endotracheal anesthesia, gastric tube insertion, urinary catheter, peripheral and central vein placement. Disinfection of the abdominal area extending from below the nipple to the pubic bone is an important step.
Step 2: Laparotomy
The doctor can choose the laparotomy line or the white line between the top and bottom of the navel or the line below the ribs extending to the sternal nose (Mercedes line) or the right lower rib line. The incision will depend on the size of the lesion that is performed.
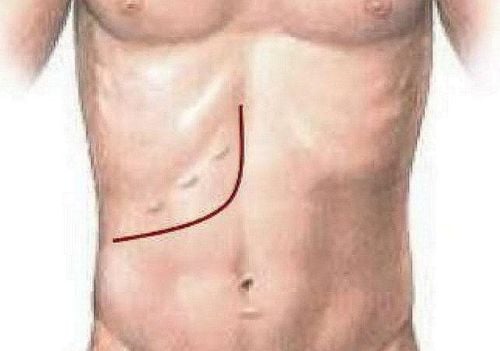
Đường Mercedes có thể sử dụng trong phẫu thuật cắt lọc nhu mô gan
Step 3: Assess liver damage and examine other parts
The doctor probes the gross damage of the entire liver, inserts gauze for bleeding liver organization. At the same time, assess the condition of the adjacent organs such as: stomach, intestines, small intestine,...
Step 4: Release the liver
Proceed to release the liver by cutting round ligaments, sickle ligaments, and ligaments triangle.
Step 5: Control the liver stalk
Can control the entire pedicle or selectively half of the pedicle by threading the wire to control the entire hepatic peduncle before performing parenchymal resection.
Step 6: Liver parenchymal removal surgery
Cut necrotic liver tissue by pincer, by ultrasound knife. Perform a complete pair of liver stalks every 15 minutes and rest for 5 minutes between pairs. Using a bipolar knife, clip blood vessels to remove vascular branches in the area of liver resection. Use the ultrasound knife to stop the bleeding of small branches. Check hemostasis of liver resection. Patients with coagulopathy must insert gauze in the area of liver resection or suture the entire area of liver resection. Step 7: Place drainage at the cut site, abscess and close the abdomen according to anatomical layers.
3. Monitor and manage complications after liver parenchymal resection
3.1. After the surgery is over, the patient will be extubated and taken to the ward to breathe oxygen for about 2-3 days. The supply of nutrients to the body is done by intravenous infusion until the patient passes stool.
Besides, the doctor will always check and evaluate the biochemical blood test indicators. If there is any abnormality in this indicator, it will be diagnosed and treated immediately.
3.2. Management of complications Postoperative liver failure will be managed by fighting infections, ensuring kidney function, supplementing with Albumin, drugs to support liver function, and diuretics. Intra-abdominal bleeding: bleeding through drainage, decreased hematocrit, tachycardia and decreased blood pressure requiring blood transfusion and surgical intervention to stop bleeding. Bile leak: when bile through drainage > 50ml/day for 3 days. Follow-up and medical treatment, retain abdominal drainage for a long time and always open biliary drainage to reduce biliary pressure. Abdominal effusion will be treated medically with Albumin compensation, diuretics... Some other complications may be encountered such as: surgical site infection, pneumonia, urinary infection... Risks This will mainly be prescribed antibiotics to treat.

Sau phẫu thuật cắt lọc nhu mô gan người bệnh cần được theo dõi và chăm sóc
The combination of diagnostic imaging equipment right in the operating room will help avoid the need to transport patients to different imaging areas in the hospital. Patients are diagnosed and operated right in the operating room, the quality of the surgery will be best guaranteed, saving time, enhancing patient safety, especially preventing infection, helping patients recover faster.
In the operating room Hybrid is the combination of a sterile surgical environment with the above-mentioned imaging system, which helps to reduce surgery time and bring the best surgical efficiency to patients in specialized specialties such as: cardiovascular, neurological, hepatobiliary, urinary, musculoskeletal.
Laparoscopic surgery and less invasive interventions. Reduce surgery time and bring the best surgical effect to the patient. Reduced risk of infection as there is no need to transport the patient between the radiology department and the operating room. The complication rate is low, shortening the hospital stay for the patient. Allows to clearly reveal the lesion, access and treat the lesions of large blood vessels and in difficult and distant locations quickly, effectively and safely. Hybrid operating room with a modern information integration system helps to connect the operating room with the hospital information system, allowing doctors to access the patient's medical records, laboratory test results and other results. Scan for consultation before, during and after the surgery right in the operating room.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.





![[Video] Don't be subjective with gallstone disease](/static/uploads/small_20191104_030711_425223_soi_omc_max_1800x1800_jpg_2e7a54defa.jpg)




