This is an automatically translated article.
Lipomas are usually painless, benign, causing many patients to be subjective, let the tumor grow to a large size, pressing on nerves, affecting large blood vessels and causing many diseases. other illness. So what is lipoma? Are lipomas dangerous?
1. What is lipoma?
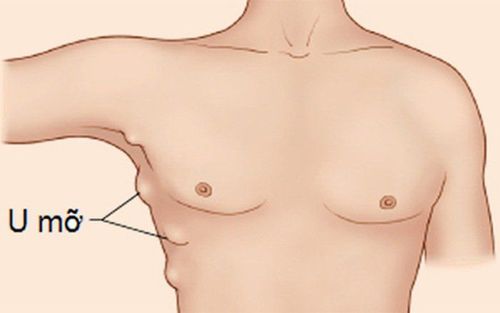
What is lipoma is a question that many people wonder. In fact, lipoma is a condition where the fat layer gradually accumulates under the skin, has a round shape, different sizes, there are tumors as small as a pea but also a tumor as big as a tangerine. Tumors can appear anywhere in the body such as: back, shoulder, arm, liver, intestine... A person can have from one to many tumors.
Lipomas are usually benign, movable, and painless. Lipomas have 2 characteristics for the doctor to recognize: they have many lobes and have a soft density, sometimes with liquid inside.
Anyone can get lipomas, but the condition is quite common in middle-aged women. To determine whether a lipoma is benign or malignant, the patient needs to see a doctor for a diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
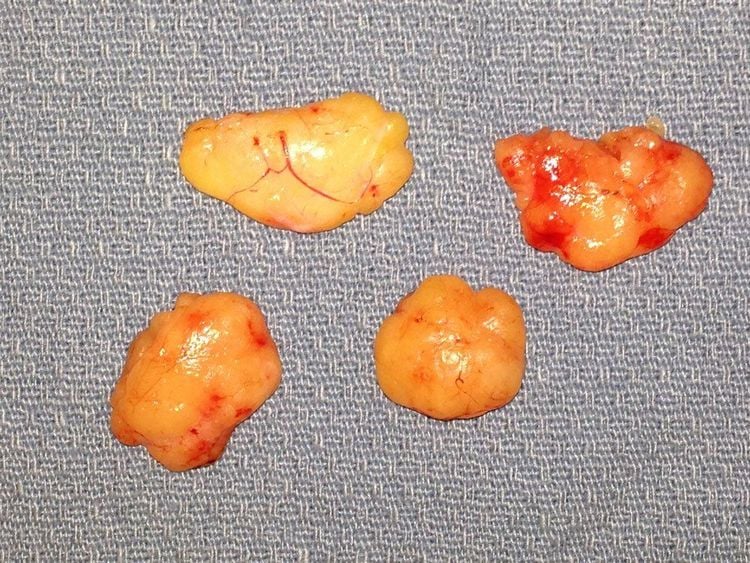
Hình ảnh thực thế khối u mỡ
2. Symptoms of lipomas
Usually, a person will not find out that they have a lipoma, unless it is easily felt by touching or pressing, the tumor is painful or abnormally large. At this point, the patient will ask, "Is lipoma dangerous?"
Lipomas can be one or more soft, round lumps under the skin and are usually painless. Tumors can be slightly mushy, soft or hard depending on the lipoma. They can be easily teleported to neighboring areas.
In many cases, a lipoma is painful because it presses on a nerve or if there are blood vessels inside the tumor. Don't have a fat tumor larger than 8 cm. Lipomas can also be unsightly. In these cases, lipomas should be surgically removed.
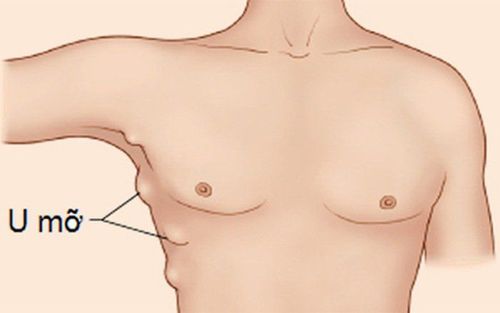
U mỡ dễ nhận biết bằng mắt thường
3. Are lipomas dangerous?
As for the question of whether lipomas are dangerous, according to experts, most benign lipomas do not cause much harm to the patient's health. Lipomas are rarely dangerous. However, that does not mean that you are subjective. Just seeing any lump or swelling anywhere on the body requires a visit to the doctor.
The size of the lipoma increases significantly (eg, doubling) within 12 months. Signs of dangerous lipoma such as slow growth, increase in size. With tumors appearing in the abdomen, it causes abdominal distension, compressing some internal organs, leading to dysfunction of many parts of the body, the cause is that they grow bigger. Large tumors in the head, neck and shoulders will put pressure on the nerves, resulting in paralysis, or affect large blood vessels when they grow larger. Patients may have difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, even respiratory failure, if the fatty tumor grows deep into the wall of the pharynx, pharynx, chest, liver, and mediastinum. In the positions of lipomas in the armpits, lipomas on the back, lipomas on the back of the neck, lipomas on the arms, legs... lipomas can all appear, of which the most common is... the most dangerous is when Lipomas appear in internal organs such as intestines and liver.
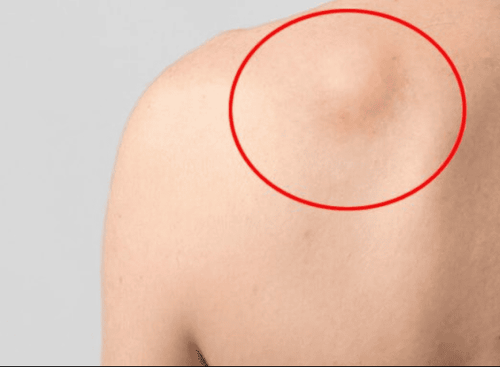
U mỡ ở sau lưng
4. Diagnosis and Treatment
Usually, to diagnose lipoma, the doctor only needs to rely on the symptoms you have and a general examination. In addition, for the most accurate results, the biopsy method is used very commonly. A known biopsy is a procedure where a small piece of tissue from a tumor is removed for microscopic examination.
With benign tumors, the doctor will advise no treatment but only monitoring. In the following cases, the doctor will proceed to remove the tumor:
The tumor grows rapidly, increasing in size The tumor causes cosmetic loss, affecting the patient's health and daily life Nature, Lipomas are benign if they are not a cyst, abscess, or cancer of the fatty tissue. Hopefully with the above information you have clearly understood what lipoma is, is it dangerous to have treatment options when necessary. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
MORE:
Other malignant tumors How do you heal? Differential diagnosis of malignant tumor - benign tumor by immunohistochemistry Is benign tumor worrisome? Is surgery needed?