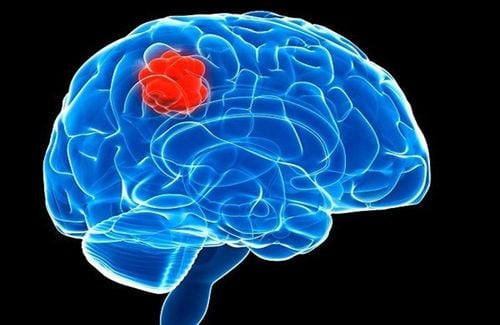
This is an automatically translated article.
Intracranial tumors may involve the brain or other structures such as cranial nerves or meninges. Tumors usually develop during early or mid-adulthood but can develop at any age and are more common in older people. Brain tumors are found in about 2% of autopsies.1. What are intracranial tumors? Types of brain tumors
1.1. Primary brain tumors Primary brain tumors originate in the brain and can develop from:Brain cells Meninges Meninges Nerve cells Glands Primary tumors can be benign or cancerous. In adults, the most common types of brain tumors are gliomas and meningioma.
1.1.1. Glioma Glioma is a tumor that develops from glial cells. These cells normally:
Support the structure of the central nervous system Provide essential nutrients to the central nervous system Clear cellular waste Break down dead nerve cells Glioma can develop from different types of glial cells. The types of glioma-initiated tumors are:
Astrocyte tumors originating in the cerebellum Epithelial tumors, usually found in the temporal lobe Brain 1.1.2 Other primary brain tumors Pituitary tumors, usually benign Pineal gland tumors, which can be benign or malignant Meningiomas, often benign Craniopharyngeal tumors, commonly occur in children and Benign but may have clinical symptoms such as vision changes and early puberty Primary CNS lymphoma, which is a malignancy Primary germ cell tumor of the brain, may be benign or malignancy Meningioma , which originates in the meninges Schwannoma tumor, which originates in the cells that make the protective covering of the nerve (myelin sheath) called Schwann cells
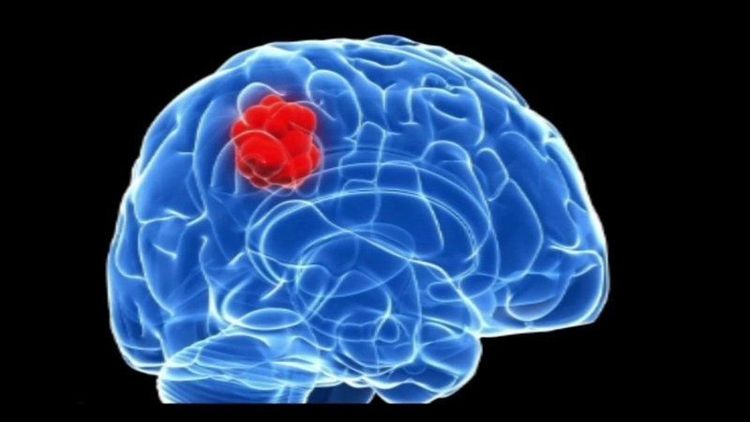
Các khối u trong sọ có thể liên quan đến não hoặc các cấu trúc khác như dây thần kinh sọ, màng não
1.2. Secondary brain tumors Secondary brain tumors make up the majority of brain cancers, starting in one organ of the body and spreading, or metastasized, to the brain. The following types of cancer can spread to the brain:
Lung cancer breast cancer Kidney cancer Skin cancer Secondary brain tumors are always malignant. Benign tumors do not spread from one organ to another.
2. Risk factors for brain tumors
2.1 Family history Only about 5 - 10% of all cancers are hereditary. Hereditary brain tumor is very rare, however, we should inform the doctor if there is a family member with brain tumor.
Chỉ khoảng 5 - 10% của tất cả các bệnh ung thư là do di truyền
2.3 Race Brain tumors are generally more common in Caucasians. However, African-Americans are more likely to get meningiomas.
2.4 Chemical Exposure Exposure to certain chemicals in the work environment may increase the risk of brain cancer.
2.5 Radiation Exposure People exposed to ionizing radiation have a higher risk of brain tumors. We may be exposed to ionizing radiation through high radiation cancer therapies. Or it can also be contaminated with radiation from nuclear fallout. The nuclear power plant failures at Fukushima and Chernobyl are examples of how humans can be exposed to ionizing radiation.
2.6 No history of chickenpox According to the American Brain Cancer Society, people with a history of chickenpox from an early age have a reduced risk of brain tumors.
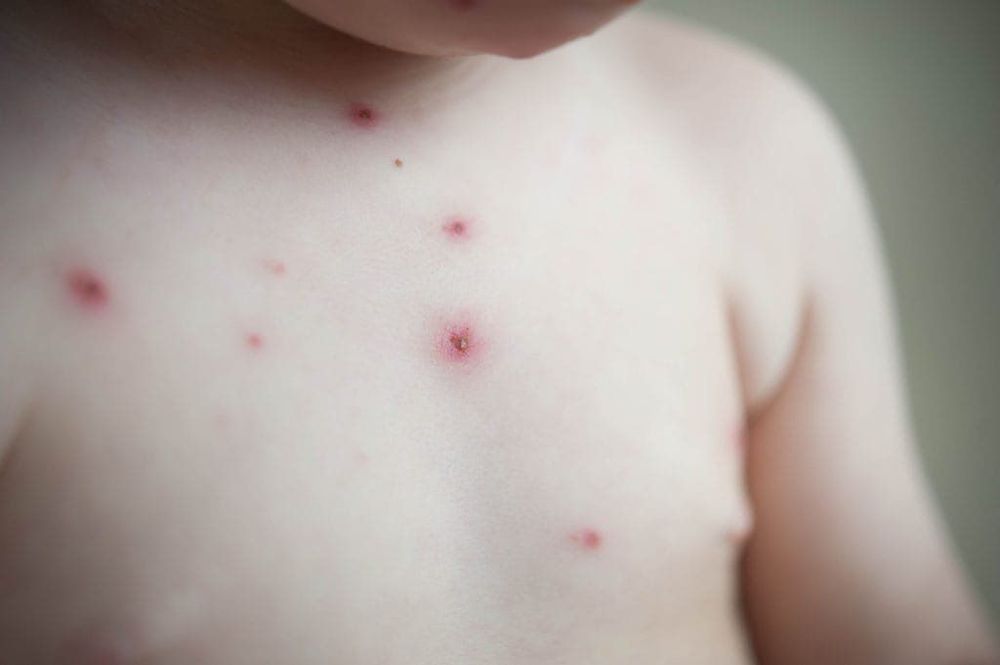
Người có tiền sử mắc thủy đậu từ khi còn nhỏ thường giảm nguy cơ bị u não
3. Common symptoms of intracranial tumors
The symptoms of a brain tumor often depend on its location and size. Some tumors cause direct damage by invading brain tissue, and some put pressure on the area around the brain.Headache is a common symptom of brain tumor. You may experience a headache in the morning when you wake up or sleep, or even while exercising or sneezing. In addition, the patient may also experience symptoms such as:
Vomiting Blurred or double vision Confusion Convulsions (especially in adults) Weakness of a limb or part of the face A change in activity Mental other common symptoms include:
Memory loss Confusion Difficulty writing or reading Changes in hearing, taste or smell Decreased alertness, which may include drowsiness and loss of consciousness Difficulty swallowing Dizziness Eye problems, such as drooping eyelids and unequal pupils Uncontrolled movements Hand tremors Loss of balance Loss of bladder or bowel control Numbness or tingling on one side of the body Difficulty say or understand what others are saying Changes in mood, personality, feelings, and behavior Difficulty walking Muscle weakness in the face, arms or legs Symptoms of a pituitary tumor:
Nipple discharge , or bleeding breast tissue growth in men, or gynecomastia Enlarged hands and feet Sensitivity to heat or cold Increased amount of body hair or hirsutism Blood pressure Low Obesity Vision changes, such as blurred vision or tunnel vision
4. Diagnosis of brain tumor
Diagnosing a brain tumor begins with a physical exam and review of the patient's medical history. A detailed neurological exam will check the integrity of the cranial nerves. Next, check the pupil's response to light with an ophthalmoscope and see if the optic nerve is swollen. With increased intracranial pressure, changes in the optic nerve can occur.The doctor may also evaluate:
Muscle strength Coordination Memory Mathematical calculation In addition, more tests may be ordered by the doctor after they have finished the neurological exam. Tests may include:
Head CT head MRI Head Angiography Angiography Cranial X-ray Biopsy

Chẩn đoán khối u não bắt đầu bằng việc khám sức khỏe và xem xét bệnh sử của người bệnh
5. How is brain tumor treated?
The treatment for a brain tumor depends on the following factors:The type of tumor The size of the tumor The location of the tumor General health The most common treatment for malignant brain tumors is surgery. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to healthy parts of the brain. While the location of some tumors allows for easy and safe removal, other tumors may be located in areas that limit the amount of tumor that can be removed. Even partial removal of brain cancer can be beneficial.
Risks of brain surgery include infection and bleeding. Clinically dangerous benign tumors are also surgically removed. Metastatic brain tumors are treated according to the guidelines for the original tumor.
Surgery can be combined with other treatments, such as radiation and chemotherapy. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help patients recover from neurosurgery.
Brain tumor is inherently a dangerous and easy disease in many people. Therefore, timely detection and treatment plays an extremely important role in helping patients stabilize their health early.
With many achievements and being a convergence of highly qualified doctors, experts and professors who are well-trained in domestic and foreign environments, Vinmec International General Hospital is now Vinmec International General Hospital. is the leading effective treatment facility for brain tumors in particular and neurological diseases in general.
The hospital is always fully equipped with modern equipment and machines such as: G.E 3.0 MRI (MRI) scanner, Toshiba 640 slices CT SCAN, cerebral angiogram, MRA and CTA... System application Modern machines help doctors easily detect and diagnose diseases and make treatment plans thanks to the clear and detailed images obtained. Not only brain tumors, but also effectively applied to other brain and spine diseases such as: brain degeneration, traumatic brain injury, cerebrovascular disease, cerebral aneurysm... Therefore, when there is a problem For health problems, customers can go to the hospital to be registered for examination and have appropriate indications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com