This is an automatically translated article.
Pulmonary lavage is a therapeutic technique to remove abnormal components adhering to the alveolar surface, in order to improve the respiratory function of the lungs. This is an intervention measure on subjects with occupational diseases, providing a chance for patients to recover after a long period of exposure to a working environment with lots of toxic dust.
1. What is the pulmonary lavage method?
The human body has two lungs, responsible for the respiratory function. When inhaled, air from the nose, according to the tracheobronchial tree system divided by many levels, goes to each alveoli. The alveoli are small sacs in the lungs where air flows in to deliver oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide. When living in a polluted and dusty environment, especially workers in the mining and chemical industries, the lungs are heavily dusty and the rate of occupational diseases is very common.
The presence of toxic molecules with dense density in the lungs causes the lungs to lose respiratory function or stimulates long-term inflammatory reactions that cause chronic damage to the lung parenchyma. Meanwhile, these molecules are very small in size, adherent and deeply ingrained, making it impossible for the patient to expel them by natural cough and sputum measures. Since then, the patient suffers from prolonged respiratory failure, the functioning of the organs is also affected, the body becomes emaciated and exhausted.
Thus, in patients with occupational diseases, in addition to the treatments to support lung function, the method of lung washing is an intervention to help remove harmful substances in the most practical way. As the name suggests, a full lung lavage is performed to wash away all material that is obstructing as well as impeding gas exchange across the alveoli. From there, the patient can reduce symptoms and restore an almost normal breathing rate, improving respiratory function.
Pulmonary lavage method for occupational disease requires the patient to be under general anesthesia. Each lung was isolated using a double-lumen endotracheal tube and treated each lung. This means that while one lung is irrigated with a large volume of isotonic electrolyte solution, the other lung is artificially ventilated. Therefore, this technique ensures that the patient is still receiving adequate oxygen in the body while the procedure is being performed.
However, because this is an interventional procedure, the pulmonary lavage must be performed in a medical facility that is fully equipped with anesthesia and resuscitation equipment and performed by doctors experienced in the specialty. respiratory as well as occupational therapists, have been trained in whole lung lavage.
Gây mê toàn thân cần được chỉ định trong phương pháp rửa phổi
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh?
Để nhận biết phổi của bạn có thật sự khỏe mạnh hay không và làm cách nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh, bạn có thể thực hiện bài trắc nghiệm sau đây.2. Indications for lung lavage
The whole lung lavage procedure has a limited scope of use and is usually indicated only in the treatment of infiltrative diseases of the air ducts and alveolar sacs such as alveolar proteinosis or occupational lung disease. Patients with this condition have difficulty breathing because the alveoli are damaged and covered with harmful substances, the transport of oxygen from the lungs to the blood is severely reduced. In addition, the patient also has other symptoms such as low-grade fever, weight loss, and fatigue.
Diagnosis of alveolar and occupational diseases with indication for lung lavage should be established through a history of long-term exposure to contaminated work environments. At the same time, it is necessary to perform chest x-ray tests and measure lung function, allowing doctors to assess the remaining volume of air that the patient can hold during the procedure, ensure the respiratory function of the whole body. However, for a definitive diagnosis, bronchoscopy may also be performed as a next step. This allows doctors to take a sample of fluid from the alveoli and a small portion of lung parenchyma to perform a biopsy.
However, whole lung lavage is not always recommended for all people with occupational lung disease. People with few or no symptoms usually do not need treatment but only other supportive measures, including isolation. However, for people with severe symptoms and disease, doctors need to do a comprehensive physical examination, ensure the function of other organ systems and ensure the procedure before appointing a lung lavage. .
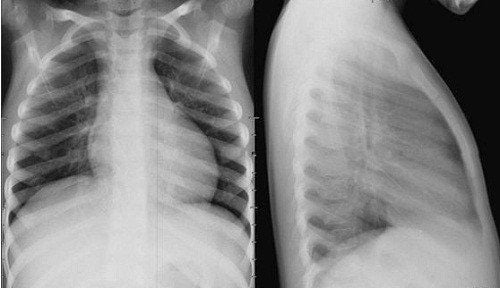
Trước khi rửa phổi, bệnh nhân cần chụp X -quang phổi để chẩn đoán
3. How is lung lavage performed?
Lung lavage is started when the patient is under general anesthesia. The physician will usually perform first lung lavage in the left lung while the right lung is ventilated using a double endotracheal tube.
Careful cardiopulmonary monitoring is performed throughout the procedure to ensure that the patient is well ventilated, achieving effective ventilation parameters. This is important because failure of the right lung to supply the body with insufficient oxygen while the procedure is ongoing will reduce the effectiveness of the intervention, delaying the patient's later recovery.
The left lung was washed for the first time with 400ml of sterile physiological saline solution. A second dose of 500ml-600ml solution will then fill the lungs for a period of time and drain the water. At this point, it is necessary to ensure that the same amount of water is drawn to ensure that there is no foreign substance in the lungs completely and to ensure the success of the entire process.
Initial wash water quality is often very polluted, white, yellow, cloudy and sometimes even slimy. This process will continue to be repeated, the next time the wastewater will gradually improve compared to the first time, until the drained water looks clean and clear. The amount of water required is usually 12 to 13 liters of brine to achieve such a requirement. The same procedure for the left lung can be performed now or delayed for several days, depending on the tolerance of the contralateral lung parenchyma.
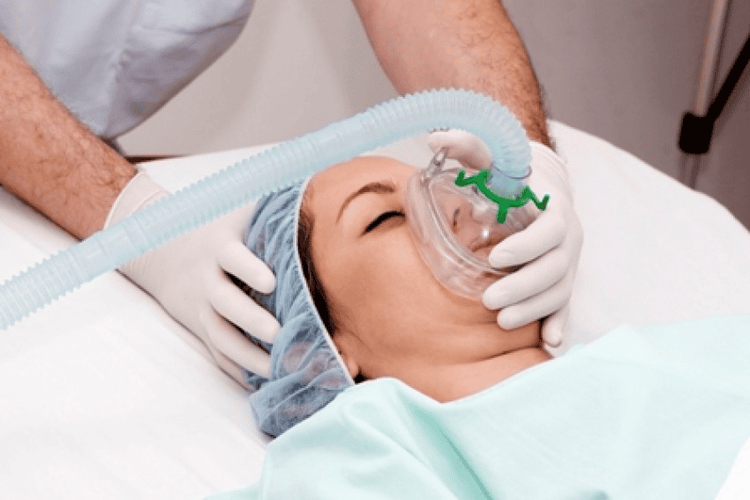
Thở máy được sử dụng trong quá trình lọc rửa phổi
4. Possible risks and complications when performing pulmonary dialysis
Pulmonary lavage procedures have been shown to be safe and extremely effective. The majority of patients globally have reported an almost 100% improvement in their general respiratory health following the procedure. However, although effective, lung lavage does not guarantee protection against recurrence.
In addition, despite its success, pulmonary lavage is still an interventional procedure and it is difficult to completely avoid the risks and complications associated with the procedure. These may include the following:
Atelectasis, respiratory failure in the remaining lung Pneumothorax, Pleural effusion, Hypotension, circulatory collapse
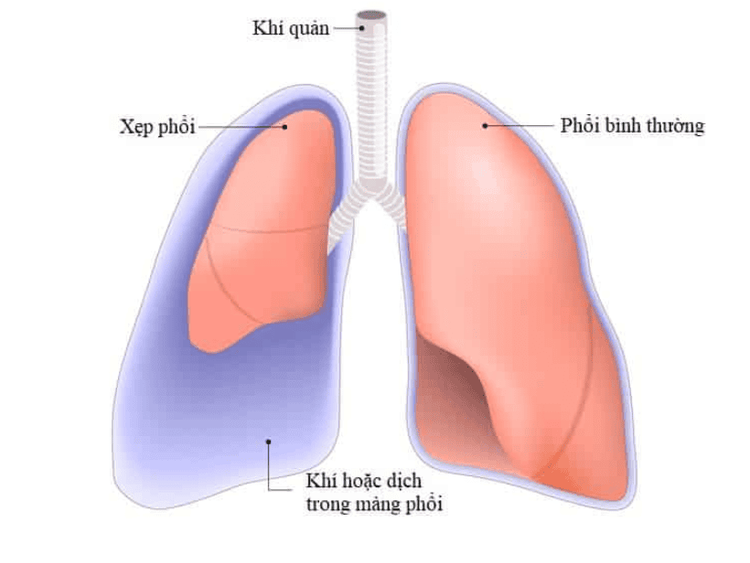
Xẹp phổi có thể xảy ra khi thực hiện lọc rửa phổi
In summary, the method of pulmonary lavage for occupational disease is an intervention method in the treatment of this group of diseases. Conditions for performing the procedure need to require that the remaining lung can be functional, and at the same time, it should be performed in specialized respiratory centers with experienced doctors. From there, the effectiveness of lung lavage will be optimal as well as help patients improve their breathing ability in the long run.
For detailed advice, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register online HERE.